Conversion attribution measurement can involve multiple parties, ranging from the publisher, advertiser, serving ad tech (the entity that delivers the ad), measurement provider, and more. In this document, we illustrate common conversion measurement scenarios, but in general any party that wishes to receive an attribution report from the Attribution Reporting API (ARA) must ensure that the integration steps described in this document are followed.
For example, it is common for a publisher to have one or more ad techs responsible for serving the ad — this could include parties responsible for supplying the markup for the creative, the parties supplying the impression or tracking pixel on the creative, and the parties supplying the SDK or tag for the ad slot on the publisher page. These ad techs may or may not want to receive attribution reports from ARA, but are positioned to ensure downstream ad techs can receive attribution reports.
Additionally, the advertiser may also be using a third-party conversion measurement provider for cross-network attribution as well as other reporting capabilities. Advertisers use that data to understand return on advertising investment across multiple unique publishers and channels, so it's important that DSPs or ad servers understand how to enable the Attribution Reporting API to support these use cases. Advertisers that want to use a third-party can continue doing so, either by using a third-party measurement provider or by setting up an in-house server to register and receive reports from the API.
The Attribution Reporting API allows multiple ad techs to register attribution sources and triggers for the same impression or conversion and receive separate reports from the API. For example, a DSP can receive its own attribution reports from the Attribution Reporting API as well as allow separate reporting for the advertiser's third-party measurement provider. An ad tech must register both attribution sources and triggers to receive reports from the API, and attribution is done among the attribution sources and triggers that the ad tech has individually registered with the API.
Common conversion measurement scenarios
In this section, we will examine two common scenarios for conversion measurement.
Scenario 1: Both serving ad tech and the third-party measurement provider need to receive reports from the Attribution Reporting API
An advertiser wishes to attribute conversions on ad inventory using a third-party measurement provider, and the ad tech hosting the creative wishes to attribute conversions on the ad inventory. This is common for DSPs or advertiser ad servers (third-party ad server — 3PAS) who provide the markup for ad creatives, perform their own attribution reporting, and work with advertisers that integrate with third-party measurement or analytics providers.
In this case, the serving ad tech is also the party that is responsible for firing click and impression events in the current setup. The serving ad tech should set the new attributionsrc in appropriate locations and ensure that the redirects are configured correctly. Also, both the serving ad tech and the third-party measurement provider should ensure they are enrolled and their servers are ready to receive and respond to Attribution Reporting API requests.
A typical campaign setup could look like:
Advertiser ad server (3PAS) supplies the markup for the ad creative to the DSP, which includes the third-party measurement provider's impression and click tracking pixels. The ad server should ensure
attributionsrcis included in the ad creative markup.The DSP offers capabilities to add additional measurement impression and click tracking pixels, and should make sure
attributionsrcis included in the final ad creative markup they are bidding with.
Scenario 2: Only the third-party measurement provider needs to receive reports from the Attribution Reporting API
An advertiser wishes to attribute conversions on ad inventory using a third-party measurement provider, but the ad tech hosting the creative has no attribution measurement requirements. This is common for publishers, SSPs, or publisher ad servers who host creatives and don't plan to use attribution reporting themselves, but who want to enable the Attribution Reporting API either for their DSP partners, or for measurement tagging companies such as a third-party ad servers, measurement or analytics providers.
In this case, the party that is responsible for firing click and impression events in the current setup needs to add the new attributionsrc attribute to creatives and ensure redirects are working as intended. This is highly dependent on each publisher's integration, but for click events, this could be the SSP, serving ad tech, or the publisher themselves. For impression events, this is more commonly the third-party measurement provider.
In the typical campaign setup example from Scenario 1, the publisher ad server, SSP, or publisher themselves may just need to ensure the attributionsrc attribute that was provided by the DSP makes it onto the publisher page.
Implementation details
The following table describes the Attribution Reporting API implementation steps at a high-level:
| Steps | Responsibility of work | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Step 1: Enable attribution source for existing creatives and measurement code | The entity responsible for firing impression events or handling click events adds the attributionsrc attribute. |
For click events, generally a buyer (DSP/advertiser ad server) that renders the creative adds the attribute.
For impression events, demand-side platform (DSP), supply-side platform (SSP), publisher, ad server, or a measurement provider adds the attribute, and it is dependent on the publisher's setup. For video ads using the VAST format, the publisher and the video SDK add the attribute. |
| Step 2: Enable Attribution Reporting for third-party origins | This works out-of-the-box if using an existing redirect path with 302 redirects. If 302 redirects cannot be used, the |
Generally, as long as the attributionsrc attribute is added to the creative, the third-party redirects should receive the Attribution Reporting API calls. |
| Step 3: Set up responses for Attribution Reporting API requests | Any entity that wants to receive reports from the Attribution Reporting API | The DSP and the third-party measurement provider used by the advertiser |
Note that specifics of each step depend on how creatives are rendered and served on the publisher page, and which ad tech entities receive reports sent by the Attribution Reporting API.
Step 1: Enable attribution source for existing creatives and measurement code
In the first step, the attribution sources are enabled.
How the attributionsrc attribute works
The new attributionsrc attribute specifies where the Attribution Reporting API requests will be sent to. The entity that is responsible for firing impression and click events must update creatives with the attributionsrc attribute. The attributionsrc should be added to existing click and impression events, and can be empty or non-empty.
For click events using redirects, the attributionsrc attribute should be added to the navigation. Any 302 redirects after the navigation don't need to add the attributionsrc attribute and will be eligible for ARA as long as the initial navigation has added attributionsrc.
When the attributionsrc is empty, the ARA requests will be sent to the URL defined in the href attribute of the anchor tag (clickthrough URL). When the attributionsrc attribute is defined, the ARA requests will be sent to the URL defined in the attributionsrc attribute. The clickthrough URL is also eligible to register sources.
Generally, use an empty attributionsrc attribute if the server hosting the clickthrough URL can receive and respond to Attribution Reporting API requests. Define your own attributionsrc URL if you want Attribution Reporting API requests to go to a different server.
Example of an empty attributionsrc attribute:
| Your existing setup | With ARA integration |
|---|---|
<a href="[CLICKTHROUGH_URL]">...</a>
|
<a href="[CLICKTHROUGH_URL]" attributionsrc>...</a>
|
When the attributionsrc attribute is empty, the Attribution Reporting API requests will be sent to the URL defined by the href attribute of the anchor tag.
Example of a non-empty attributionsrc attribute:
| Your existing setup | With ARA integration |
|---|---|
<a href="[CLICKTHROUGH_URL]">...</a>
|
<a href="[CLICKTHROUGH_URL]" attributionsrc="[ATTRIBUTION_SRC_URL]">...</a>
|
When the attributionsrc is not empty, the Attribution Reporting API requests will be sent to the URL defined by the attributionsrc tag. The clickthrough URL is also eligible to register sources.
Add attributionsrc for click and impression events
- Click events:
- The entity responsible for adding the
attributionsrcis usually the serving ad tech. - Anchor tags with click events should have an
attributionsrcattribute added. - Clicks using
window.openshould use thewindowFeaturesargument of thewindow.opencall to specify the attribution source.
- The entity responsible for adding the
- Impression events:
- The entity responsible for adding the
attributionsrcis usually the serving ad tech and the measurement provider(s). - Impression events fired from
<img>tag or<script>tag should include anattributionsrcattribute. - Impression events using the Fetch API should include an
attributionReportingobject in the options argument passed to the fetch API call.
- The entity responsible for adding the
See the following table for the summary of modifications needed for click and impression events:
| Event | Tag | Your existing setup | After ARA integration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Click | HTML |
<a href="[CLICKTHROUGH_URL]">...</a>
|
<a href="[CLICKTHROUGH_URL]" attributionsrc>...</a>
|
| JavaScript | window.open("[CLICKTHROUGH_URL]", "_blank"); |
window.open("[CLICKTHROUGH_URL]", "_blank", "attributionsrc"); |
|
| Impression | HTML <img> tag |
<img src="[IMPRESSION_URL]">
|
<img src="[IMPRESSION_URL]" attributionsrc>
|
HTML <script> tag |
<script src="[IMPRESSION_URL]"></script>
|
<script src="[IMPRESSION_URL]" attributionsrc></script>
|
|
| JavaScript |
const options = {...} |
const options = { |
Enable attribution source registration in a Protected Audience auction
For measuring conversions in a Protected Audience auctions, instead of using attributionsrc, you can use registerAdBeacon/registerAdMacro and setReportEventDataForAutomaticBeacons/reportEvent to enable registering attribution sources.
For reporting Protected Audience signals, the registerAdBeacon function is available inside reporting worklets, and registerAdMacro is available inside the buyer's win reporting worklet. Then, the event data inside the ad frame can be added to the registered beacons and macros with the reportEvent and setReportEventDataForAutomaticBeacons functions of Fenced Frame Ads Reporting API. This allows the signals of the Protected Audience reporting worklets and the ad creative frame event payload to be associated with each other.
The Attribution-Reporting-Eligible HTTP header is added to the request when the beacons and macros are triggered by the reportEvent call from a frame, or the automatic beacons are triggered by the browser. You can use the response of the beacon to register an attribution source. The beacon requests may be redirected to allow third-party measurement.
For a deeper dive, see the Support for Attribution Reporting section of the Fenced Frame Ad Reporting API explainer.
Enable attribution reporting for VAST formats
VAST is a common format for serving and measuring video ad inventory, and many of the events defined in that standard should be considered potential source events eligible for registration with the Attribution Reporting API. The VAST Addendum for Attribution Reporting Support covers this in detail, but in short, all <Tracking>, <Impression>, <*ClickThrough>, and <*ClickTracking> events are potential attribution source events. All VAST implementations should provide registration eligibility coverage for these events.
The VAST addendum defines new attributes for these elements to allow for setting a secondary URL specifically for attribution registration. When an event contains attributiontype="DOUBLE_PING" and attributionsrc="[URL]", the code firing that event should use [URL] as the value of the attributionsrc attribute when enabling the Attribution Reporting API. The VAST addendum contains examples for each scenario.
To ensure maximum coverage, VAST implementations should make all events listed are registration eligible by default when firing event pings. For example, when firing an <Impression> event URL, the (empty) attributionsrc attribute should be used on the <img> element used to send the request (or the equivalent on the fetch call), to always allow for the receiving party to potentially register that event with the Attribution Reporting API.
Step 2: Enable Attribution Reporting for third-party origins
To allow third-parties to use the Attribution Reporting API, you can use existing redirects or add a list of third-parties to the attributionsrc attribute. In most cases, each ad tech has their own independent impression tracker, so redirects are more relevant for click trackers.
Handle third-party origins in an existing redirect chain
In a typical ad clickthrough, many click trackers may be present as a chain of 302 redirects made as part of the navigation to the final landing page. Every request in the redirect chain is eligible for registration with the Attribution Reporting API if the original click target was annotated with attributionsrc or registered with registerAdBeacon/registerAdMacro in Protected Audience API. The ad tech in the redirect chain must be also enrolled.
Note that the initial request's body is not sent on redirects. For Protected Audience auctions, if eventData passed in to reportEvent and setReportEventDataForAutomaticBeacons needs to be used as part of the redirect, it must be explicitly passed on as part of the redirect URL.
In the following example, we will use a serving ad tech (serving-adtech.example) and a third-party measurement provider (3p-measurement.example) as two distinct entities that are looking to generate and receive attribution reports. The serving ad tech in this example can be a DSP that renders the creative on the publisher site, and has their own reporting product. The third-party measurement provider can be an entity that the advertiser uses for conversion reporting.
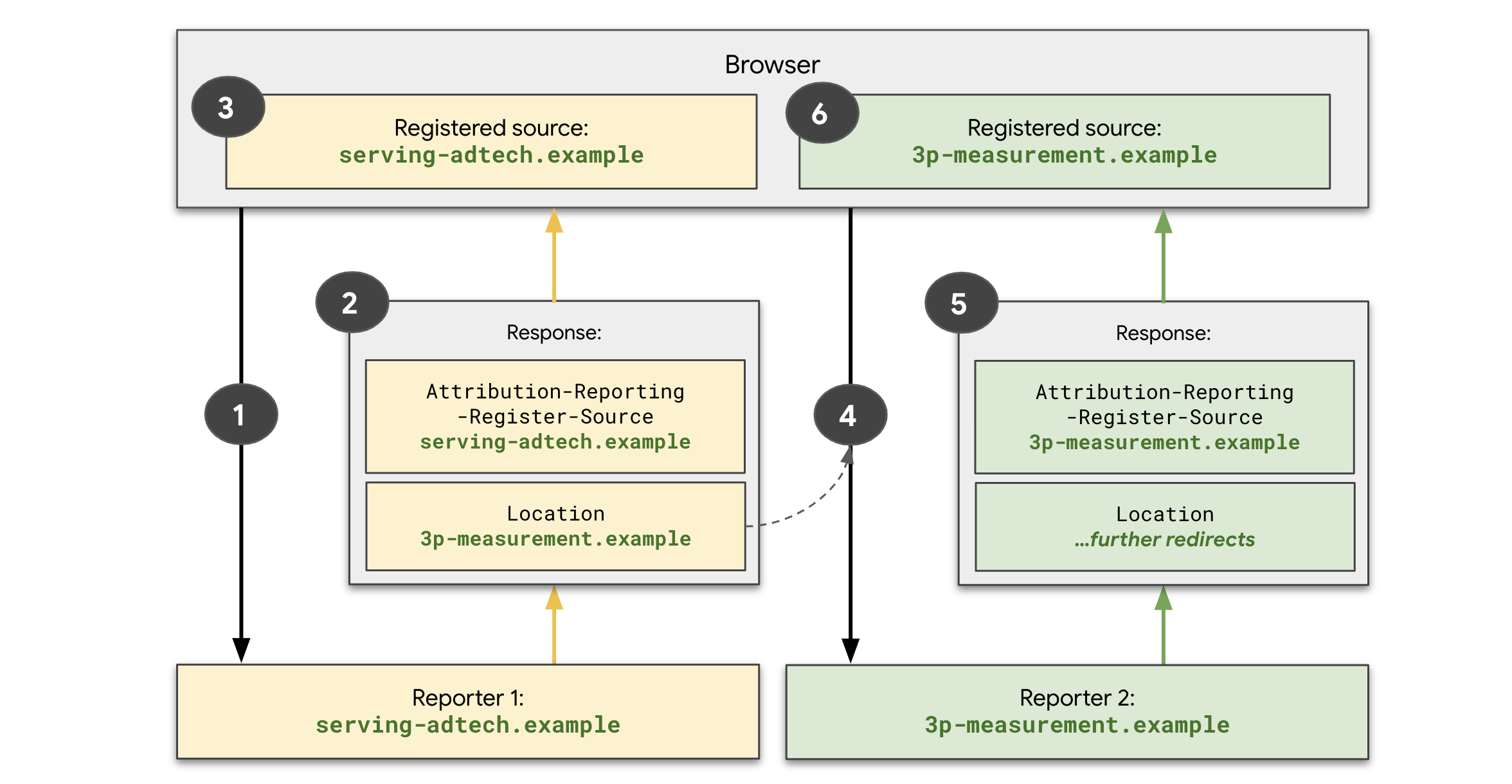
At source registration time, the following steps take place:
serving-adtech.examplesets theattributionsrcattribute in the creative.The user visits the publisher page, and the browser sends a request toserving-adtech.example.serving-adtech.exampleresponds with theAttribution-Reporting-Register-Sourceheader and theLocationheader.serving-adtech.exampleuses theAttribution-Reporting-Register-Sourceheader to respond with metadata about the source to be registered.serving-adtech.exampleuses theLocationheader to include a redirect to3p-measurement.example. Note that it's likely that theLocationheader is already being used in your existing clicktracking flows to support302redirects to a third-party.
- The browser receives the response from
serving-adtech.exampleand parses theAttribution-Reporting-Register-Sourceheader. The browser stores the source event, usingserving-adtech.exampleas the reporting origin. - Because this request is a redirect, the browser also makes a new request to
3p-measurement.example. 3p-measurement.exampleresponds with a response that contains theAttribution-Reporting-Register-Sourceheader.- The browser receives this response from
3p-measurement.exampleand reads theAttribution-Reporting-Register-Source. The browser stores the source event, using3p-measurement.exampleas the reporting origin.
Use attributionsrc for third-party origins not in a redirect chain
If multiple reporter origins want to register a source on a navigation event, but can't appear in a redirect chain for any reason, you can list multiple sites as attribution sources in attributionsrc as an alternative solution.
| Your existing setup | With ARA modification |
|---|---|
<a href="[CLICKTHROUGH_URL]">...</a>
|
<a href="[CLICKTHROUGH_URL]" attributionsrc="[REPORTING_URL_1] [REPORTING_URL_2]">...</a>
|
In this example, Attribution Reporting API-eligible requests will be sent to both REPORTING_URL_1 and.REPORTING_URL_2. The navigation request sent to the clickthrough URL is also eligible to register attribution sources.
Step 3: Set up responses for Attribution Reporting API requests
For all origins receiving an Attribution Reporting API request, ensure that the server responds with the appropriate Attribution-Reporting-Register-Source header. See the Register sources guide and the explainer to learn how the response should be constructed.
Register multiple triggers
You can register multiple attribution triggers by adding multiple pixel elements on the conversion side (one per trigger). The attributionsrc element is optional for trigger registration.
You can also register multiple triggers from a single pixel element by using redirect requests or listing multiple URLs in the attributionsrc element in the same way as for source registration. Source events and trigger events that have been generated by the same origins will be matched.
