Tổng quan
Tính năng Liên kết đơn giản hoá Đăng nhập bằng Google dựa trên OAuth sẽ thêm tính năng Đăng nhập bằng Google vào bên trên tính năng liên kết OAuth. Điều này mang lại trải nghiệm liên kết liền mạch cho người dùng Google, đồng thời cho phép tạo tài khoản, nhờ đó người dùng có thể tạo tài khoản mới trên dịch vụ của bạn bằng Tài khoản Google của họ.
Để liên kết tài khoản bằng OAuth và tính năng Đăng nhập bằng Google, hãy làm theo các bước chung sau:
- Trước tiên, hãy yêu cầu người dùng đồng ý truy cập vào hồ sơ Google của họ.
- Sử dụng thông tin trong hồ sơ của họ để kiểm tra xem tài khoản người dùng có tồn tại hay không.
- Đối với người dùng hiện tại, hãy liên kết các tài khoản.
- Nếu bạn không tìm thấy kết quả trùng khớp cho người dùng Google trong hệ thống xác thực, hãy xác thực mã thông báo nhận dạng nhận được từ Google. Sau đó, bạn có thể tạo người dùng dựa trên thông tin hồ sơ có trong mã thông báo nhận dạng.
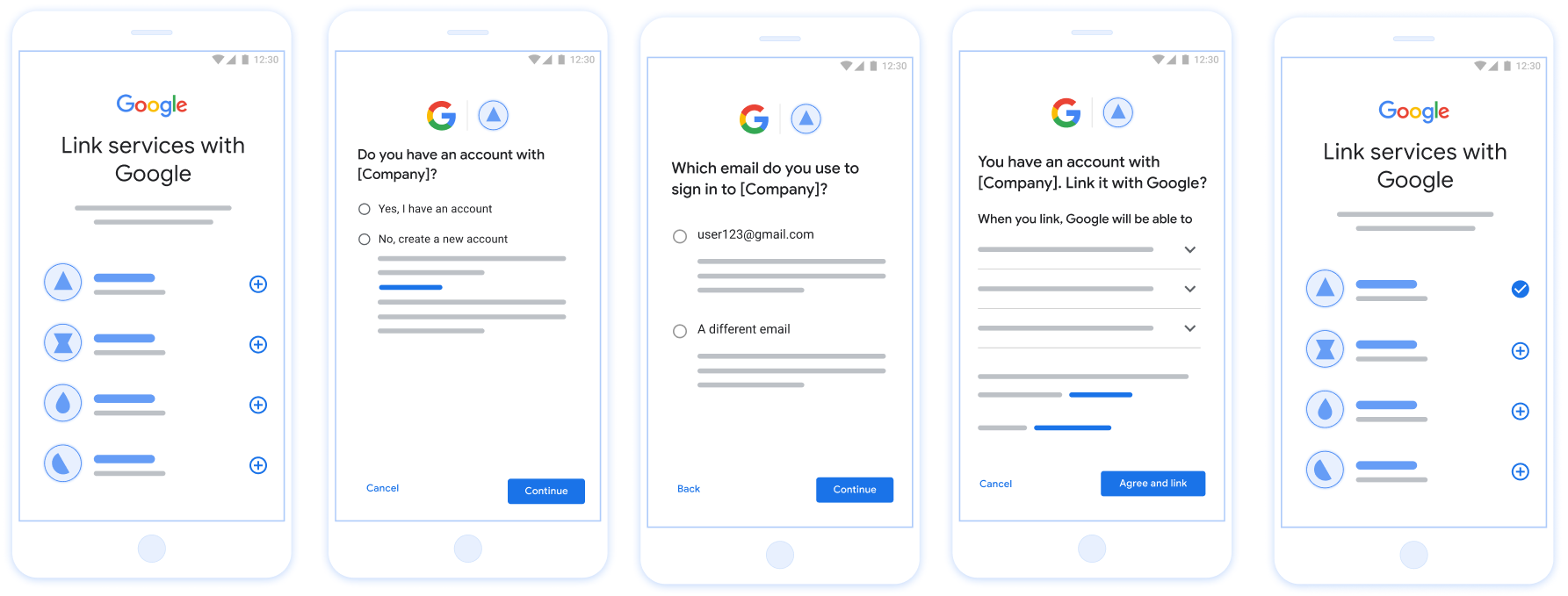
Hình 1 Liên kết tài khoản trên điện thoại của người dùng bằng tính năng Liên kết đơn giản
Yêu cầu đối với tính năng Liên kết đơn giản
- Triển khai quy trình liên kết OAuth cơ bản trên web. Dịch vụ của bạn phải hỗ trợ các điểm cuối uỷ quyền và trao đổi mã thông báo tuân thủ OAuth 2.0.
- Điểm cuối trao đổi mã thông báo phải hỗ trợ các câu nhận định Mã thông báo web JSON (JWT) và triển khai ý định
check,createvàget.
Triển khai máy chủ OAuth
Điểm cuối giao dịch mã thông báo phải hỗ trợ các ý định check, create, get. Phần dưới đây cho thấy các bước đã hoàn tất thông qua quy trình liên kết tài khoản và cho biết thời điểm các ý định khác nhau được gọi:
- Người dùng có tài khoản trong hệ thống xác thực của bạn không? (Người dùng quyết định bằng cách chọn CÓ hoặc KHÔNG)
- CÓ : Người dùng có sử dụng email liên kết với Tài khoản Google của họ để đăng nhập vào nền tảng của bạn không? (Người dùng quyết định bằng cách chọn CÓ hoặc KHÔNG)
- CÓ : Người dùng có tài khoản khớp trong hệ thống xác thực của bạn không? (
check intentđược gọi để xác nhận)- CÓ :
get intentđược gọi và tài khoản được liên kết nếu get intent trả về thành công. - KHÔNG : Tạo tài khoản mới? (Người dùng quyết định bằng cách chọn CÓ hoặc KHÔNG)
- CÓ :
create intentđược gọi và tài khoản được liên kết nếu ý định tạo trả về thành công. - KHÔNG : Quy trình OAuth trên web được kích hoạt, người dùng được chuyển hướng đến trình duyệt và có thể chọn liên kết với một email khác.
- CÓ :
- CÓ :
- KHÔNG : Luồng OAuth trên web được kích hoạt, người dùng được chuyển hướng đến trình duyệt và có thể chọn liên kết với một email khác.
- CÓ : Người dùng có tài khoản khớp trong hệ thống xác thực của bạn không? (
- KHÔNG : Người dùng có tài khoản khớp trong hệ thống xác thực của bạn không? (
check intentđược gọi để xác nhận)- CÓ :
get intentđược gọi và tài khoản được liên kết nếu get intent trả về thành công. - KHÔNG :
create intentđược gọi và tài khoản được liên kết nếu ý định tạo trả về thành công.
- CÓ :
- CÓ : Người dùng có sử dụng email liên kết với Tài khoản Google của họ để đăng nhập vào nền tảng của bạn không? (Người dùng quyết định bằng cách chọn CÓ hoặc KHÔNG)
Kiểm tra tài khoản người dùng hiện có (kiểm tra ý định)
Sau khi người dùng đồng ý truy cập vào hồ sơ trên Google của họ, Google sẽ gửi yêu cầu chứa xác nhận có chữ ký về danh tính của người dùng Google. Chiến lược phát hành đĩa đơn xác nhận chứa thông tin bao gồm ID Tài khoản Google của người dùng, tên và địa chỉ email của bạn. Điểm cuối trao đổi mã thông báo được định cấu hình cho dự án sẽ xử lý yêu cầu đó.
Nếu đã có Tài khoản Google tương ứng trong quá trình xác thực
hệ thống, điểm cuối trao đổi mã thông báo của bạn sẽ phản hồi bằng account_found=true. Nếu
Tài khoản Google không khớp với người dùng hiện có, điểm cuối trao đổi mã thông báo của bạn
trả về lỗi HTTP 404 Not found (Không tìm thấy) với account_found=false.
Yêu cầu có biểu mẫu sau:
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded grant_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer&intent=check&assertion=JWT&scope=SCOPES&client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET
Điểm cuối trao đổi mã thông báo của bạn phải có khả năng xử lý các tham số sau:
| Tham số điểm cuối của mã thông báo | |
|---|---|
intent |
Đối với các yêu cầu này, giá trị của thông số này là
check. |
grant_type |
Loại mã thông báo đang được trao đổi. Đối với các yêu cầu này,
tham số có giá trị urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer. |
assertion |
Mã thông báo web JSON (JWT) cung cấp xác nhận có chữ ký của Google danh tính của người dùng. JWT chứa thông tin bao gồm Mã Tài khoản Google, tên và địa chỉ email. |
client_id |
Mã ứng dụng khách mà bạn đã chỉ định cho Google. |
client_secret |
Mật khẩu ứng dụng khách mà bạn đã chỉ định cho Google. |
Để phản hồi các yêu cầu về ý định check, điểm cuối trao đổi mã thông báo phải thực hiện các bước sau:
- Xác thực và giải mã câu nhận định JWT.
- Kiểm tra xem Tài khoản Google đã có trong hệ thống xác thực của bạn hay chưa.
Xác thực và giải mã câu nhận định JWT
Bạn có thể xác thực và giải mã câu nhận định JWT bằng cách sử dụng Thư viện giải mã JWT cho ngôn ngữ của bạn. Sử dụng Khoá công khai của Google, có trong JWK hoặc Định dạng PEM để xác minh chữ ký của mã thông báo.
Khi được giải mã, câu nhận định JWT sẽ có dạng như ví dụ sau:
{ "sub": "1234567890", // The unique ID of the user's Google Account "iss": "https://accounts.google.com", // The assertion's issuer "aud": "123-abc.apps.googleusercontent.com", // Your server's client ID "iat": 233366400, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's creation time "exp": 233370000, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's expiration time "name": "Jan Jansen", "given_name": "Jan", "family_name": "Jansen", "email": "jan@gmail.com", // If present, the user's email address "email_verified": true, // true, if Google has verified the email address "hd": "example.com", // If present, the host domain of the user's GSuite email address // If present, a URL to user's profile picture "picture": "https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/a-/AOh14GjlTnZKHAeb94A-FmEbwZv7uJD986VOF1mJGb2YYQ", "locale": "en_US" // User's locale, from browser or phone settings }
Ngoài việc xác minh chữ ký của mã thông báo, hãy xác minh rằng câu lệnh
công ty phát hành (trường iss) là https://accounts.google.com, mà đối tượng
(trường aud) là mã ứng dụng khách được chỉ định và mã thông báo chưa hết hạn
(trường exp).
Bằng cách sử dụng các trường email, email_verified và hd, bạn có thể xác định xem
Google lưu trữ và có thẩm quyền đối với một địa chỉ email. Trong trường hợp Google
có thẩm quyền mà người dùng hiện được biết là chủ sở hữu tài khoản hợp pháp
và bạn có thể bỏ qua mật khẩu hoặc các phương thức xác thực khác. Nếu không, các phương thức này
có thể dùng để xác minh tài khoản trước khi liên kết.
Những trường hợp mà Google có thẩm quyền:
emailcó hậu tố@gmail.com, đây là một tài khoản Gmail.email_verifiedlà đúng vàhdđã được đặt, đây là tài khoản G Suite.
Người dùng có thể đăng ký Tài khoản Google mà không cần sử dụng Gmail hoặc G Suite. Thời gian
email không chứa hậu tố @gmail.com và hd không có Google thì không
xác thực và sử dụng mật khẩu hoặc các phương pháp xác thực khác để xác minh
người dùng. email_verified cũng có thể đúng vì ban đầu Google đã xác minh
người dùng khi tài khoản Google được tạo, tuy nhiên quyền sở hữu đối với bên thứ ba
tài khoản email có thể đã thay đổi.
Kiểm tra xem Tài khoản Google đã có trong hệ thống xác thực của bạn hay chưa
Kiểm tra xem một trong các điều kiện sau có đúng hay không:
- Mã Tài khoản Google (trong trường
subcủa câu nhận định) nằm trong tài khoản người dùng của bạn cơ sở dữ liệu. - Địa chỉ email trong câu nhận định khớp với một người dùng trong cơ sở dữ liệu người dùng của bạn.
Nếu một trong hai điều kiện đúng, thì người dùng đã đăng ký. Trong trường hợp đó, trả về phản hồi như sau:
HTTP/1.1 200 Success
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
{
"account_found":"true",
}
Nếu cả mã Tài khoản Google và địa chỉ email được chỉ định trong
khớp với người dùng trong cơ sở dữ liệu của bạn, người dùng chưa đăng ký. Trong
trong trường hợp này, điểm cuối trao đổi mã thông báo của bạn cần phải trả lời bằng lỗi HTTP 404
chỉ định "account_found": "false", như trong ví dụ sau:
HTTP/1.1 404 Not found
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
{
"account_found":"false",
}
Xử lý tính năng liên kết tự động (nhận ý định)
Sau khi người dùng đồng ý truy cập vào hồ sơ trên Google của họ, Google sẽ gửi yêu cầu chứa xác nhận có chữ ký về danh tính của người dùng Google. Chiến lược phát hành đĩa đơn xác nhận chứa thông tin bao gồm ID Tài khoản Google của người dùng, tên và địa chỉ email của bạn. Điểm cuối trao đổi mã thông báo được định cấu hình cho dự án sẽ xử lý yêu cầu đó.
Nếu đã có Tài khoản Google tương ứng trong quá trình xác thực
điểm cuối trao đổi mã thông báo của bạn sẽ trả về một mã thông báo cho người dùng. Nếu
Tài khoản Google không khớp với người dùng hiện có, điểm cuối trao đổi mã thông báo của bạn
sẽ trả về lỗi linking_error và login_hint tuỳ chọn.
Yêu cầu có biểu mẫu sau:
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded grant_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer&intent=get&assertion=JWT&scope=SCOPES&client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET
Điểm cuối trao đổi mã thông báo của bạn phải có khả năng xử lý các tham số sau:
| Tham số điểm cuối của mã thông báo | |
|---|---|
intent |
Đối với các yêu cầu này, giá trị của tham số này là get. |
grant_type |
Loại mã thông báo đang được trao đổi. Đối với các yêu cầu này,
tham số có giá trị urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer. |
assertion |
Mã thông báo web JSON (JWT) cung cấp xác nhận có chữ ký của Google danh tính của người dùng. JWT chứa thông tin bao gồm Mã Tài khoản Google, tên và địa chỉ email. |
scope |
Không bắt buộc: Mọi phạm vi mà bạn đã định cấu hình Google để yêu cầu từ đó người dùng. |
client_id |
Mã ứng dụng khách mà bạn đã chỉ định cho Google. |
client_secret |
Mật khẩu ứng dụng khách mà bạn đã chỉ định cho Google. |
Để phản hồi các yêu cầu về ý định get, điểm cuối trao đổi mã thông báo phải thực hiện các bước sau:
- Xác thực và giải mã câu nhận định JWT.
- Kiểm tra xem Tài khoản Google đã có trong hệ thống xác thực của bạn hay chưa.
Xác thực và giải mã câu nhận định JWT
Bạn có thể xác thực và giải mã câu nhận định JWT bằng cách sử dụng Thư viện giải mã JWT cho ngôn ngữ của bạn. Sử dụng Khoá công khai của Google, có trong JWK hoặc Định dạng PEM để xác minh chữ ký của mã thông báo.
Khi được giải mã, câu nhận định JWT sẽ có dạng như ví dụ sau:
{ "sub": "1234567890", // The unique ID of the user's Google Account "iss": "https://accounts.google.com", // The assertion's issuer "aud": "123-abc.apps.googleusercontent.com", // Your server's client ID "iat": 233366400, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's creation time "exp": 233370000, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's expiration time "name": "Jan Jansen", "given_name": "Jan", "family_name": "Jansen", "email": "jan@gmail.com", // If present, the user's email address "email_verified": true, // true, if Google has verified the email address "hd": "example.com", // If present, the host domain of the user's GSuite email address // If present, a URL to user's profile picture "picture": "https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/a-/AOh14GjlTnZKHAeb94A-FmEbwZv7uJD986VOF1mJGb2YYQ", "locale": "en_US" // User's locale, from browser or phone settings }
Ngoài việc xác minh chữ ký của mã thông báo, hãy xác minh rằng câu lệnh
công ty phát hành (trường iss) là https://accounts.google.com, mà đối tượng
(trường aud) là mã ứng dụng khách được chỉ định và mã thông báo chưa hết hạn
(trường exp).
Bằng cách sử dụng các trường email, email_verified và hd, bạn có thể xác định xem
Google lưu trữ và có thẩm quyền đối với một địa chỉ email. Trong trường hợp Google
có thẩm quyền mà người dùng hiện được biết là chủ sở hữu tài khoản hợp pháp
và bạn có thể bỏ qua mật khẩu hoặc các phương thức xác thực khác. Nếu không, các phương thức này
có thể dùng để xác minh tài khoản trước khi liên kết.
Những trường hợp mà Google có thẩm quyền:
emailcó hậu tố@gmail.com, đây là một tài khoản Gmail.email_verifiedlà đúng vàhdđã được đặt, đây là tài khoản G Suite.
Người dùng có thể đăng ký Tài khoản Google mà không cần sử dụng Gmail hoặc G Suite. Thời gian
email không chứa hậu tố @gmail.com và hd không có Google thì không
xác thực và sử dụng mật khẩu hoặc các phương pháp xác thực khác để xác minh
người dùng. email_verified cũng có thể đúng vì ban đầu Google đã xác minh
người dùng khi tài khoản Google được tạo, tuy nhiên quyền sở hữu đối với bên thứ ba
tài khoản email có thể đã thay đổi.
Kiểm tra xem Tài khoản Google đã có trong hệ thống xác thực của bạn hay chưa
Kiểm tra xem một trong các điều kiện sau có đúng hay không:
- Mã Tài khoản Google (trong trường
subcủa câu nhận định) nằm trong tài khoản người dùng của bạn cơ sở dữ liệu. - Địa chỉ email trong câu nhận định khớp với một người dùng trong cơ sở dữ liệu người dùng của bạn.
Nếu tìm thấy tài khoản cho người dùng, hãy cấp mã truy cập và trả về các giá trị trong đối tượng JSON trong phần nội dung của phản hồi HTTPS, như trong ví dụ sau:
{ "token_type": "Bearer", "access_token": "ACCESS_TOKEN", "refresh_token": "REFRESH_TOKEN", "expires_in": SECONDS_TO_EXPIRATION }
Trong một số trường hợp, người dùng có thể không liên kết được tài khoản dựa trên mã thông báo mã nhận dạng. Nếu
làm như vậy vì bất kỳ lý do gì, điểm cuối trao đổi mã thông báo của bạn cần phải trả lời bằng HTTP
Lỗi 401 chỉ định error=linking_error, như trong ví dụ sau:
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
{
"error":"linking_error",
"login_hint":"foo@bar.com"
}
Khi nhận được phản hồi lỗi 401 với linking_error, Google sẽ gửi
người dùng đến điểm cuối uỷ quyền của bạn bằng tham số login_hint. Chiến lược phát hành đĩa đơn
người dùng hoàn tất quá trình liên kết tài khoản bằng quy trình liên kết OAuth trong trình duyệt của họ.
Xử lý việc tạo tài khoản thông qua tính năng Đăng nhập bằng Google (tạo ý định)
Khi người dùng cần tạo một tài khoản trên dịch vụ của bạn, Google sẽ đưa ra yêu cầu
đến điểm cuối trao đổi mã thông báo chỉ định intent=create.
Yêu cầu có biểu mẫu sau:
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded response_type=token&grant_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer&scope=SCOPES&intent=create&assertion=JWT&client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET
Điểm cuối trao đổi mã thông báo của bạn phải có khả năng xử lý các tham số sau:
| Tham số điểm cuối của mã thông báo | |
|---|---|
intent |
Đối với các yêu cầu này, giá trị của tham số này là create. |
grant_type |
Loại mã thông báo đang được trao đổi. Đối với các yêu cầu này,
tham số có giá trị urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer. |
assertion |
Mã thông báo web JSON (JWT) cung cấp xác nhận có chữ ký của Google danh tính của người dùng. JWT chứa thông tin bao gồm Mã Tài khoản Google, tên và địa chỉ email. |
client_id |
Mã ứng dụng khách mà bạn đã chỉ định cho Google. |
client_secret |
Mật khẩu ứng dụng khách mà bạn đã chỉ định cho Google. |
JWT trong tham số assertion chứa ID Tài khoản Google của người dùng,
tên và địa chỉ email mà bạn có thể sử dụng để tạo tài khoản mới trên
.
Để phản hồi các yêu cầu về ý định create, điểm cuối trao đổi mã thông báo phải thực hiện các bước sau:
- Xác thực và giải mã câu nhận định JWT.
- Xác thực thông tin người dùng và tạo tài khoản mới.
Xác thực và giải mã câu nhận định JWT
Bạn có thể xác thực và giải mã câu nhận định JWT bằng cách sử dụng Thư viện giải mã JWT cho ngôn ngữ của bạn. Sử dụng Khoá công khai của Google, có trong JWK hoặc Định dạng PEM để xác minh chữ ký của mã thông báo.
Khi được giải mã, câu nhận định JWT sẽ có dạng như ví dụ sau:
{ "sub": "1234567890", // The unique ID of the user's Google Account "iss": "https://accounts.google.com", // The assertion's issuer "aud": "123-abc.apps.googleusercontent.com", // Your server's client ID "iat": 233366400, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's creation time "exp": 233370000, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's expiration time "name": "Jan Jansen", "given_name": "Jan", "family_name": "Jansen", "email": "jan@gmail.com", // If present, the user's email address "email_verified": true, // true, if Google has verified the email address "hd": "example.com", // If present, the host domain of the user's GSuite email address // If present, a URL to user's profile picture "picture": "https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/a-/AOh14GjlTnZKHAeb94A-FmEbwZv7uJD986VOF1mJGb2YYQ", "locale": "en_US" // User's locale, from browser or phone settings }
Ngoài việc xác minh chữ ký của mã thông báo, hãy xác minh rằng câu lệnh
công ty phát hành (trường iss) là https://accounts.google.com, mà đối tượng
(trường aud) là mã ứng dụng khách được chỉ định và mã thông báo chưa hết hạn
(trường exp).
Bằng cách sử dụng các trường email, email_verified và hd, bạn có thể xác định xem
Google lưu trữ và có thẩm quyền đối với một địa chỉ email. Trong trường hợp Google
có thẩm quyền mà người dùng hiện được biết là chủ sở hữu tài khoản hợp pháp
và bạn có thể bỏ qua mật khẩu hoặc các phương thức xác thực khác. Nếu không, các phương thức này
có thể dùng để xác minh tài khoản trước khi liên kết.
Những trường hợp mà Google có thẩm quyền:
emailcó hậu tố@gmail.com, đây là một tài khoản Gmail.email_verifiedlà đúng vàhdđã được đặt, đây là tài khoản G Suite.
Người dùng có thể đăng ký Tài khoản Google mà không cần sử dụng Gmail hoặc G Suite. Thời gian
email không chứa hậu tố @gmail.com và hd không có Google thì không
xác thực và sử dụng mật khẩu hoặc các phương pháp xác thực khác để xác minh
người dùng. email_verified cũng có thể đúng vì ban đầu Google đã xác minh
người dùng khi tài khoản Google được tạo, tuy nhiên quyền sở hữu đối với bên thứ ba
tài khoản email có thể đã thay đổi.
Xác thực thông tin người dùng và tạo tài khoản mới
Kiểm tra xem một trong các điều kiện sau có đúng hay không:
- Mã Tài khoản Google (trong trường
subcủa câu nhận định) nằm trong tài khoản người dùng của bạn cơ sở dữ liệu. - Địa chỉ email trong câu nhận định khớp với một người dùng trong cơ sở dữ liệu người dùng của bạn.
Nếu một trong hai điều kiện đúng, hãy nhắc người dùng liên kết tài khoản hiện có của họ
bằng Tài khoản Google của họ. Để thực hiện việc này, hãy phản hồi yêu cầu với lỗi HTTP 401
chỉ định error=linking_error và cung cấp địa chỉ email của người dùng làm
login_hint Sau đây là phản hồi mẫu:
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
{
"error":"linking_error",
"login_hint":"foo@bar.com"
}
Khi nhận được phản hồi lỗi 401 với linking_error, Google sẽ gửi
người dùng đến điểm cuối uỷ quyền của bạn bằng tham số login_hint. Chiến lược phát hành đĩa đơn
người dùng hoàn tất quá trình liên kết tài khoản bằng quy trình liên kết OAuth trong trình duyệt của họ.
Nếu không có điều kiện nào đúng, hãy tạo tài khoản người dùng mới có thông tin đó được cung cấp trong JWT. Các tài khoản mới thường chưa đặt mật khẩu. Bây giờ bạn nên thêm tính năng Đăng nhập bằng Google vào các nền tảng khác để người dùng có thể đăng nhập bằng Google trên các nền tảng của ứng dụng. Ngoài ra, bạn có thể gửi email cho người dùng một liên kết bắt đầu quy trình khôi phục mật khẩu để cho phép đặt mật khẩu để đăng nhập trên các nền tảng khác.
Khi quá trình tạo hoàn tất, hãy cấp một mã truy cập và làm mới mã thông báo rồi trả về các giá trị trong đối tượng JSON trong nội dung của phản hồi HTTPS, như trong ví dụ sau:
{ "token_type": "Bearer", "access_token": "ACCESS_TOKEN", "refresh_token": "REFRESH_TOKEN", "expires_in": SECONDS_TO_EXPIRATION }
Lấy mã ứng dụng khách Google API
Bạn sẽ phải cung cấp Mã ứng dụng Google API trong quá trình đăng ký tính năng Liên kết tài khoản.
Để lấy mã ứng dụng API bằng dự án bạn đã tạo trong khi hoàn tất các bước Liên kết OAuth. Để thực hiện điều này, vui lòng hoàn thành các bước sau:
Tạo hoặc chọn một dự án API của Google.
Nếu dự án của bạn không có Mã ứng dụng cho Loại ứng dụng web, hãy nhấp vào Tạo ứng dụng để tạo mã ứng dụng. Hãy nhớ thêm miền của trang web vào hộp Nguồn gốc JavaScript được uỷ quyền. Khi thực hiện kiểm thử hoặc phát triển cục bộ, bạn phải thêm cả
http://localhostvàhttp://localhost:<port_number>vào trường Nguồn gốc JavaScript được uỷ quyền.
Xác thực quá trình triển khai
Bạn có thể xác thực phương thức triển khai bằng cách sử dụng công cụ OAuth 2.0 Playground.
Trong công cụ này, hãy làm theo các bước sau:
- Nhấp vào biểu tượng Configuration (Cấu hình) để mở cửa sổ OAuth 2.0 Configuration (Cấu hình OAuth 2.0).
- Trong trường Quy trình OAuth, hãy chọn Phía máy khách.
- Trong trường OAuth Endpoints (Điểm cuối OAuth), hãy chọn Custom (Tuỳ chỉnh).
- Chỉ định điểm cuối OAuth 2.0 và mã ứng dụng khách mà bạn đã chỉ định cho Google trong các trường tương ứng.
- Trong phần Bước 1, đừng chọn bất kỳ phạm vi nào của Google. Thay vào đó, hãy để trống trường này hoặc nhập một phạm vi hợp lệ cho máy chủ của bạn (hoặc một chuỗi tuỳ ý nếu bạn không sử dụng phạm vi OAuth). Khi bạn hoàn tất, hãy nhấp vào Uỷ quyền cho API.
- Trong các mục Bước 2 và Bước 3, hãy thực hiện quy trình OAuth 2.0 và xác minh rằng mỗi bước hoạt động như dự kiến.
Bạn có thể xác thực việc triển khai của mình bằng cách sử dụng công cụ Bản minh hoạ về cách liên kết Tài khoản Google.
Trong công cụ này, hãy làm theo các bước sau:
- Nhấp vào nút Đăng nhập bằng Google.
- Chọn tài khoản mà bạn muốn liên kết.
- Nhập mã dịch vụ.
- Bạn có thể nhập một hoặc nhiều phạm vi mà bạn sẽ yêu cầu quyền truy cập.
- Nhấp vào Bắt đầu bản minh hoạ.
- Khi được nhắc, hãy xác nhận rằng bạn có thể đồng ý và từ chối yêu cầu liên kết.
- Xác nhận rằng bạn được chuyển hướng đến nền tảng của mình.