ภาพรวม
การลิงก์ Google Sign-In ที่ใช้ OAuth ได้รับการปรับปรุงให้มีประสิทธิภาพมากขึ้นจะเพิ่ม Google Sign-In ไว้เหนือการลิงก์ OAuth ซึ่งจะช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ Google ลิงก์บัญชีได้อย่างราบรื่น ทั้งยังเปิดใช้การสร้างบัญชี ซึ่งช่วยให้ผู้ใช้สร้างบัญชีใหม่ในบริการของคุณโดยใช้บัญชี Google ได้
หากต้องการลิงก์บัญชีด้วย OAuth และ Google Sign-In ให้ทําตามขั้นตอนทั่วไปต่อไปนี้
- ก่อนอื่น ให้ขอให้ผู้ใช้ให้ความยินยอมในการเข้าถึงโปรไฟล์ Google
- ใช้ข้อมูลในโปรไฟล์เพื่อตรวจสอบว่าบัญชีผู้ใช้มีอยู่หรือไม่
- สำหรับผู้ใช้เดิม ให้ลิงก์บัญชี
- หากไม่พบผู้ใช้ Google ที่ตรงกันในระบบการตรวจสอบสิทธิ์ ให้ตรวจสอบโทเค็นระบุตัวตนที่ได้รับจาก Google จากนั้นคุณจะสร้างผู้ใช้โดยอิงตามข้อมูลโปรไฟล์ที่อยู่ในโทเค็นระบุตัวตนได้
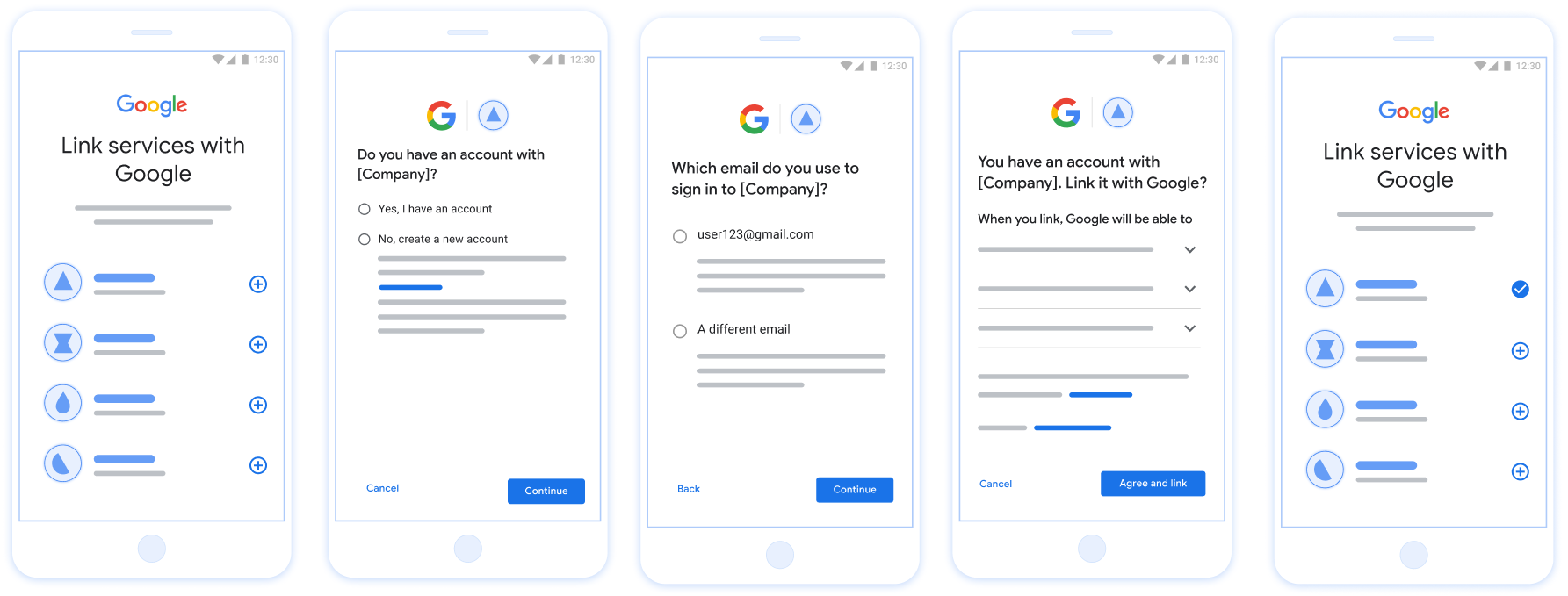
รูปที่ 1 การลิงก์บัญชีในโทรศัพท์ของผู้ใช้ด้วยการลิงก์แบบมีประสิทธิภาพ
ข้อกำหนดสำหรับการลิงก์แบบมีประสิทธิภาพ
- ใช้โฟลว์การลิงก์ OAuth พื้นฐานบนเว็บ บริการของคุณต้องรองรับปลายทางการให้สิทธิ์และการเปลี่ยนโทเค็นที่เป็นไปตามข้อกำหนด OAuth 2.0
- ปลายทางการแลกเปลี่ยนโทเค็นต้องรองรับการยืนยัน JSON Web Token (JWT) และใช้ Intent
check,createและget
ใช้เซิร์ฟเวอร์ OAuth
ปลายทางการแลกเปลี่ยนโทเค็นต้องรองรับ Intent check, create, get ด้านล่างแสดงขั้นตอนที่เสร็จสมบูรณ์ผ่านขั้นตอนการลิงก์บัญชี และระบุเวลาที่เรียกใช้ Intent ต่างๆ
- ผู้ใช้มีบัญชีในระบบการตรวจสอบสิทธิ์หรือไม่ (ผู้ใช้ตัดสินใจโดยเลือก "ใช่" หรือ "ไม่")
- ใช่ : ผู้ใช้ใช้อีเมลที่เชื่อมโยงกับบัญชี Google เพื่อลงชื่อเข้าใช้แพลตฟอร์มของคุณหรือไม่ (ผู้ใช้ตัดสินใจโดยเลือก "ใช่" หรือ "ไม่")
- ใช่ : ผู้ใช้มีบัญชีที่ตรงกันในระบบการตรวจสอบสิทธิ์หรือไม่ (โทรหา
check intentเพื่อยืนยัน)- ใช่ : มีการเรียกใช้
get intentและระบบจะลิงก์บัญชีหาก get intent แสดงผลสําเร็จ - ไม่ : สร้างบัญชีใหม่ (ผู้ใช้ตัดสินใจโดยเลือก "ใช่" หรือ "ไม่")
- ใช่ : มีการเรียกใช้
create intentและลิงก์บัญชีหากสร้าง Intent สำเร็จ - ไม่ : ระบบจะเรียกใช้ขั้นตอนการลงชื่อเข้าใช้ด้วย OAuth บนเว็บ ระบบจะนําผู้ใช้ไปยังเบราว์เซอร์ และผู้ใช้จะมีตัวเลือกให้ลิงก์กับอีเมลอื่น
- ใช่ : มีการเรียกใช้
- ใช่ : มีการเรียกใช้
- ไม่ : ระบบจะเรียกใช้ขั้นตอนการลงชื่อเข้าใช้ด้วย OAuth บนเว็บ ระบบจะนําผู้ใช้ไปยังเบราว์เซอร์ และผู้ใช้จะมีตัวเลือกให้ลิงก์กับอีเมลอื่น
- ใช่ : ผู้ใช้มีบัญชีที่ตรงกันในระบบการตรวจสอบสิทธิ์หรือไม่ (โทรหา
- ไม่ : ผู้ใช้มีบัญชีที่ตรงกันในระบบการตรวจสอบสิทธิ์หรือไม่ (โทรหา
check intentเพื่อยืนยัน)- ใช่ : มีการเรียกใช้
get intentและระบบจะลิงก์บัญชีหาก get intent แสดงผลสําเร็จ - ไม่ : มีการเรียกใช้
create intentและระบบจะลิงก์บัญชีหาก createIntent แสดงผลสำเร็จ
- ใช่ : มีการเรียกใช้
- ใช่ : ผู้ใช้ใช้อีเมลที่เชื่อมโยงกับบัญชี Google เพื่อลงชื่อเข้าใช้แพลตฟอร์มของคุณหรือไม่ (ผู้ใช้ตัดสินใจโดยเลือก "ใช่" หรือ "ไม่")
Check for an existing user account (check intent)
After the user gives consent to access their Google profile, Google sends a request that contains a signed assertion of the Google user's identity. The assertion contains information that includes the user's Google Account ID, name, and email address. The token exchange endpoint configured for your project handles that request.
If the corresponding Google account is already present in your authentication
system, your token exchange endpoint responds with account_found=true. If the
Google account doesn't match an existing user, your token exchange endpoint
returns an HTTP 404 Not Found error with account_found=false.
The request has the following form:
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded grant_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer&intent=check&assertion=JWT&scope=SCOPES&client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET
Your token exchange endpoint must be able to handle the following parameters:
| Token endpoint parameters | |
|---|---|
intent |
For these requests, the value of this parameter is
check. |
grant_type |
The type of token being exchanged. For these requests, this
parameter has the value urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer. |
assertion |
A JSON Web Token (JWT) that provides a signed assertion of the Google user's identity. The JWT contains information that includes the user's Google Account ID, name, and email address. |
client_id |
The client ID you assigned to Google. |
client_secret |
The client secret you assigned to Google. |
To respond to the check intent requests, your token exchange endpoint must perform the following steps:
- Validate and decode the JWT assertion.
- Check if the Google account is already present in your authentication system.
Validate and decode the JWT assertion
You can validate and decode the JWT assertion by using a JWT-decoding library for your language. Use Google's public keys, available in JWK or PEM formats, to verify the token's signature.
When decoded, the JWT assertion looks like the following example:
{ "sub": "1234567890", // The unique ID of the user's Google Account "iss": "https://accounts.google.com", // The assertion's issuer "aud": "123-abc.apps.googleusercontent.com", // Your server's client ID "iat": 233366400, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's creation time "exp": 233370000, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's expiration time "name": "Jan Jansen", "given_name": "Jan", "family_name": "Jansen", "email": "jan@gmail.com", // If present, the user's email address "email_verified": true, // true, if Google has verified the email address "hd": "example.com", // If present, the host domain of the user's GSuite email address // If present, a URL to user's profile picture "picture": "https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/a-/AOh14GjlTnZKHAeb94A-FmEbwZv7uJD986VOF1mJGb2YYQ", "locale": "en_US" // User's locale, from browser or phone settings }
In addition to verifying the token's signature, verify that the assertion's
issuer (iss field) is https://accounts.google.com, that the audience
(aud field) is your assigned client ID, and that the token has not expired
(exp field).
Using the email, email_verified and hd fields you can determine if
Google hosts and is authoritative for an email address. In cases where Google is
authoritative the user is currently known to be the legitimate account owner
and you may skip password or other challenges methods. Otherwise, these methods
can be used to verify the account prior to linking.
Cases where Google is authoritative:
emailhas a@gmail.comsuffix, this is a Gmail account.email_verifiedis true andhdis set, this is a G Suite account.
Users may register for Google Accounts without using Gmail or G Suite. When
email does not contain a @gmail.com suffix and hd is absent Google is not
authoritative and password or other challenge methods are recommended to verify
the user. email_verified can also be true as Google initially verified the
user when the Google account was created, however ownership of the third party
email account may have since changed.
Check if the Google account is already present in your authentication system
Check whether either of the following conditions are true:
- The Google Account ID, found in the assertion's
subfield, is in your user database. - The email address in the assertion matches a user in your user database.
If either condition is true, the user has already signed up. In that case, return a response like the following:
HTTP/1.1 200 Success
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
{
"account_found":"true",
}
If neither the Google Account ID nor the email address specified in the
assertion matches a user in your database, the user hasn't signed up yet. In
this case, your token exchange endpoint needs to reply with a HTTP 404 error
that specifies "account_found": "false", as in the following example:
HTTP/1.1 404 Not found
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
{
"account_found":"false",
}
Handle automatic linking (get intent)
After the user gives consent to access their Google profile, Google sends a request that contains a signed assertion of the Google user's identity. The assertion contains information that includes the user's Google Account ID, name, and email address. The token exchange endpoint configured for your project handles that request.
If the corresponding Google Account is already present in your authentication
system, your token exchange endpoint returns a token for the user. If the
Google Account doesn't match an existing user, your token exchange endpoint
returns a linking_error error and optional login_hint.
The request has the following form:
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded grant_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer&intent=get&assertion=JWT&scope=SCOPES&client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET
Your token exchange endpoint must be able to handle the following parameters:
| Token endpoint parameters | |
|---|---|
intent |
For these requests, the value of this parameter is get. |
grant_type |
The type of token being exchanged. For these requests, this
parameter has the value urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer. |
assertion |
A JSON Web Token (JWT) that provides a signed assertion of the Google user's identity. The JWT contains information that includes the user's Google Account ID, name, and email address. |
scope |
Optional: Any scopes that you've configured Google to request from users. |
client_id |
The client ID you assigned to Google. |
client_secret |
The client secret you assigned to Google. |
To respond to the get intent requests, your token exchange endpoint must perform the following steps:
- Validate and decode the JWT assertion.
- Check if the Google account is already present in your authentication system.
Validate and decode the JWT assertion
You can validate and decode the JWT assertion by using a JWT-decoding library for your language. Use Google's public keys, available in JWK or PEM formats, to verify the token's signature.
When decoded, the JWT assertion looks like the following example:
{ "sub": "1234567890", // The unique ID of the user's Google Account "iss": "https://accounts.google.com", // The assertion's issuer "aud": "123-abc.apps.googleusercontent.com", // Your server's client ID "iat": 233366400, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's creation time "exp": 233370000, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's expiration time "name": "Jan Jansen", "given_name": "Jan", "family_name": "Jansen", "email": "jan@gmail.com", // If present, the user's email address "email_verified": true, // true, if Google has verified the email address "hd": "example.com", // If present, the host domain of the user's GSuite email address // If present, a URL to user's profile picture "picture": "https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/a-/AOh14GjlTnZKHAeb94A-FmEbwZv7uJD986VOF1mJGb2YYQ", "locale": "en_US" // User's locale, from browser or phone settings }
In addition to verifying the token's signature, verify that the assertion's
issuer (iss field) is https://accounts.google.com, that the audience
(aud field) is your assigned client ID, and that the token has not expired
(exp field).
Using the email, email_verified and hd fields you can determine if
Google hosts and is authoritative for an email address. In cases where Google is
authoritative the user is currently known to be the legitimate account owner
and you may skip password or other challenges methods. Otherwise, these methods
can be used to verify the account prior to linking.
Cases where Google is authoritative:
emailhas a@gmail.comsuffix, this is a Gmail account.email_verifiedis true andhdis set, this is a G Suite account.
Users may register for Google Accounts without using Gmail or G Suite. When
email does not contain a @gmail.com suffix and hd is absent Google is not
authoritative and password or other challenge methods are recommended to verify
the user. email_verified can also be true as Google initially verified the
user when the Google account was created, however ownership of the third party
email account may have since changed.
Check if the Google account is already present in your authentication system
Check whether either of the following conditions are true:
- The Google Account ID, found in the assertion's
subfield, is in your user database. - The email address in the assertion matches a user in your user database.
If an account is found for the user, issue an access token and return the values in a JSON object in the body of your HTTPS response, like in the following example:
{ "token_type": "Bearer", "access_token": "ACCESS_TOKEN", "refresh_token": "REFRESH_TOKEN", "expires_in": SECONDS_TO_EXPIRATION }
In some cases, account linking based on ID token might fail for the user. If it
does so for any reason, your token exchange endpoint needs to reply with a HTTP
401 error that specifies error=linking_error, as the following example shows:
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
{
"error":"linking_error",
"login_hint":"foo@bar.com"
}
When Google receives a 401 error response with linking_error, Google sends
the user to your authorization endpoint with login_hint as a parameter. The
user completes account linking using the OAuth linking flow in their browser.
Handle account creation via Google Sign-In (create intent)
When a user needs to create an account on your service, Google makes a request
to your token exchange endpoint that specifies intent=create.
The request has the following form:
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded response_type=token&grant_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer&scope=SCOPES&intent=create&assertion=JWT&client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET
Your token exchange endpoint must able to handle the following parameters:
| Token endpoint parameters | |
|---|---|
intent |
For these requests, the value of this parameter is create. |
grant_type |
The type of token being exchanged. For these requests, this
parameter has the value urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer. |
assertion |
A JSON Web Token (JWT) that provides a signed assertion of the Google user's identity. The JWT contains information that includes the user's Google Account ID, name, and email address. |
client_id |
The client ID you assigned to Google. |
client_secret |
The client secret you assigned to Google. |
The JWT within the assertion parameter contains the user's Google Account ID,
name, and email address, which you can use to create a new account on your
service.
To respond to the create intent requests, your token exchange endpoint must perform the following steps:
- Validate and decode the JWT assertion.
- Validate user information and create new account.
Validate and decode the JWT assertion
You can validate and decode the JWT assertion by using a JWT-decoding library for your language. Use Google's public keys, available in JWK or PEM formats, to verify the token's signature.
When decoded, the JWT assertion looks like the following example:
{ "sub": "1234567890", // The unique ID of the user's Google Account "iss": "https://accounts.google.com", // The assertion's issuer "aud": "123-abc.apps.googleusercontent.com", // Your server's client ID "iat": 233366400, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's creation time "exp": 233370000, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's expiration time "name": "Jan Jansen", "given_name": "Jan", "family_name": "Jansen", "email": "jan@gmail.com", // If present, the user's email address "email_verified": true, // true, if Google has verified the email address "hd": "example.com", // If present, the host domain of the user's GSuite email address // If present, a URL to user's profile picture "picture": "https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/a-/AOh14GjlTnZKHAeb94A-FmEbwZv7uJD986VOF1mJGb2YYQ", "locale": "en_US" // User's locale, from browser or phone settings }
In addition to verifying the token's signature, verify that the assertion's
issuer (iss field) is https://accounts.google.com, that the audience
(aud field) is your assigned client ID, and that the token has not expired
(exp field).
Using the email, email_verified and hd fields you can determine if
Google hosts and is authoritative for an email address. In cases where Google is
authoritative the user is currently known to be the legitimate account owner
and you may skip password or other challenges methods. Otherwise, these methods
can be used to verify the account prior to linking.
Cases where Google is authoritative:
emailhas a@gmail.comsuffix, this is a Gmail account.email_verifiedis true andhdis set, this is a G Suite account.
Users may register for Google Accounts without using Gmail or G Suite. When
email does not contain a @gmail.com suffix and hd is absent Google is not
authoritative and password or other challenge methods are recommended to verify
the user. email_verified can also be true as Google initially verified the
user when the Google account was created, however ownership of the third party
email account may have since changed.
Validate user information and create new account
Check whether either of the following conditions are true:
- The Google Account ID, found in the assertion's
subfield, is in your user database. - The email address in the assertion matches a user in your user database.
If either condition is true, prompt the user to link their existing account
with their Google Account. To do so, respond to the request with an HTTP 401 error
that specifies error=linking_error and gives the user's email address as the
login_hint. The following is a sample response:
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
{
"error":"linking_error",
"login_hint":"foo@bar.com"
}
When Google receives a 401 error response with linking_error, Google sends
the user to your authorization endpoint with login_hint as a parameter. The
user completes account linking using the OAuth linking flow in their browser.
If neither condition is true, create a new user account with the information provided in the JWT. New accounts don't typically have a password set. It's recommended that you add Google Sign-In to other platforms to enable users to log in with Google across the surfaces of your application. Alternatively, you can email the user a link that starts your password recovery flow to allow the user to set a password to sign in on other platforms.
When the creation is completed, issue an access token and return the values in a JSON object in the body of your HTTPS response, like in the following example:
{ "token_type": "Bearer", "access_token": "ACCESS_TOKEN", "refresh_token": "REFRESH_TOKEN", "expires_in": SECONDS_TO_EXPIRATION }
รับรหัสไคลเอ็นต์ Google API
คุณจะต้องระบุรหัสไคลเอ็นต์ Google API ในระหว่างกระบวนการลงทะเบียนการลิงก์บัญชี
วิธีรับรหัสไคลเอ็นต์ API โดยใช้โปรเจ็กต์ที่คุณสร้างขึ้นขณะทำตามขั้นตอนการลิงก์ OAuth โดยทำตามขั้นตอนต่อไปนี้
สร้างหรือเลือกโปรเจ็กต์ Google APIs
หากโปรเจ็กต์ไม่มีรหัสไคลเอ็นต์สำหรับประเภทเว็บแอปพลิเคชัน ให้คลิกสร้างไคลเอ็นต์เพื่อสร้างรหัส อย่าลืมใส่โดเมนของเว็บไซต์ในช่องต้นทางของ JavaScript ที่ได้รับอนุญาต เมื่อทำการทดสอบหรือพัฒนาในเครื่อง คุณต้องเพิ่มทั้ง
http://localhostและhttp://localhost:<port_number>ลงในช่องต้นทาง JavaScript ที่อนุญาต
ตรวจสอบการติดตั้งใช้งาน
You can validate your implementation by using the OAuth 2.0 Playground tool.
In the tool, do the following steps:
- Click Configuration to open the OAuth 2.0 Configuration window.
- In the OAuth flow field, select Client-side.
- In the OAuth Endpoints field, select Custom.
- Specify your OAuth 2.0 endpoint and the client ID you assigned to Google in the corresponding fields.
- In the Step 1 section, don't select any Google scopes. Instead, leave this field blank or type a scope valid for your server (or an arbitrary string if you don't use OAuth scopes). When you're done, click Authorize APIs.
- In the Step 2 and Step 3 sections, go through the OAuth 2.0 flow and verify that each step works as intended.
You can validate your implementation by using the Google Account Linking Demo tool.
In the tool, do the following steps:
- Click the Sign-in with Google button.
- Choose the account you'd like to link.
- Enter the service ID.
- Optionally enter one or more scopes that you will request access for.
- Click Start Demo.
- When prompted, confirm that you may consent and deny the linking request.
- Confirm that you are redirected to your platform.