계정은 업계 표준 OAuth 2.0 암시적 흐름 및 승인 코드 흐름을 사용하여 연결됩니다. 서비스가 OAuth 2.0을 준수하는 승인 및 토큰 교환 엔드포인트를 지원해야 합니다.
암시적 흐름에서는 Google이 사용자의 브라우저에서 승인 엔드포인트를 엽니다. 로그인에 성공하면 장기 액세스 토큰을 Google에 반환합니다. 이제 Google에서 전송하는 모든 요청에 이 액세스 토큰이 포함됩니다.
승인 코드 흐름에는 두 개의 엔드포인트가 필요합니다.
아직 로그인하지 않은 사용자에게 로그인 UI를 표시하는 승인 엔드포인트입니다. 승인 엔드포인트는 요청된 액세스에 대한 사용자의 동의를 기록하기 위해 단기 승인 코드도 만듭니다.
두 가지 유형의 교환을 담당하는 토큰 교환 엔드포인트:
- 승인 코드를 사용 기간이 긴 갱신 토큰 및 사용 기간이 짧은 액세스 토큰으로 교환합니다. 이 교환은 사용자가 계정 연결 흐름을 진행할 때 발생합니다.
- 장기 갱신 토큰을 단기 액세스 토큰으로 교환합니다. 이 교환은 만료된 액세스 토큰으로 인해 Google에 새 액세스 토큰이 필요할 때 발생합니다.
OAuth 2.0 흐름 선택
암시적 흐름은 구현하기가 더 간단하지만 암시적 흐름에서 발급된 액세스 토큰은 만료되지 않도록 하는 것이 좋습니다. 이는 암시적 흐름으로 토큰이 만료된 후 사용자가 계정을 다시 연결해야 하기 때문입니다. 보안상의 이유로 토큰 만료가 필요한 경우에는 승인 코드 흐름을 대신 사용하는 것이 좋습니다.
디자인 가이드라인
이 섹션에서는 OAuth 연결 흐름을 위해 호스팅하는 사용자 화면에 대한 디자인 요구사항과 권장사항을 설명합니다. Google 앱에서 호출하면 플랫폼에서 사용자에게 Google 로그인 페이지와 계정 연결 동의 화면을 표시합니다. 사용자가 계정 연결에 동의하면 Google 앱으로 다시 리디렉션됩니다.
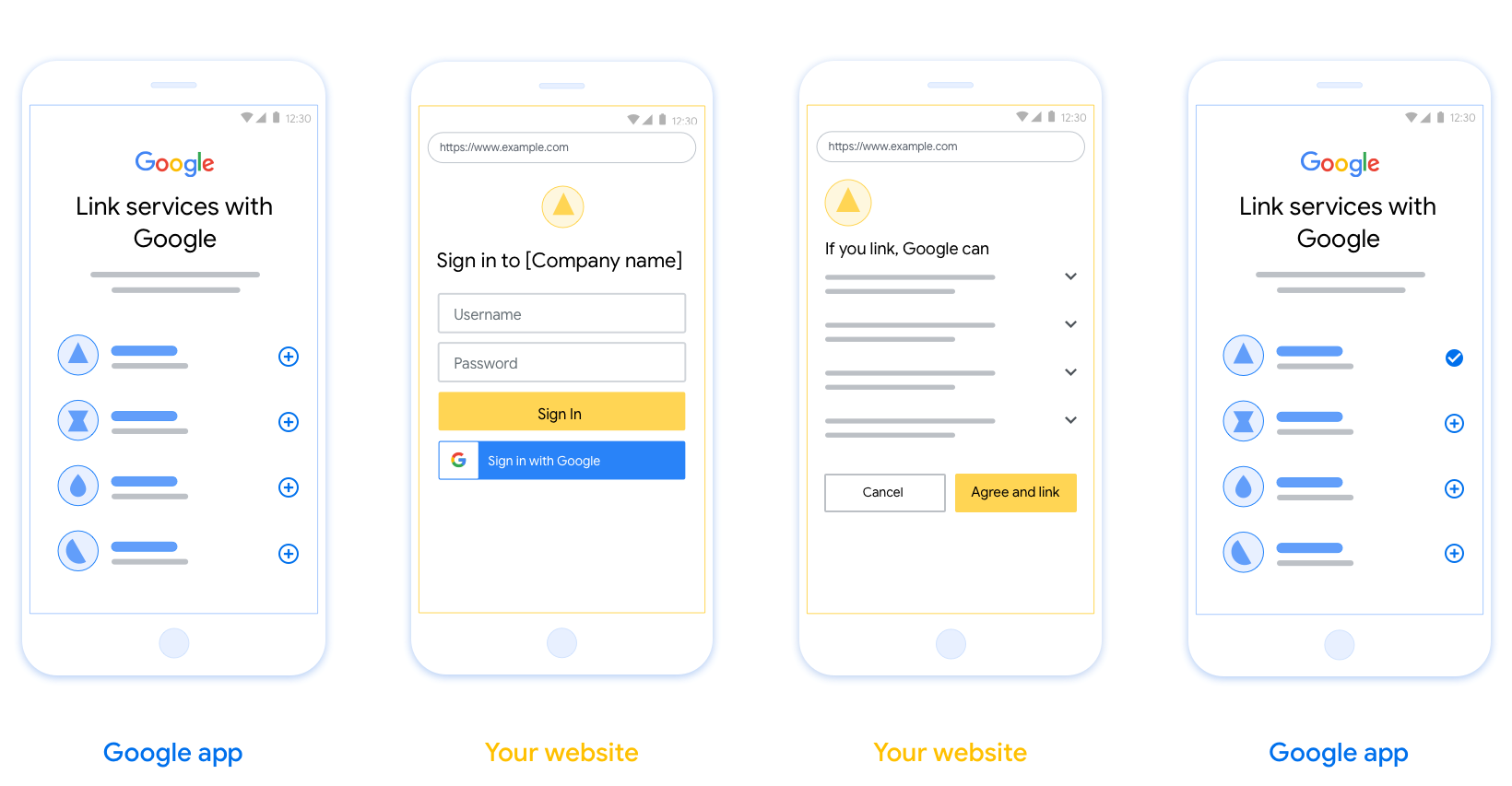
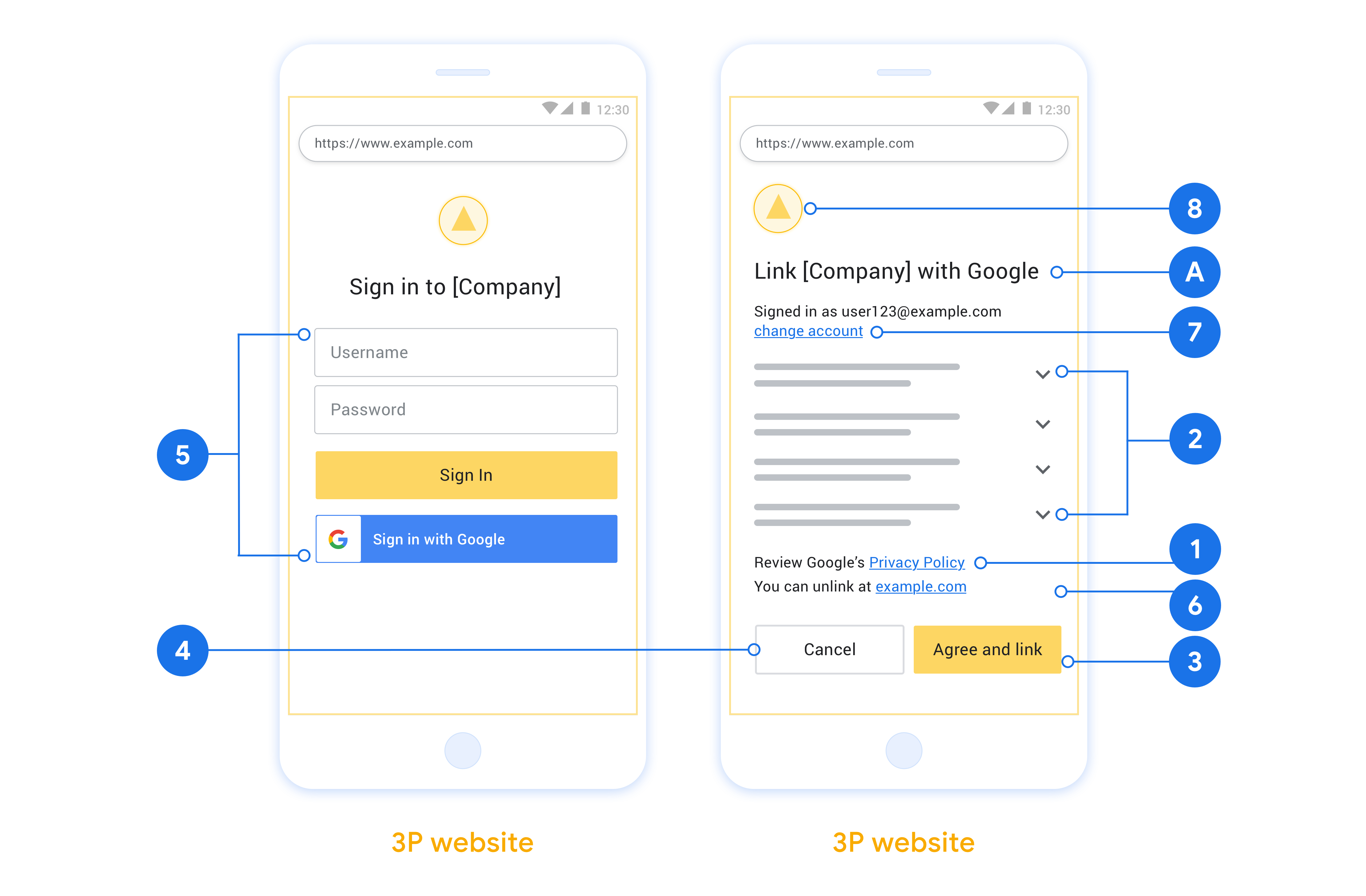
요구사항
- 사용자의 계정이 Google Home 또는 Google 어시스턴트와 같은 특정 Google 제품이 아닌 Google에 연결된다고 안내해야 합니다.
권장사항
다음을 수행하는 것이 좋습니다.
Google 개인정보처리방침을 표시합니다. 동의 화면에 Google 개인정보처리방침 링크를 포함합니다.
공유할 데이터 Google에서 필요로 하는 데이터와 그 이유를 사용자에게 명확하고 간결한 언어로 전달하세요.
명확한 클릭 유도 문구 '동의 및 연결'과 같은 명확한 클릭 유도 문구를 동의 화면에 표시합니다. 이는 사용자가 계정을 연결하기 위해 Google과 공유해야 하는 데이터를 이해해야 하기 때문입니다.
취소 기능 사용자가 연결하지 않기로 선택한 경우 뒤로 돌아가거나 취소할 수 있는 방법을 제공합니다.
명확한 로그인 절차. 사용자에게 사용자 이름 및 비밀번호 입력란이나 Google 계정으로 로그인과 같이 Google 계정에 로그인하는 명확한 방법이 제공되어야 합니다.
연결 해제 기능. 사용자가 연결을 해제할 수 있는 메커니즘(예: 플랫폼의 계정 설정 URL)을 제공합니다. 또는 사용자가 연결된 계정을 관리할 수 있는 Google 계정 링크를 포함할 수 있습니다.
사용자 계정을 변경할 수 있는 기능 사용자가 계정을 전환할 수 있는 방법을 제안합니다. 이는 사용자가 여러 계정을 사용하는 경향이 있는 경우에 특히 유용합니다.
- 사용자가 계정을 전환하려면 동의 화면을 닫아야 하는 경우 사용자가 OAuth 연결 및 암시적 흐름으로 원하는 계정에 로그인할 수 있도록 복구 가능한 오류를 Google에 전송합니다.
로고를 포함합니다. 동의 화면에 회사 로고를 표시합니다. 스타일 가이드라인에 따라 로고를 배치합니다. Google 로고도 표시하려면 로고 및 상표를 참고하세요.
프로젝트 만들기
계정 연결을 사용할 프로젝트를 만들려면 다음 단계를 따르세요.
- 프로젝트 만들기를 클릭합니다.
- 이름을 입력하거나 생성된 추천을 수락합니다.
- 나머지 필드를 확인하거나 수정합니다.
- 만들기를 클릭합니다.
프로젝트 ID를 확인하려면 다음 단계를 따르세요.
- 방문 페이지의 표에서 프로젝트를 찾습니다. 프로젝트 ID는 ID 열에 표시됩니다.
OAuth 동의 화면 구성
Google 계정 연결 프로세스에는 사용자에게 데이터 액세스를 요청하는 애플리케이션, 요청하는 데이터의 종류, 적용되는 약관을 알려주는 동의 화면이 포함됩니다. Google API 클라이언트 ID를 생성하기 전에 OAuth 동의 화면을 구성해야 합니다.
- Google API 콘솔의 OAuth 동의 화면 페이지를 엽니다.
- 메시지가 표시되면 방금 만든 프로젝트를 선택합니다.
'OAuth 동의 화면' 페이지에서 양식을 작성하고 '저장' 버튼을 클릭합니다.
애플리케이션 이름: 동의를 요청하는 애플리케이션의 이름입니다. 이름은 애플리케이션을 정확하게 반영해야 하며 사용자가 다른 곳에서 보는 애플리케이션 이름과 일치해야 합니다. 애플리케이션 이름은 계정 연결 동의 화면에 표시됩니다.
애플리케이션 로고: 사용자가 앱을 인식하는 데 도움이 되는 동의 화면의 이미지입니다. 로고는 계정 연결 동의 화면과 계정 설정에 표시됩니다.
지원 이메일: 사용자가 동의에 대해 문의할 수 있습니다.
Google API 범위: 범위를 사용하면 애플리케이션이 사용자의 비공개 Google 데이터에 액세스할 수 있습니다. Google 계정 연결 사용 사례의 경우 기본 범위 (이메일, 프로필, openid)로 충분하며 민감한 범위를 추가할 필요가 없습니다. 일반적으로 액세스가 필요한 시점에 미리 요청하는 대신 점진적으로 범위를 요청하는 것이 좋습니다. 자세히 알아보기
승인된 도메인: 나와 내 사용자를 보호하기 위해 Google에서는 OAuth를 사용하여 인증하는 애플리케이션만 승인된 도메인을 사용할 수 있도록 허용합니다. 애플리케이션의 링크는 승인된 도메인에서 호스팅되어야 합니다. 자세히 알아보기
애플리케이션 홈페이지 링크: 애플리케이션의 홈페이지입니다. 승인된 도메인에서 호스팅해야 합니다.
애플리케이션 개인정보처리방침 링크: Google 계정 연결 동의 화면에 표시됩니다. 승인된 도메인에서 호스팅해야 합니다.
애플리케이션 서비스 약관 링크 (선택사항): 승인된 도메인에서 호스팅되어야 합니다.
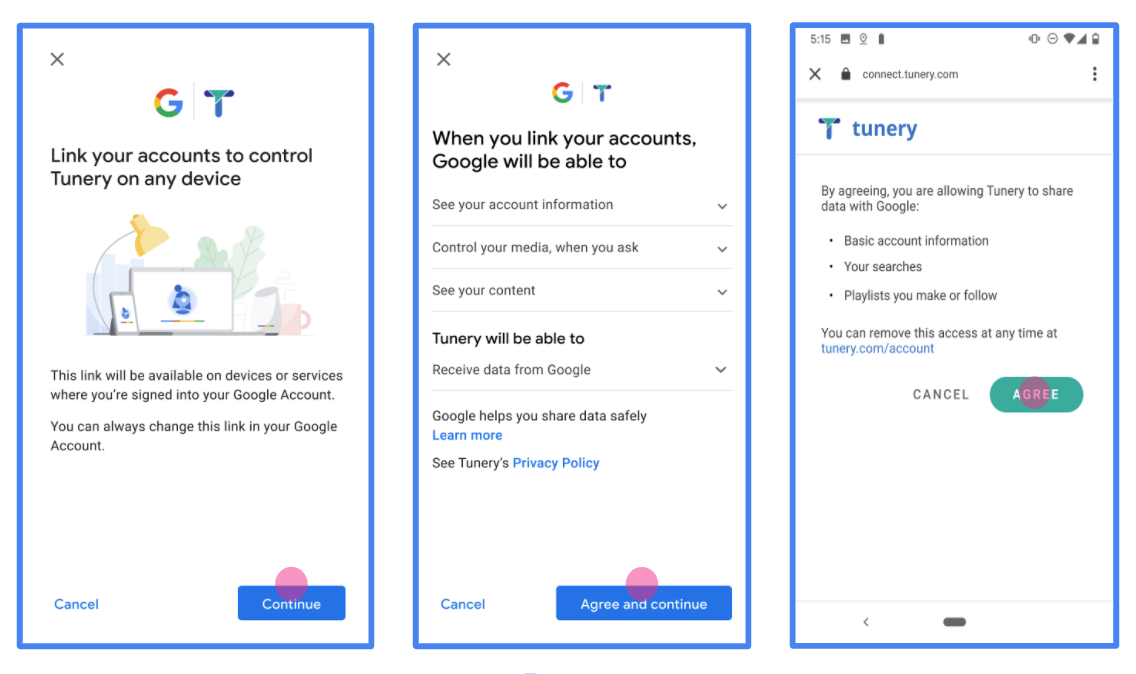
그림 1. 가상 애플리케이션 Tunery의 Google 계정 연결 동의 화면
'인증 상태'를 확인합니다. 애플리케이션에 인증이 필요한 경우 '인증을 위해 제출' 버튼을 클릭하여 인증을 위해 애플리케이션을 제출합니다. 자세한 내용은 OAuth 인증 요구사항을 참고하세요.
OAuth 서버 구현
승인 코드 흐름의 OAuth 2.0 서버 구현은 다음으로 구성됩니다. 서비스가 HTTPS를 통해 사용할 수 있도록 하는 두 개의 엔드포인트 첫 번째 엔드포인트는 승인 엔드포인트로, 승인 엔드포인트는 사용자의 동의를 얻어야 합니다. 승인 엔드포인트는 로그인 UI를 사용자에게 제공하고 이에 대한 동의를 기록 액세스 권한을 요청합니다. 두 번째 엔드포인트는 토큰 교환 엔드포인트로, 토큰이라는 암호화된 문자열을 가져오는 데 사용되며, 이 문자열은 사용자에게 서비스에 액세스할 수 있습니다
Google 애플리케이션이 서비스의 API 중 하나를 호출해야 하는 경우 Google은 이러한 API를 호출할 수 있는 권한을 사용자로부터 얻기 위해 이러한 엔드포인트를 함께 모읍니다. 위임할 수 있습니다
Google에서 시작한 OAuth 2.0 승인 코드 흐름 세션에는 다음 흐름을 따라 하세요.
- Google은 사용자의 브라우저에서 승인 엔드포인트를 엽니다. 흐름이 작업을 위해 음성 전용 기기에서 시작된 경우 Google은 실행되는 것입니다.
- 사용자가 아직 로그인하지 않은 경우 로그인하여 Google에 다음 권한을 부여합니다. 아직 권한을 부여하지 않은 경우 API를 통해 데이터에 액세스할 수 있습니다.
- 서비스에서 승인 코드를 생성하여 Google에 반환합니다. 해야 할 일 승인 코드를 사용하여 사용자의 브라우저를 Google로 다시 리디렉션합니다. 이 요청에 첨부됩니다.
- Google은 토큰 교환 엔드포인트로 승인 코드를 전송합니다. 코드의 신뢰성을 확인하고 액세스 토큰과 갱신 토큰을 선택합니다. 액세스 토큰은 사용자 인증 정보로 수락합니다. 갱신 토큰은 새 액세스 토큰을 획득할 때 Google이 저장하고 사용할 수 있는 만료됩니다.
- 사용자가 계정 연결 흐름을 완료한 후 Google에서 전송한 요청에는 액세스 토큰이 포함됩니다.
승인 요청 처리
OAuth 2.0 승인 코드를 사용하여 계정 연결을 수행해야 하는 경우 Google은 승인 엔드포인트로 에는 다음 매개변수가 포함됩니다.
| 승인 엔드포인트 매개변수 | |
|---|---|
client_id |
Google에 할당한 클라이언트 ID입니다. |
redirect_uri |
이 요청에 대한 응답을 보낼 URL입니다. |
state |
정해진 기간에 변경되지 않고 Google에 다시 전달되는 리디렉션 URI를 사용할 수 있습니다. |
scope |
선택사항: 공백으로 구분된 범위 문자열 집합으로, Google이 승인을 요청하는 데이터입니다. |
response_type |
응답에서 반환할 값의 유형입니다. OAuth 2.0의 경우
승인 코드 흐름에서 응답 유형은 항상 code입니다.
|
user_locale |
Google 계정 언어 설정 RFC5646 형식으로, 사용자가 선호하는 언어로 콘텐츠를 현지화하는 데 사용됩니다. |
예를 들어 승인 엔드포인트를
https://myservice.example.com/auth인 경우 요청은 다음과 같을 수 있습니다.
GET https://myservice.example.com/auth?client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&redirect_uri=REDIRECT_URI&state=STATE_STRING&scope=REQUESTED_SCOPES&response_type=code&user_locale=LOCALE
승인 엔드포인트가 로그인 요청을 처리하도록 하려면 다음을 수행합니다. 단계:
client_id이 Google에 할당한 클라이언트 ID와 일치하고redirect_uri가 Google에서 서비스에 제공한 리디렉션 URL과 일치하는지 확인합니다. 이러한 확인은 서비스 계정에 의도하지 않거나 잘못 구성된 클라이언트 앱에 액세스할 수 없습니다. 여러 개의 OAuth 2.0 흐름에서response_type가code인지도 확인합니다.- 사용자가 서비스에 로그인했는지 확인합니다. 사용자가 로그인하지 않은 경우 서비스의 로그인 또는 가입 흐름을 완료할 수 있습니다.
- Google에서 API에 액세스하는 데 사용할 승인 코드를 생성합니다. 승인 코드는 임의의 문자열 값이 될 수 있지만 고유해야 합니다. 사용자, 토큰의 대상 클라이언트, 코드의 만료 시간을 나타내는 추측할 수 없어야 합니다. 일반적으로 승인을 발행합니다. 코드는 약 10분 후에 만료됩니다.
redirect_uri매개변수로 지정된 URL에 다음 양식을 제출해 주세요.https://oauth-redirect.googleusercontent.com/r/YOUR_PROJECT_ID https://oauth-redirect-sandbox.googleusercontent.com/r/YOUR_PROJECT_ID
- 사용자의 브라우저를
redirect_uri매개변수 제출한 승인 코드 포함 리디렉션할 때 수정되지 않은 원래 상태 값과code및state매개변수를 추가합니다. 다음은 결과 URL의 예는 다음과 같습니다.https://oauth-redirect.googleusercontent.com/r/YOUR_PROJECT_ID?code=AUTHORIZATION_CODE&state=STATE_STRING
토큰 교환 요청 처리
서비스의 토큰 교환 엔드포인트는 두 가지 종류의 토큰을 담당합니다. 있습니다.
- 승인 코드를 액세스 토큰 및 갱신 토큰으로 교환
- 갱신 토큰을 액세스 토큰으로 교환
토큰 교환 요청에는 다음 매개변수가 포함됩니다.
| 토큰 교환 엔드포인트 매개변수 | |
|---|---|
client_id |
요청 출처를 Google로 식별하는 문자열입니다. 이 문자열은 시스템 내에 Google의 고유 식별자로 등록되어 있어야 합니다. |
client_secret |
서비스를 위해 Google에 등록한 비밀번호 문자열입니다. |
grant_type |
교환되는 토큰의 유형입니다. 다음 중 하나에 해당합니다.
authorization_code 또는 refresh_token |
code |
grant_type=authorization_code인 경우 이 매개변수는
Google이 로그인 또는 토큰 교환에서 수신한 코드
할 수 있습니다 |
redirect_uri |
grant_type=authorization_code인 경우 이 매개변수는
초기 승인 요청에 사용된 URL입니다. |
refresh_token |
grant_type=refresh_token인 경우 이 매개변수는
Google이 토큰 교환 엔드포인트에서 수신한 갱신 토큰입니다. |
승인 코드를 액세스 토큰 및 갱신 토큰으로 교환
사용자가 로그인하고 승인 엔드포인트에서 단기 응답을 반환한 후 Google에서 토큰 교환으로 요청을 엔드포인트에서 승인 코드를 액세스 토큰으로 교환하고 토큰입니다.
이러한 요청에서 grant_type 값은 authorization_code이고
code 값은 이전에 부여한 승인 코드의 값입니다.
Google에 문의하기 다음은
승인 코드는 다음과 같습니다.
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET&grant_type=authorization_code&code=AUTHORIZATION_CODE&redirect_uri=REDIRECT_URI
승인 코드를 액세스 토큰 및 갱신 토큰으로 교환하려면
토큰 교환 엔드포인트는 다음을 실행하여 POST 요청에 응답합니다.
단계:
client_id이 요청 출처를 승인된 출처이고client_secret가 예상값과 일치하는지 확인합니다.- 승인 코드가 유효하고 만료되지 않았는지, 요청에 지정된 클라이언트 ID가 승인 코드가 필요합니다.
redirect_uri매개변수로 지정된 URL이 동일한지 확인 초기 승인 요청에 사용된 값으로 설정합니다.- 위의 기준을 모두 확인할 수 없는 경우
{"error": "invalid_grant"}이 본문으로 있는 400 잘못된 요청 오류입니다. - 그렇지 않은 경우 승인 코드의 사용자 ID를 사용하여 새로고침을 생성하세요. 액세스 토큰을 만들 수 있습니다 토큰은 임의의 문자열 값이 될 수 있지만 토큰이 대상으로 하는 사용자와 클라이언트를 고유하게 나타내야 하며, 추측할 수 없어야 합니다. 액세스 토큰의 경우 이 시간은 일반적으로 토큰을 발급하고 한 시간 후에 이뤄집니다 갱신 토큰은 만료되지 않습니다.
- HTTPS 응답 본문에 다음 JSON 객체를 반환합니다.
{ "token_type": "Bearer", "access_token": "ACCESS_TOKEN", "refresh_token": "REFRESH_TOKEN", "expires_in": SECONDS_TO_EXPIRATION }
Google에서 사용자 및 기록의 액세스 토큰과 갱신 토큰을 저장함 만료되어야 합니다 액세스 토큰이 만료되면 Google은 토큰 교환 엔드포인트에서 새 액세스 토큰을 가져옵니다.
갱신 토큰을 액세스 토큰으로 교환
액세스 토큰이 만료되면 Google에서 토큰 교환으로 요청을 전송합니다. 새 액세스 토큰으로 교환합니다.
이러한 요청에서 grant_type 값은 refresh_token이고
refresh_token는 이전에 부여한 갱신 토큰의 값입니다.
Google 다음은 갱신 토큰 교환 요청의 예시입니다.
다음을 수행합니다.
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET&grant_type=refresh_token&refresh_token=REFRESH_TOKEN
갱신 토큰을 액세스 토큰으로 교환하려면 토큰 교환 엔드포인트
다음 단계를 실행하여 POST 요청에 응답합니다.
client_id가 요청 출처를 Google로 식별하는지 확인합니다.client_secret가 예상값과 일치하는지 확인합니다.- 갱신 토큰이 유효하고 요청이 갱신 토큰과 연결된 클라이언트 ID와 일치하는지 확인합니다.
- 위의 기준을 모두 확인할 수 없는 경우 HTTP 400을 반환합니다.
본문이
{"error": "invalid_grant"}인 잘못된 요청 오류입니다. - 그렇지 않은 경우 갱신 토큰의 사용자 ID를 사용하여 액세스 권한을 생성하세요. 토큰입니다. 토큰은 임의의 문자열 값이 될 수 있지만 고유하게 사용자와 클라이언트를 나타내야 하며 있습니다. 액세스 토큰의 경우 토큰의 만료 시간도 기록합니다. 일반적으로 토큰을 발급하고 1시간 후에
- HTTPS의 본문에서 다음 JSON 객체를 반환합니다.
응답:
{ "token_type": "Bearer", "access_token": "ACCESS_TOKEN", "expires_in": SECONDS_TO_EXPIRATION }
사용자 정보 요청 처리
userinfo 엔드포인트는 연결된 사용자에 대한 클레임을 반환하는 OAuth 2.0 보호 리소스입니다. 다음 사용 사례를 제외하고 userinfo 엔드포인트를 구현하고 호스팅하는 것은 선택사항입니다.
- Google 원탭을 사용한 연결된 계정 로그인
- AndroidTV의 원활한 구독
토큰 엔드포인트에서 액세스 토큰을 성공적으로 가져오면 Google은 사용자 정보 엔드포인트에 요청을 보내 연결된 사용자에 대한 기본 프로필 정보를 가져옵니다.
| 사용자 정보 엔드포인트 요청 헤더 | |
|---|---|
Authorization header |
Bearer 유형의 액세스 토큰입니다. |
예를 들어
https://myservice.example.com/userinfo인 경우 요청은 다음과 같을 수 있습니다.
GET /userinfo HTTP/1.1 Host: myservice.example.com Authorization: Bearer ACCESS_TOKEN
userinfo 엔드포인트에서 요청을 처리하려면 다음 단계를 수행합니다.
- 승인 헤더에서 액세스 토큰을 추출하고 액세스 토큰과 연결된 사용자의 정보를 반환합니다.
- 액세스 토큰이 유효하지 않은 경우
WWW-Authenticate응답 헤더를 사용하여 HTTP 401 승인되지 않은 오류를 반환합니다. 다음은 userinfo 오류 응답의 예입니다.HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized WWW-Authenticate: error="invalid_token", error_description="The Access Token expired"
액세스 토큰이 유효하면 HTTPS 본문에 다음 JSON 객체가 포함된 HTTP 200 응답을 반환합니다. 응답:
{ "sub": "USER_UUID", "email": "EMAIL_ADDRESS", "given_name": "FIRST_NAME", "family_name": "LAST_NAME", "name": "FULL_NAME", "picture": "PROFILE_PICTURE", }사용자 정보 엔드포인트 응답 sub시스템에서 사용자를 식별하는 고유 ID email사용자의 이메일 주소입니다. given_name선택사항: 사용자의 이름입니다. family_name선택사항: 사용자의 성. name선택사항: 사용자의 전체 이름입니다. picture선택사항: 사용자의 프로필 사진입니다.
구현 확인
OAuth 2.0 플레이그라운드 도구를 사용하여 구현을 검증할 수 있습니다.
도구에서 다음 단계를 수행합니다.
- 구성 을 클릭하여 OAuth 2.0 구성 창을 엽니다.
- OAuth 흐름 입력란에서 클라이언트 측을 선택합니다.
- OAuth 엔드포인트 필드에서 맞춤을 선택합니다.
- 해당 필드에 OAuth 2.0 엔드포인트와 Google에 할당한 클라이언트 ID를 지정합니다.
- 1단계 섹션에서 Google 범위를 선택하지 않습니다. 대신 이 필드를 비워 두거나 서버에 유효한 범위 (또는 OAuth 범위를 사용하지 않는 경우 임의의 문자열)를 입력합니다. 완료되면 API 승인을 클릭합니다.
- 2단계 및 3단계 섹션에서 OAuth 2.0 흐름을 진행하고 각 단계가 의도한 대로 작동하는지 확인합니다.
Google 계정 연결 데모 도구를 사용하여 구현을 확인할 수 있습니다.
도구에서 다음 단계를 수행합니다.
- Google 계정으로 로그인 버튼을 클릭합니다.
- 연결할 계정을 선택합니다.
- 서비스 ID를 입력합니다.
- 원하는 경우 액세스를 요청할 범위를 하나 이상 입력합니다.
- 데모 시작을 클릭합니다.
- 메시지가 표시되면 연결 요청에 동의하고 거부할 수 있음을 확인합니다.
- 플랫폼으로 리디렉션되는지 확인합니다.