इस सेक्शन में, WebP लाइब्रेरी में शामिल एनकोडर और डिकोडर के लिए एपीआई के बारे में बताया गया है. एपीआई की यह जानकारी, वर्शन 1.6.0 के बारे में है.
हेडर और लाइब्रेरी
libwebp को इंस्टॉल करने पर, webp/ नाम की एक डायरेक्ट्री आपके प्लैटफ़ॉर्म की सामान्य जगह पर इंस्टॉल हो जाएगी. उदाहरण के लिए, Unix प्लैटफ़ॉर्म पर, यहां दी गई हेडर फ़ाइलें /usr/local/include/webp/ में कॉपी की जाएंगी.
decode.h
encode.h
types.h
लाइब्रेरी, लाइब्रेरी की सामान्य डायरेक्ट्री में मौजूद होती हैं. स्टैटिक और डाइनैमिक लाइब्रेरी, Unix प्लैटफ़ॉर्म पर /usr/local/lib/ में होती हैं.
Simple Decoding API
डिकोडिंग एपीआई का इस्तेमाल शुरू करने के लिए, पक्का करें कि आपने ऊपर बताए गए तरीके से लाइब्रेरी और हेडर फ़ाइलें इंस्टॉल की हों.
अपने C/C++ कोड में, डिकोडिंग एपीआई हेडर को इस तरह शामिल करें:
#include "webp/decode.h"
int WebPGetInfo(const uint8_t* data, size_t data_size, int* width, int* height);
यह फ़ंक्शन, WebP इमेज हेडर की पुष्टि करेगा और इमेज की चौड़ाई और ऊंचाई को वापस लाएगा. अगर पॉइंटर *width और *height काम के नहीं हैं, तो उन्हें NULL के तौर पर पास किया जा सकता है.
इनपुट एट्रिब्यूट
- डेटा
- WebP इमेज डेटा का पॉइंटर
- data_size
- यह
dataसे पॉइंट किए गए मेमोरी ब्लॉक का साइज़ है. इसमें इमेज का डेटा मौजूद होता है.
रिटर्न
- गलत
- फ़ॉर्मैट से जुड़ी गड़बड़ियों के मामले में, यह गड़बड़ी कोड दिखता है.
- सही
- On success.
*widthऔर*heightसिर्फ़ तब मान्य होते हैं, जब सामान वापस कर दिया जाता है. - चौड़ाई
- पूर्णांक वैल्यू. इसकी रेंज 1 से 16383 तक होती है.
- ऊंचाई
- पूर्णांक वैल्यू. इसकी सीमा 1 से 16383 तक होती है.
struct WebPBitstreamFeatures {
int width; // Width in pixels.
int height; // Height in pixels.
int has_alpha; // True if the bitstream contains an alpha channel.
int has_animation; // True if the bitstream is an animation.
int format; // 0 = undefined (/mixed), 1 = lossy, 2 = lossless
}
VP8StatusCode WebPGetFeatures(const uint8_t* data,
size_t data_size,
WebPBitstreamFeatures* features);
यह फ़ंक्शन, बिटस्ट्रीम से सुविधाओं को वापस लाएगा. *features
स्ट्रक्चर में, बिटस्ट्रीम से इकट्ठा की गई जानकारी भरी जाती है:
इनपुट एट्रिब्यूट
- डेटा
- WebP इमेज डेटा का पॉइंटर
- data_size
- यह
dataसे पॉइंट किए गए मेमोरी ब्लॉक का साइज़ है. इसमें इमेज का डेटा मौजूद होता है.
रिटर्न
VP8_STATUS_OK- जब सुविधाओं को वापस पा लिया जाता है.
VP8_STATUS_NOT_ENOUGH_DATA- जब हेडर से सुविधाएं वापस पाने के लिए ज़्यादा डेटा की ज़रूरत हो.
अन्य मामलों में, VP8StatusCode की अतिरिक्त गड़बड़ी वाली वैल्यू.
- सुविधाएं
- WebPBitstreamFeatures स्ट्रक्चर का पॉइंटर.
uint8_t* WebPDecodeRGBA(const uint8_t* data, size_t data_size, int* width, int* height);
uint8_t* WebPDecodeARGB(const uint8_t* data, size_t data_size, int* width, int* height);
uint8_t* WebPDecodeBGRA(const uint8_t* data, size_t data_size, int* width, int* height);
uint8_t* WebPDecodeRGB(const uint8_t* data, size_t data_size, int* width, int* height);
uint8_t* WebPDecodeBGR(const uint8_t* data, size_t data_size, int* width, int* height);
ये फ़ंक्शन, data से दिखाई गई WebP इमेज को डिकोड करते हैं.
WebPDecodeRGBA,[r0, g0, b0, a0, r1, g1, b1, a1, ...]क्रम में RGBA इमेज के सैंपल दिखाता है.WebPDecodeARGB, ARGB इमेज के सैंपल को[a0, r0, g0, b0, a1, r1, g1, b1, ...]क्रम में दिखाता है.WebPDecodeBGRA,[b0, g0, r0, a0, b1, g1, r1, a1, ...]क्रम में BGRA इमेज के सैंपल दिखाता है.WebPDecodeRGB, आरजीबी इमेज के सैंपल को[r0, g0, b0, r1, g1, b1, ...]क्रम में दिखाता है.WebPDecodeBGR,[b0, g0, r0, b1, g1, r1, ...]क्रम में BGR इमेज के सैंपल दिखाता है.
इनमें से किसी भी फ़ंक्शन को कॉल करने वाले कोड को, इन फ़ंक्शन से मिले डेटा बफ़र (uint8_t*) को WebPFree() के साथ मिटाना होगा.
इनपुट एट्रिब्यूट
- डेटा
- WebP इमेज डेटा का पॉइंटर
- data_size
- यह
dataसे पॉइंट किए गए मेमोरी ब्लॉक का साइज़ है. इसमेंdataइमेज डेटा शामिल है
- चौड़ाई
- पूर्णांक वैल्यू. फ़िलहाल, इसकी रेंज 1 से 16383 तक सीमित है.
- ऊंचाई
- पूर्णांक वैल्यू. फ़िलहाल, इसकी रेंज 1 से 16383 तक है.
रिटर्न
- uint8_t*
- डिकोड की गई WebP इमेज के सैंपल के लिए पॉइंटर. ये सैंपल, लीनियर आरजीबीए/एआरजीबी/बीजीआरए/आरजीबी/बीजीआर ऑर्डर में होते हैं.
uint8_t* WebPDecodeRGBAInto(const uint8_t* data, size_t data_size,
uint8_t* output_buffer, int output_buffer_size, int output_stride);
uint8_t* WebPDecodeARGBInto(const uint8_t* data, size_t data_size,
uint8_t* output_buffer, int output_buffer_size, int output_stride);
uint8_t* WebPDecodeBGRAInto(const uint8_t* data, size_t data_size,
uint8_t* output_buffer, int output_buffer_size, int output_stride);
uint8_t* WebPDecodeRGBInto(const uint8_t* data, size_t data_size,
uint8_t* output_buffer, int output_buffer_size, int output_stride);
uint8_t* WebPDecodeBGRInto(const uint8_t* data, size_t data_size,
uint8_t* output_buffer, int output_buffer_size, int output_stride);
ये फ़ंक्शन, ऊपर दिए गए फ़ंक्शन के वैरिएंट हैं. ये इमेज को सीधे तौर पर पहले से तय किए गए बफ़र output_buffer में डिकोड करते हैं. इस बफ़र में ज़्यादा से ज़्यादा output_buffer_size स्टोरेज उपलब्ध है. अगर यह स्टोरेज ज़रूरत के हिसाब से नहीं है या कोई गड़बड़ी हुई है, तो NULL दिखता है. इसके अलावा, सुविधा के लिए output_buffer दिखाया जाता है.
output_stride पैरामीटर, स्कैनलाइन के बीच की दूरी (बाइट में) तय करता है. इसलिए, output_buffer_size कम से कम output_stride * picture - height होना चाहिए.
इनपुट एट्रिब्यूट
- डेटा
- WebP इमेज डेटा का पॉइंटर
- data_size
- यह
dataसे पॉइंट किए गए मेमोरी ब्लॉक का साइज़ है. इसमेंdataइमेज डेटा शामिल है
- output_buffer_size
- पूर्णांक वैल्यू. बंटवारा किए गए बफ़र का साइज़
- output_stride
- पूर्णांक वैल्यू. यह स्कैनलाइन के बीच की दूरी तय करता है.
रिटर्न
- output_buffer
- डिकोड की गई WebP इमेज का पॉइंटर.
- uint8_t*
output_bufferअगर फ़ंक्शन काम करता है;NULLऐसा न होने पर.
Advanced Decoding API
WebP डिकोडिंग में एक बेहतर एपीआई काम करता है. इससे इमेज को तुरंत क्रॉप और रीस्केल किया जा सकता है. यह सुविधा, मोबाइल फ़ोन जैसे कम मेमोरी वाले डिवाइसों के लिए बहुत फ़ायदेमंद है. असल में, मेमोरी का इस्तेमाल आउटपुट के साइज़ के हिसाब से होगा, न कि इनपुट के साइज़ के हिसाब से. ऐसा तब होगा, जब किसी व्यक्ति को सिर्फ़ एक झलक देखनी हो या किसी बड़ी इमेज का ज़ूम किया गया हिस्सा देखना हो. कुछ सीपीयू को भी सेव किया जा सकता है.
WebP डिकोडिंग दो तरह से की जाती है: पूरी इमेज डिकोड करना और छोटे इनपुट बफ़र पर इंक्रीमेंटल डिकोडिंग. उपयोगकर्ता चाहें, तो इमेज को डिकोड करने के लिए बाहरी मेमोरी बफ़र उपलब्ध करा सकते हैं. नीचे दिए गए कोड सैंपल में, अडवांस डिकोडिंग एपीआई इस्तेमाल करने का तरीका बताया गया है.
सबसे पहले, हमें कॉन्फ़िगरेशन ऑब्जेक्ट को शुरू करना होगा:
#include "webp/decode.h"
WebPDecoderConfig config;
CHECK(WebPInitDecoderConfig(&config));
// One can adjust some additional decoding options:
config.options.no_fancy_upsampling = 1;
config.options.use_scaling = 1;
config.options.scaled_width = scaledWidth();
config.options.scaled_height = scaledHeight();
// etc.
डिकोड करने के विकल्पों को WebPDecoderConfig स्ट्रक्चर में इकट्ठा किया जाता है:
struct WebPDecoderOptions {
int bypass_filtering; // if true, skip the in-loop filtering
int no_fancy_upsampling; // if true, use faster pointwise upsampler
int use_cropping; // if true, cropping is applied first
int crop_left, crop_top; // top-left position for cropping.
// Will be snapped to even values.
int crop_width, crop_height; // dimension of the cropping area
int use_scaling; // if true, scaling is applied afterward
int scaled_width, scaled_height; // final resolution
int use_threads; // if true, use multi-threaded decoding
int dithering_strength; // dithering strength (0=Off, 100=full)
int flip; // if true, flip output vertically
int alpha_dithering_strength; // alpha dithering strength in [0..100]
};
अगर हमें बिटस्ट्रीम की सुविधाओं के बारे में पहले से जानना है, तो उन्हें config.input में पढ़ा जा सकता है. हालांकि, ऐसा करना ज़रूरी नहीं है. उदाहरण के लिए, यह जानना मददगार हो सकता है कि इमेज में पारदर्शिता है या नहीं. ध्यान दें कि इससे बिटस्ट्रीम के हेडर को भी पार्स किया जाएगा. इसलिए, यह जानने का सबसे सही तरीका है कि बिटस्ट्रीम, मान्य WebP फ़ाइल की तरह दिखता है या नहीं.
CHECK(WebPGetFeatures(data, data_size, &config.input) == VP8_STATUS_OK);
इसके बाद, हमें डिकोडिंग मेमोरी बफ़र सेट अप करना होगा. ऐसा तब करना होता है, जब हमें इसे सीधे तौर पर उपलब्ध कराना हो. इसके लिए, हमें डिकोडर पर भरोसा करने की ज़रूरत नहीं होती. हमें सिर्फ़ मेमोरी के लिए पॉइंटर, बफ़र का कुल साइज़, और लाइन स्ट्राइड (स्कैनलाइन के बीच बाइट में दूरी) की जानकारी देनी होती है.
// Specify the desired output colorspace:
config.output.colorspace = MODE_BGRA;
// Have config.output point to an external buffer:
config.output.u.RGBA.rgba = (uint8_t*)memory_buffer;
config.output.u.RGBA.stride = scanline_stride;
config.output.u.RGBA.size = total_size_of_the_memory_buffer;
config.output.is_external_memory = 1;
इमेज को डिकोड किया जा सकता है. इमेज को डिकोड करने के लिए, दो संभावित वैरिएंट हैं. हम इस इमेज को एक बार में डिकोड कर सकते हैं. इसके लिए, हमें इनका इस्तेमाल करना होगा:
CHECK(WebPDecode(data, data_size, &config) == VP8_STATUS_OK);
इसके अलावा, हम इंक्रीमेंटल तरीके का इस्तेमाल करके, इमेज को धीरे-धीरे डिकोड कर सकते हैं. ऐसा तब किया जाता है, जब नए बाइट उपलब्ध होते हैं:
WebPIDecoder* idec = WebPINewDecoder(&config.output);
CHECK(idec != NULL);
while (additional_data_is_available) {
// ... (get additional data in some new_data[] buffer)
VP8StatusCode status = WebPIAppend(idec, new_data, new_data_size);
if (status != VP8_STATUS_OK && status != VP8_STATUS_SUSPENDED) {
break;
}
// The above call decodes the current available buffer.
// Part of the image can now be refreshed by calling
// WebPIDecGetRGB()/WebPIDecGetYUVA() etc.
}
WebPIDelete(idec); // the object doesn't own the image memory, so it can
// now be deleted. config.output memory is preserved.
डिकोड की गई इमेज अब config.output में है. हालांकि, इस मामले में यह config.output.u.RGBA में है, क्योंकि अनुरोध किया गया आउटपुट कलरस्पेस MODE_BGRA था. इमेज को सेव किया जा सकता है, दिखाया जा सकता है या किसी अन्य तरीके से प्रोसेस किया जा सकता है. इसके बाद, हमें सिर्फ़ कॉन्फ़िगरेशन के ऑब्जेक्ट में असाइन की गई मेमोरी को वापस पाना होता है. अगर मेमोरी बाहरी है और उसे WebPDecode() ने असाइन नहीं किया है, तब भी इस फ़ंक्शन को कॉल करना सुरक्षित है:
WebPFreeDecBuffer(&config.output);
इस एपीआई का इस्तेमाल करके, इमेज को YUV और YUVA फ़ॉर्मैट में भी डिकोड किया जा सकता है. इसके लिए, क्रमशः MODE_YUV और MODE_YUVA का इस्तेमाल करें. इस फ़ॉर्मैट को Y'CbCr भी कहा जाता है.
Simple Encoding API
सबसे सामान्य लेआउट में RGBA सैंपल के ऐरे को एन्कोड करने के लिए, कुछ बहुत ही सामान्य फ़ंक्शन दिए गए हैं. इन्हें webp/encode.h हेडर में इस तरह से दिखाया जाता है:
size_t WebPEncodeRGB(const uint8_t* rgb, int width, int height, int stride, float quality_factor, uint8_t** output);
size_t WebPEncodeBGR(const uint8_t* bgr, int width, int height, int stride, float quality_factor, uint8_t** output);
size_t WebPEncodeRGBA(const uint8_t* rgba, int width, int height, int stride, float quality_factor, uint8_t** output);
size_t WebPEncodeBGRA(const uint8_t* bgra, int width, int height, int stride, float quality_factor, uint8_t** output);
क्वालिटी फ़ैक्टर quality_factor की वैल्यू 0 से 100 के बीच होती है. यह कंप्रेस करने के दौरान होने वाले डेटा के नुकसान और क्वालिटी को कंट्रोल करता है. वैल्यू 0 का मतलब है कि क्वालिटी खराब है और आउटपुट का साइज़ छोटा है. वहीं, 100 का मतलब है कि क्वालिटी सबसे अच्छी है और आउटपुट का साइज़ सबसे बड़ा है.
सफल होने पर, कंप्रेस किए गए बाइट को *output पॉइंटर में रखा जाता है. साथ ही, बाइट में साइज़ दिखाया जाता है. अगर ऐसा नहीं होता है, तो गड़बड़ी होने पर 0 दिखाया जाता है. मेमोरी वापस पाने के लिए, कॉल करने वाले को *output पॉइंटर पर WebPFree() को कॉल करना होगा.
इनपुट ऐरे, बाइट का पैक्ड ऐरे होना चाहिए. हर चैनल के लिए एक बाइट होनी चाहिए, जैसा कि फ़ंक्शन के नाम से पता चलता है. stride का मतलब है कि एक लाइन से दूसरी लाइन पर जाने के लिए ज़रूरी बाइट की संख्या. उदाहरण के लिए, BGRA लेआउट यह है:
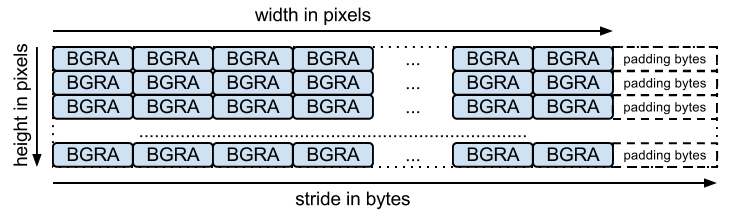
बिना डेटा खोए एन्कोड करने के लिए, मिलते-जुलते फ़ंक्शन उपलब्ध हैं. इनके सिग्नेचर ये हैं:
size_t WebPEncodeLosslessRGB(const uint8_t* rgb, int width, int height, int stride, uint8_t** output);
size_t WebPEncodeLosslessBGR(const uint8_t* bgr, int width, int height, int stride, uint8_t** output);
size_t WebPEncodeLosslessRGBA(const uint8_t* rgba, int width, int height, int stride, uint8_t** output);
size_t WebPEncodeLosslessBGRA(const uint8_t* bgra, int width, int height, int stride, uint8_t** output);
ध्यान दें कि ये फ़ंक्शन, लाइब्रेरी की डिफ़ॉल्ट सेटिंग का इस्तेमाल करते हैं. जैसे, लॉस वाले वर्शन. बिना डेटा के नुकसान वाली क्वालिटी के लिए, इसका मतलब है कि 'बिलकुल सही' सेटिंग बंद है. पूरी तरह से पारदर्शी क्षेत्रों (यानी कि ऐसे क्षेत्र जिनकी ऐल्फ़ा वैल्यू 0 के बराबर होती है) में आरजीबी वैल्यू में बदलाव किया जाएगा, ताकि कंप्रेशन को बेहतर बनाया जा सके. इससे बचने के लिए, WebPEncode() का इस्तेमाल करें और WebPConfig::exact को 1 पर सेट करें.
Advanced Encoding API
एनकोडर में, कई बेहतर एनकोडिंग पैरामीटर होते हैं.
ये, कंप्रेस करने की क्षमता और प्रोसेसिंग में लगने वाले समय के बीच बेहतर संतुलन बनाने में मददगार हो सकते हैं.
इन पैरामीटर को WebPConfig स्ट्रक्चर में इकट्ठा किया जाता है.
इस स्ट्रक्चर के सबसे ज़्यादा इस्तेमाल किए जाने वाले फ़ील्ड ये हैं:
struct WebPConfig {
int lossless; // Lossless encoding (0=lossy(default), 1=lossless).
float quality; // between 0 and 100. For lossy, 0 gives the smallest
// size and 100 the largest. For lossless, this
// parameter is the amount of effort put into the
// compression: 0 is the fastest but gives larger
// files compared to the slowest, but best, 100.
int method; // quality/speed trade-off (0=fast, 6=slower-better)
WebPImageHint image_hint; // Hint for image type (lossless only for now).
// Parameters related to lossy compression only:
int target_size; // if non-zero, set the desired target size in bytes.
// Takes precedence over the 'compression' parameter.
float target_PSNR; // if non-zero, specifies the minimal distortion to
// try to achieve. Takes precedence over target_size.
int segments; // maximum number of segments to use, in [1..4]
int sns_strength; // Spatial Noise Shaping. 0=off, 100=maximum.
int filter_strength; // range: [0 = off .. 100 = strongest]
int filter_sharpness; // range: [0 = off .. 7 = least sharp]
int filter_type; // filtering type: 0 = simple, 1 = strong (only used
// if filter_strength > 0 or autofilter > 0)
int autofilter; // Auto adjust filter's strength [0 = off, 1 = on]
int alpha_compression; // Algorithm for encoding the alpha plane (0 = none,
// 1 = compressed with WebP lossless). Default is 1.
int alpha_filtering; // Predictive filtering method for alpha plane.
// 0: none, 1: fast, 2: best. Default if 1.
int alpha_quality; // Between 0 (smallest size) and 100 (lossless).
// Default is 100.
int pass; // number of entropy-analysis passes (in [1..10]).
int show_compressed; // if true, export the compressed picture back.
// In-loop filtering is not applied.
int preprocessing; // preprocessing filter (0=none, 1=segment-smooth)
int partitions; // log2(number of token partitions) in [0..3]
// Default is set to 0 for easier progressive decoding.
int partition_limit; // quality degradation allowed to fit the 512k limit on
// prediction modes coding (0: no degradation,
// 100: maximum possible degradation).
int use_sharp_yuv; // if needed, use sharp (and slow) RGB->YUV conversion
};
ध्यान दें कि इनमें से ज़्यादातर पैरामीटर, cwebp कमांड लाइन टूल का इस्तेमाल करके एक्सपेरिमेंट के लिए ऐक्सेस किए जा सकते हैं.
इनपुट सैंपल को WebPPicture स्ट्रक्चर में रैप किया जाना चाहिए.
इस स्ट्रक्चर में, इनपुट सैंपल को RGBA या YUVA फ़ॉर्मैट में सेव किया जा सकता है. यह use_argb फ़्लैग की वैल्यू पर निर्भर करता है.
स्ट्रक्चर को इस तरह व्यवस्थित किया जाता है:
struct WebPPicture {
int use_argb; // To select between ARGB and YUVA input.
// YUV input, recommended for lossy compression.
// Used if use_argb = 0.
WebPEncCSP colorspace; // colorspace: should be YUVA420 or YUV420 for now (=Y'CbCr).
int width, height; // dimensions (less or equal to WEBP_MAX_DIMENSION)
uint8_t *y, *u, *v; // pointers to luma/chroma planes.
int y_stride, uv_stride; // luma/chroma strides.
uint8_t* a; // pointer to the alpha plane
int a_stride; // stride of the alpha plane
// Alternate ARGB input, recommended for lossless compression.
// Used if use_argb = 1.
uint32_t* argb; // Pointer to argb (32 bit) plane.
int argb_stride; // This is stride in pixels units, not bytes.
// Byte-emission hook, to store compressed bytes as they are ready.
WebPWriterFunction writer; // can be NULL
void* custom_ptr; // can be used by the writer.
// Error code for the latest error encountered during encoding
WebPEncodingError error_code;
};
इस स्ट्रक्चर में, कंप्रेस किए गए बाइट को उपलब्ध होने पर भेजने का फ़ंक्शन भी होता है. मेमोरी में मौजूद राइटर का इस्तेमाल करने का उदाहरण यहां दिया गया है.
अन्य लेखक, डेटा को सीधे किसी फ़ाइल में सेव कर सकते हैं. ऐसे उदाहरण के लिए, examples/cwebp.c देखें.
एडवांस एपीआई का इस्तेमाल करके एन्कोड करने का सामान्य फ़्लो इस तरह दिखता है:
सबसे पहले, हमें एक एन्कोडिंग कॉन्फ़िगरेशन सेट अप करना होगा. इसमें कंप्रेशन पैरामीटर शामिल होंगे. ध्यान दें कि एक ही कॉन्फ़िगरेशन का इस्तेमाल, बाद में कई अलग-अलग इमेज को कंप्रेस करने के लिए किया जा सकता है.
#include "webp/encode.h"
WebPConfig config;
if (!WebPConfigPreset(&config, WEBP_PRESET_PHOTO, quality_factor)) return 0; // version error
// Add additional tuning:
config.sns_strength = 90;
config.filter_sharpness = 6;
config.alpha_quality = 90;
config_error = WebPValidateConfig(&config); // will verify parameter ranges (always a good habit)
इसके बाद, इनपुट सैंपल को WebPPicture में रेफ़रंस या कॉपी करके शामिल करना होगा. यहां सैंपल को सेव करने के लिए बफ़र को असाइन करने का एक उदाहरण दिया गया है. हालांकि, पहले से असाइन किए गए सैंपल ऐरे के लिए, कोई "व्यू" आसानी से सेट अप किया जा सकता है. WebPPictureView() फ़ंक्शन देखें.
// Setup the input data, allocating a picture of width x height dimension
WebPPicture pic;
if (!WebPPictureInit(&pic)) return 0; // version error
pic.width = width;
pic.height = height;
if (!WebPPictureAlloc(&pic)) return 0; // memory error
// At this point, 'pic' has been initialized as a container, and can receive the YUVA or RGBA samples.
// Alternatively, one could use ready-made import functions like WebPPictureImportRGBA(), which will take
// care of memory allocation. In any case, past this point, one will have to call WebPPictureFree(&pic)
// to reclaim allocated memory.
कंप्रेस किए गए बाइट को भेजने के लिए, हर बार नए बाइट उपलब्ध होने पर एक हुक को कॉल किया जाता है. यहां एक आसान उदाहरण दिया गया है, जिसमें webp/encode.h में मेमोरी-राइटर को घोषित किया गया है. हर इमेज को कंप्रेस करने के लिए, इस तरह के इनिशियलाइज़ेशन की ज़रूरत पड़ सकती है:
// Set up a byte-writing method (write-to-memory, in this case):
WebPMemoryWriter writer;
WebPMemoryWriterInit(&writer);
pic.writer = WebPMemoryWrite;
pic.custom_ptr = &writer;
अब हम इनपुट सैंपल को कंप्रेस करने के लिए तैयार हैं. इसके बाद, हम उनकी मेमोरी खाली कर देंगे:
int ok = WebPEncode(&config, &pic);
WebPPictureFree(&pic); // Always free the memory associated with the input.
if (!ok) {
printf("Encoding error: %d\n", pic.error_code);
} else {
printf("Output size: %d\n", writer.size);
}
एपीआई और स्ट्रक्चर का बेहतर तरीके से इस्तेमाल करने के लिए, हमारा सुझाव है कि आप webp/encode.h हेडर में उपलब्ध दस्तावेज़ देखें.
उदाहरण कोड examples/cwebp.c पढ़ने से, कम इस्तेमाल किए जाने वाले पैरामीटर के बारे में पता चल सकता है.
