Vous pouvez utiliser le SDK grand public pour créer et exécuter Application grand public intégrée aux services de backend de la solution On-demand Rides and Deliveries. Vous pouvez créer une application de progression de trajet et de commande qui peut afficher un trajet actif, répondre aux mises à jour des trajets et traiter les erreurs associées.
Comme le SDK grand public possède une architecture modulaire, vous pouvez utiliser les parties de l'API que vous souhaitez utiliser pour votre application et intégrez-les à vos propres API, aux services de backend fournis par le parc et d'autres API de Google Maps Platform.
Configuration système minimale requise
Configuration du projet
Gestionnaire de paquets Swift
Le SDK grand public peut être installé via Gestionnaire de paquets Swift. Pour ajouter le SDK, assurez-vous d'avoir supprimé toutes les dépendances existantes du SDK client.
Pour ajouter le SDK à un projet nouveau ou existant, procédez comme suit:
-
Ouvrez votre Xcode
projectouworkspace, puis accédez à File > (Fichier >) Ajouter des dépendances de packages - Saisissez https://github.com/googlemaps/ios-consumer-sdk comme URL, puis appuyez sur Entrée. pour extraire le package et cliquez sur « Ajouter un package ».
-
Pour installer un
versionspécifique, définissez le champ Règle de dépendance sur l'une des les options basées sur les versions. Pour les nouveaux projets, nous vous recommandons de spécifier la dernière version et à l'aide de la colonne "Version exacte", . Une fois l'opération terminée, cliquez sur "Ajouter un package". -
Dans la fenêtre Choose Package Products (Sélectionner les produits du package), vérifiez que
GoogleRidesharingConsumersera ajouté à votremaincible désignée. Une fois l'opération terminée, cliquez sur "Ajouter un package". -
Pour vérifier votre installation, accédez au volet
Generalde votre cible. Les packages installés devraient s'afficher dans Cadres, bibliothèques et contenu intégré. Vous pouvez également afficher les "Dépendances des packages" de la section "Navigateur de projets" pour vérifier le package et sa version.
Pour mettre à jour le package pour un projet existant, procédez comme suit:
Si vous effectuez la mise à niveau à partir d'une version antérieure à la version 9.0.0,vous devez supprimer les dépendances suivantes:
GoogleMapsBase,GoogleMapsCoreetGoogleMapsM4Baprès la mise à niveau. Ne supprimez pas la dépendance pourGoogleMapsPour en savoir plus, consultez les Notes de version de la version 9.0.0Dans les paramètres de configuration de votre projet Xcode, recherchez Frameworks, Bibliothèques, et les contenus intégrés. Utilisez le signe moins(-) pour supprimer le framework suivant:
GoogleMapsBase(uniquement pour les mises à niveau à partir de versions antérieures à la version 9.0.0)GoogleMapsCore(uniquement pour les mises à niveau à partir de versions antérieures à la version 9.0.0)GoogleMapsM4B(uniquement pour les mises à niveau à partir de versions antérieures à la version 9.0.0)
- Dans Xcode, accédez à Fichier > Packages > Update To Latest Package Versions" (Mise à jour vers les dernières versions du package).
- Pour vérifier votre installation, accédez à la section Package Dependencies (Dépendances des packages) du Project Navigator (Navigateur de projets). pour vérifier le package et sa version.
Pour supprimer les dépendances existantes du SDK grand public ajoutées à l'aide de
CocoaPods, procédez comme suit:
- Fermez votre espace de travail Xcode. Ouvrez le terminal et exécutez la commande suivante:
sudo gem install cocoapods-deintegrate cocoapods-clean pod deintegrate pod cache clean --all
-
Supprimez
Podfile,Podfile.resolvedet les Xcodeworkspacesi vous ne les utilisez pas pour d'autres produits que CocoaPods.
Pour supprimer le SDK Consumer SDK existant manuellement, procédez comme suit:
Dans les paramètres de configuration de votre projet Xcode, recherchez Frameworks, bibliothèques et contenus intégrés. Utilisez le signe moins
(-)pour supprimer le framework suivant:GoogleRidesharingConsumer.xcframework
Dans le répertoire de premier niveau de votre projet Xcode, supprimez le Lot
GoogleRidesharingConsumer.
CocoaPods
Pour configurer le SDK grand public à l'aide de CocoaPods, vous devez ont besoin des éléments suivants:
Outil CocoaPods: pour installer cet outil, ouvrez le terminal et exécutez la la commande suivante.
sudo gem install cocoapods
Reportez-vous au document Premiers pas avec CocoaPods pour en savoir plus plus de détails.
Créer un Podfile pour le SDK client et l'utiliser pour installer l'API et ses dépendances. Tout d'abord, créez un fichier nommé Podfile dans le répertoire de votre projet. Ce fichier définit les paramètres les dépendances. Ensuite, modifiez le Podfile et ajoutez vos dépendances. Voici Voici un exemple qui inclut les dépendances:
source "https://github.com/CocoaPods/Specs.git" target 'YOUR_APPLICATION_TARGET_NAME_HERE' do pod 'GoogleRidesharingConsumer' endEnregistrez le Podfile. Ouvrez un terminal et accédez au répertoire contenant le Podfile:
cd <path-to-project>Exécutez la commande d'installation du pod. Les API spécifiées dans la section Podfile, ainsi que ses éventuelles dépendances.
pod installFermez Xcode, puis ouvrez (double-cliquez) le fichier .xcworkspace de votre projet. pour lancer Xcode. Pour ouvrir le projet ultérieurement, utilisez l'extension .xcworkspace .
Installation manuelle
Un XCFramework est un paquet binaire que vous utilisez pour installer Consumer SDK. Vous pouvez utiliser ce package sur plusieurs plateformes, y compris les machines utilisant le chipset M1. Ce guide vous explique comment ajoutez manuellement le XCFramework contenant le SDK grand public à votre projet, puis configurez paramètres de compilation dans Xcode.
Téléchargez le binaire du SDK et ses ressources:
Décompressez les fichiers compressés pour accéder au XCFramework et aux ressources.
Démarrez Xcode, puis ouvrez un projet existant ou créez-en un. projet. Si vous n'avez jamais utilisé iOS, créez un projet et sélectionnez l'application iOS Modèle d'application.
Créez un groupe Frameworks sous votre groupe de projets s'il n'en existe pas. déjà.
Pour installer le SDK grand public, faites glisser le fichier
GoogleRidesharingConsumer.xcframeworkdans votre projet sous Cadres, bibliothèques et contenu intégré. Lorsque vous y êtes invité, sélectionnez "Copier les éléments si nécessaire".Faites glisser le fichier
GoogleRidesharingConsumer.bundletéléchargé dans le répertoire de premier niveau de votre projet Xcode. Lorsque vous y êtes invité, sélectionnezCopy items if needed.Sélectionnez votre projet dans le navigateur de projets, puis choisissez votre cible de votre application.
Ouvrez l'onglet Build Phases et, dans Link Binary with libraries, ajoutez le Les frameworks et bibliothèques suivants s'ils ne sont pas déjà présents:
Accelerate.frameworkCoreData.frameworkCoreGraphics.frameworkCoreImage.frameworkCoreLocation.frameworkCoreTelephony.frameworkCoreText.frameworkGLKit.frameworkImageIO.frameworklibc++.tbdlibz.tbdMetal.frameworkOpenGLES.frameworkQuartzCore.frameworkSystemConfiguration.frameworkUIKit.framework
Choisissez votre projet plutôt qu'une cible spécifique, puis ouvrez le panneau Build Paramètres. Dans la section Other Linker Flags (Autres indicateurs Linker), ajoutez
-ObjCpour à la fois au débogage et à la publication. Si ces paramètres ne sont pas visibles, modifiez dans la barre "Paramètres de compilation" en passant de Standard à Tous.
Inspecter le fichier manifeste de confidentialité Apple
Apple exige des informations sur la confidentialité des applications disponibles sur l'App Store. Pour obtenir des mises à jour et d'autres informations, consultez la page Informations sur la confidentialité sur l'App Store d'Apple.
Le fichier manifeste de confidentialité Apple est inclus dans le bundle de ressources pour le SDK. Pour vérifier que le fichier manifeste de confidentialité a été inclus et pour inspecter son contenu, créez une archive de votre application et générez un rapport sur la confidentialité à partir de cette archive.
Intégration d'applications
Fournir un jeton d'authentification
Lorsque votre application consommateur demande des mises à jour de trajet à Fleet Engine, les requêtes
doit inclure des jetons d'accès valides. Pour autoriser et authentifier
ces requêtes,
le SDK grand public appelle votre objet conformément au
Protocole GMTCAuthorization. L'objet est chargé de fournir
et le jeton d'accès requis.
En tant que développeur de l'application, vous choisissez la façon dont les jetons sont générés. Votre implémentation doit permettre d'effectuer les opérations suivantes:
- Extrayez un jeton d'accès, éventuellement au format JSON, à partir d'un serveur HTTPS.
- Analyser et mettre en cache le jeton.
- Actualisez le jeton lorsqu'il expire.
Pour plus d'informations sur les jetons attendus par le serveur Fleet Engine, consultez la section Créer un Jeton Web JSON (JWT) pour autorisation.
L'ID du fournisseur est identique à l'ID du projet Google Cloud. Pour plus d'informations, consultez la page Getting Started with Fleet Compute Engine.
L'exemple suivant met en œuvre un fournisseur de jetons d'accès:
Swift
/*
* SampleAccessTokenProvider.swift
*/
import GoogleRidesharingConsumer
private let providerURL = "INSERT_YOUR_TOKEN_PROVIDER_URL"
class SampleAccessTokenProvider: NSObject, GMTCAuthorization {
private struct AuthToken {
// The cached trip token.
let token: String
// Keep track of when the token expires for caching.
let expiration: TimeInterval
// Keep track of the trip ID the cached token is for.
let tripID: String
}
enum AccessTokenError: Error {
case missingAuthorizationContext
case missingData
}
private var authToken: AuthToken?
func fetchToken(
with authorizationContext: GMTCAuthorizationContext?,
completion: @escaping GMTCAuthTokenFetchCompletionHandler
) {
// Get the trip ID from the authorizationContext. This is set by the Consumer SDK.
guard let authorizationContext = authorizationContext else {
completion(nil, AccessTokenError.missingAuthorizationContext)
return
}
let tripID = authorizationContext.tripID
// If appropriate, use the cached token.
if let authToken = authToken,
authToken.expiration > Date.now.timeIntervalSince1970 && authToken.tripID == tripID
{
completion(authToken.token, nil)
return
}
// Otherwise, try to fetch a new token from your server.
let request = URLRequest(url: URL(string: providerURL))
let task = URLSession.shared.dataTask(with: request) { [weak self] data, _, error in
guard let strongSelf = self else { return }
guard error == nil else {
completion(nil, error)
return
}
// Replace the following key values with the appropriate keys based on your
// server's expected response.
let tripTokenKey = "TRIP_TOKEN_KEY"
let tokenExpirationKey = "TOKEN_EXPIRATION"
guard let data = data,
let fetchData = try? JSONSerialization.jsonObject(with: data) as? [String: Any],
let token = fetchData[tripTokenKey] as? String,
let expiration = fetchData[tokenExpirationKey] as? Double
else {
completion(nil, AccessTokenError.missingData)
return
}
strongSelf.authToken = AuthToken(token: token, expiration: expiration, tripID: tripID)
completion(token, nil)
}
task.resume()
}
}
Objective-C
/*
* SampleAccessTokenProvider.h
*/
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import <GoogleRidesharingConsumer/GoogleRidesharingConsumer.h>
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_BEGIN
@interface SampleAccessTokenProvider : NSObject <GMTCAuthorization>
@end
NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_END
/*
* SampleAccessTokenProvider.m
*/
#import "SampleAccessTokenProvider.h"
#import "GoogleRidesharingConsumer/GoogleRidesharingConsumer.h"
static NSString *const PROVIDER_URL = @"INSERT_YOUR_TOKEN_PROVIDER_URL";
// SampleAccessTokenProvider.m
@implementation SampleAccessTokenProvider {
// The cached token with claims to the current trip.
NSString *_cachedTripToken;
// Keep track of the Trip ID the cached token is for.
NSString *_lastKnownTripID;
// Keep track of when tokens expire for caching.
NSTimeInterval _tokenExpiration;
}
- (void)fetchTokenWithContext:(nullable GMTCAuthorizationContext *)authorizationContext
completion:(nonnull GMTCAuthTokenFetchCompletionHandler)completion {
// Get the trip ID from the authorizationContext. This is set by the Consumer SDK.
NSString *tripID = authorizationContext.tripID;
// Clear cached trip token if trip ID has changed.
if (![_lastKnownTripID isEqual:tripID]) {
_tokenExpiration = 0.0;
_cachedTripToken = nil;
}
_lastKnownTripID = tripID;
// Clear cached tripToken if it has expired.
if ([[NSDate date] timeIntervalSince1970] > _tokenExpiration) {
_cachedTripToken = nil;
}
// If appropriate, use the cached token.
if (_cachedTripToken) {
completion(_cachedTripToken, nil);
return;
}
// Otherwise, try to fetch a new token from your server.
NSURL *requestURL = [NSURL URLWithString:PROVIDER_URL];
NSMutableURLRequest *request =
[[NSMutableURLRequest alloc] initWithURL:requestURL];
request.HTTPMethod = @"GET";
// Replace the following key values with the appropriate keys based on your
// server's expected response.
NSString *tripTokenKey = @"TRIP_TOKEN_KEY";
NSString *tokenExpirationKey = @"TOKEN_EXPIRATION";
__weak typeof(self) weakSelf = self;
void (^handler)(NSData *_Nullable data, NSURLResponse *_Nullable response,
NSError *_Nullable error) =
^(NSData *_Nullable data, NSURLResponse *_Nullable response, NSError *_Nullable error) {
typeof(self) strongSelf = weakSelf;
if (error) {
completion(nil, error);
return;
}
NSError *JSONError;
NSMutableDictionary *JSONResponse =
[NSJSONSerialization JSONObjectWithData:data options:kNilOptions error:&JSONError];
if (JSONError) {
completion(nil, JSONError);
return;
} else {
// Sample code only. No validation logic.
id expirationData = JSONResponse[tokenExpirationKey];
if ([expirationData isKindOfClass:[NSNumber class]]) {
NSTimeInterval expirationTime = ((NSNumber *)expirationData).doubleValue;
strongSelf->_tokenExpiration = [[NSDate date] timeIntervalSince1970] + expirationTime;
}
strongSelf->_cachedTripToken = JSONResponse[tripTokenKey];
completion(JSONResponse[tripTokenKey], nil);
}
};
NSURLSessionConfiguration *config = [NSURLSessionConfiguration defaultSessionConfiguration];
NSURLSession *mainQueueURLSession =
[NSURLSession sessionWithConfiguration:config delegate:nil
delegateQueue:[NSOperationQueue mainQueue]];
NSURLSessionDataTask *task = [mainQueueURLSession dataTaskWithRequest:request completionHandler:handler];
[task resume];
}
@end
Initialisation de l'application
Swift
/*
* AppDelegate.swift
*/
import GoogleRidesharingConsumer
import GoogleMaps
@UIApplicationMain
class AppDelegate: UIResponder, UIApplicationDelegate {
func application(_ application: UIApplication,
didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplication.LaunchOptionsKey: Any]?) -> Bool {
// Register your API key for GMSServices.
GMSServices.provideAPIKey(yourMapsAPIKey)
// Set the instance of the SampleAccessTokenProvider.
GMTCServices.setAccessTokenProvider(SampleAccessTokenProvider(), providerID: yourProviderID)
// Other initialization code ...
return true
}
}
Objective-C
/*
* AppDelegate.m
*/
#import <GoogleMaps/GoogleMaps.h>
#import <GoogleRidesharingConsumer/GoogleRidesharingConsumer.h>
@implementation AppDelegate
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application
didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions {
//Register your API key for GMSServices.
[GMSServices provideAPIKey:yourMapsAPIKey];
//Set the instance of the AccessTokenFactory.
[GMTCServices setAccessTokenProvider:[[SampleAccessTokenProvider alloc] init]
providerID:yourProviderID];
// Other initialization code ...
return YES;
}
@end
Intégration de la vue plan
Initialiser la vue plan
L'exemple suivant montre comment initialiser GMTCMapView.
Swift
/*
* MapViewController.swift
*/
class ViewController: UIViewController, GMTCMapViewDelegate {
private var rideSharingMap: GMTCMapView?
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
self.rideSharingMap = GMTCMapView(frame: UIScreen.main.bounds)
self.rideSharingMap.delegate = self
self.rideSharingMap?.settings.myLocationButton = true
self.view.addSubview(self.rideSharingMap!)
...
}
Objective-C
/*
* MapViewController.h
*/
@interface MapViewController : UIViewController<GMTCMapViewDelegate>
...
@end
/*
* MapViewController.m
*/
@implementation MapViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
...
self.mapView = [[GMTCMapView alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectZero];
self.mapView.settings.myLocationButton = YES;
self.mapView.delegate = self;
...
}
...
@end
Gérer les événements de vue plan
L'exemple suivant montre comment implémenter un délégué pour gérer l'état du client événements.
Swift
func mapViewDidInitialize(_ mapview: GMTCMapView) {
// Handle the update to the state of the map view to browsing.
}
func mapView(_ mapView: GMSMapView, didTapConsumerMarker mapMarker: GMSMarker, markerType: GMTCMapViewMarkerType) -> Bool {
// Handle the mapView marker was tapped.
}
Objective-C
/*
* MapViewController.m
*/
#pragma mark - GMTCMapViewDelegate implementation
// Handle state update of map view.
- (void)mapViewDidInitializeCustomerState:(GMTCMapView *)mapview {
// Handle the update to the state of the map view to browsing.
}
- (void)mapView:(GMSMapView *)mapView
didTapConsumerMarker:(nonnull GMSMarker *)mapMarker
markerType:(GMTCMapViewMarkerType)markerType {
// Handle the mapView marker was tapped.
}
Partage de parcours
Démarrer un nouveau trajet lorsque la vue s'est chargée
L'exemple suivant montre comment démarrer un partage de parcours juste après le
chargements de vues. Vous pouvez collecter toutes les entrées utilisateur, comme les lieux de dépôt et de prise en charge
à partir d'un ViewController, puis créez un ViewController pour démarrer
le partage de parcours
directement.
Swift
/*
* MapViewController.swift
*/
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
...
self.mapView = GMTCMapView(frame: UIScreen.main.bounds)
self.mapView.delegate = self
self.view.addSubview(self.mapView)
}
func mapViewDidInitializeCustomerState(_: GMTCMapView) {
self.mapView.pickupLocation = self.selectedPickupLocation
self.mapView.dropoffLocation = self.selectedDropoffLocation
self.startConsumerMatchWithLocations(
pickupLocation: self.mapView.pickupLocation!,
dropoffLocation: self.mapView.dropoffLocation!
) { [weak self] (tripName, error) in
guard let strongSelf = self else { return }
if error != nil {
// print error message.
return
}
let tripService = GMTCServices.shared().tripService
// Create a tripModel instance for listening the update of the trip
// specified by this trip name.
let tripModel = tripService.tripModel(forTripName: tripName)
// Create a journeySharingSession instance based on the tripModel
let journeySharingSession = GMTCJourneySharingSession(tripModel: tripModel)
// Add the journeySharingSession instance on the mapView for UI updating.
strongSelf.mapView.show(journeySharingSession)
// Register for the trip update events.
tripModel.register(strongSelf)
strongSelf.currentTripModel = tripModel
strongSelf.currentJourneySharingSession = journeySharingSession
strongSelf.hideLoadingView()
}
self.showLoadingView()
}
Objective-C
/*
* MapViewController.m
*/
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
...
self.mapView = [[GMTCMapView alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectZero];
self.mapView.delegate = self;
[self.view addSubview:self.mapView];
}
// Handle the callback when the GMTCMapView did initialized.
- (void)mapViewDidInitializeCustomerState:(GMTCMapView *)mapview {
self.mapView.pickupLocation = self.selectedPickupLocation;
self.mapView.dropoffLocation = self.selectedDropoffLocation;
__weak __typeof(self) weakSelf = self;
[self startTripBookingWithPickupLocation:self.selectedPickupLocation
dropoffLocation:self.selectedDropoffLocation
completion:^(NSString *tripName, NSError *error) {
__typeof(self) strongSelf = weakSelf;
GMTCTripService *tripService = [GMTCServices sharedServices].tripService;
// Create a tripModel instance for listening to updates to the trip specified by this trip name.
GMTCTripModel *tripModel = [tripService tripModelForTripName:tripName];
// Create a journeySharingSession instance based on the tripModel.
GMTCJourneySharingSession *journeySharingSession =
[[GMTCJourneySharingSession alloc] initWithTripModel:tripModel];
// Add the journeySharingSession instance on the mapView for updating the UI.
[strongSelf.mapView showMapViewSession:journeySharingSession];
// Register for trip update events.
[tripModel registerSubscriber:self];
strongSelf.currentTripModel = tripModel;
strongSelf.currentJourneySharingSession = journeySharingSession;
[strongSelf hideLoadingView];
}];
[self showLoadingView];
}
Annuler le trajet en cours
L'exemple suivant montre comment réinitialiser le trajet actif en cours.
Swift
/*
* MapViewController.swift
*/
func cancelCurrentActiveTrip() {
// Stop the tripModel
self.currentTripModel.unregisterSubscriber(self)
// Remove the journey sharing session from the mapView's UI stack.
self.mapView.hide(journeySharingSession)
}
Objective-C
/*
* MapViewController.m
*/
- (void)cancelCurrentActiveTrip {
// Stop the tripModel
[self.currentTripModel unregisterSubscriber:self];
// Remove the journey sharing session from the mapView's UI stack.
[self.mapView hideMapViewSession:journeySharingSession];
}
Écouter les informations sur le trajet
L'exemple suivant montre comment enregistrer le rappel tripModel.
Swift
/*
* MapViewController.swift
*/
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
// Register for trip update events.
self.currentTripModel.register(self)
}
Objective-C
/*
* MapViewController.m
*/
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
// Register for trip update events.
[self.currentTripModel registerSubscriber:self];
...
}
L'exemple suivant montre comment annuler l'enregistrement de tripModel.
.
Swift
/*
* MapViewController.swift
*/
deinit {
self.currentTripModel.unregisterSubscriber(self)
}
Objective-C
/*
* MapViewController.m
*/
- (void)dealloc {
[self.currentTripModel unregisterSubscriber:self];
...
}
L'exemple suivant montre comment implémenter l'GMTCTripModelSubscriber
protocole permettant de gérer les rappels lorsque l'état du trajet est mis à jour.
Swift
/*
* MapViewController.swift
*/
func tripModel(_: GMTCTripModel, didUpdate trip: GMTSTrip?, updatedPropertyFields: GMTSTripPropertyFields) {
// Update the UI with the new `trip` data.
self.updateUI(with: trip)
}
func tripModel(_: GMTCTripModel, didUpdate tripStatus: GMTSTripStatus) {
// Handle trip status did change.
}
func tripModel(_: GMTCTripModel, didUpdateActiveRouteRemainingDistance activeRouteRemainingDistance: Int32) {
// Handle remaining distance of active route did update.
}
func tripModel(_: GMTCTripModel, didUpdateActiveRoute activeRoute: [GMTSLatLng]?) {
// Handle trip active route did update.
}
func tripModel(_: GMTCTripModel, didUpdate vehicleLocation: GMTSVehicleLocation?) {
// Handle vehicle location did update.
}
func tripModel(_: GMTCTripModel, didUpdatePickupLocation pickupLocation: GMTSTerminalLocation?) {
// Handle pickup location did update.
}
func tripModel(_: GMTCTripModel, didUpdateDropoffLocation dropoffLocation: GMTSTerminalLocation?) {
// Handle drop off location did update.
}
func tripModel(_: GMTCTripModel, didUpdatePickupETA pickupETA: TimeInterval) {
// Handle the pickup ETA did update.
}
func tripModel(_: GMTCTripModel, didUpdateDropoffETA dropoffETA: TimeInterval) {
// Handle the drop off ETA did update.
}
func tripModel(_: GMTCTripModel, didUpdateRemaining remainingWaypoints: [GMTSTripWaypoint]?) {
// Handle updates to the pickup, dropoff or intermediate destinations of the trip.
}
func tripModel(_: GMTCTripModel, didFailUpdateTripWithError error: Error?) {
// Handle the error.
}
func tripModel(_: GMTCTripModel, didUpdateIntermediateDestinations intermediateDestinations: [GMTSTerminalLocation]?) {
// Handle the intermediate destinations being updated.
}
func tripModel(_: GMTCTripModel, didUpdateActiveRouteTraffic activeRouteTraffic: GMTSTrafficData?) {
// Handle trip active route traffic being updated.
}
Objective-C
/*
* MapViewController.m
*/
#pragma mark - GMTCTripModelSubscriber implementation
- (void)tripModel:(GMTCTripModel *)tripModel
didUpdateTrip:(nullable GMTSTrip *)trip
updatedPropertyFields:(enum GMTSTripPropertyFields)updatedPropertyFields {
// Update the UI with the new `trip` data.
[self updateUIWithTrip:trip];
...
}
- (void)tripModel:(GMTCTripModel *)tripModel didUpdateTripStatus:(enum GMTSTripStatus)tripStatus {
// Handle trip status did change.
}
- (void)tripModel:(GMTCTripModel *)tripModel
didUpdateActiveRouteRemainingDistance:(int32_t)activeRouteRemainingDistance {
// Handle remaining distance of active route did update.
}
- (void)tripModel:(GMTCTripModel *)tripModel
didUpdateActiveRoute:(nullable NSArray<GMTSLatLng *> *)activeRoute {
// Handle trip active route did update.
}
- (void)tripModel:(GMTCTripModel *)tripModel
didUpdateVehicleLocation:(nullable GMTSVehicleLocation *)vehicleLocation {
// Handle vehicle location did update.
}
- (void)tripModel:(GMTCTripModel *)tripModel
didUpdatePickupLocation:(nullable GMTSTerminalLocation *)pickupLocation {
// Handle pickup location did update.
}
- (void)tripModel:(GMTCTripModel *)tripModel
didUpdateDropoffLocation:(nullable GMTSTerminalLocation *)dropoffLocation {
// Handle drop off location did update.
}
- (void)tripModel:(GMTCTripModel *)tripModel didUpdatePickupETA:(NSTimeInterval)pickupETA {
// Handle the pickup ETA did update.
}
- (void)tripModel:(GMTCTripModel *)tripModel
didUpdateRemainingWaypoints:(nullable NSArray<GMTSTripWaypoint *> *)remainingWaypoints {
// Handle updates to the pickup, dropoff or intermediate destinations of the trip.
}
- (void)tripModel:(GMTCTripModel *)tripModel didUpdateDropoffETA:(NSTimeInterval)dropoffETA {
// Handle the drop off ETA did update.
}
- (void)tripModel:(GMTCTripModel *)tripModel didFailUpdateTripWithError:(nullable NSError *)error {
// Handle the error.
}
- (void)tripModel:(GMTCTripModel *)tripModel
didUpdateIntermediateDestinations:
(nullable NSArray<GMTSTerminalLocation *> *)intermediateDestinations {
// Handle the intermediate destinations being updated.
}
- (void)tripModel:(GMTCTripModel *)tripModel
didUpdateActiveRouteTraffic:(nullable GMTSTrafficData *)activeRouteTraffic {
// Handle trip active route traffic being updated.
}
Gestion des exceptions
Si vous vous êtes abonné à tripModel et qu'une erreur se produit, vous pouvez obtenir le rappel de
tripModel en implémentant la méthode déléguée
tripModel(_:didFailUpdateTripWithError:) Fleet Engine a généré l'erreur
qui respecte la norme d'erreur Google Cloud. Pour l'erreur de détails
et tous les codes d'erreur indiqués dans la section Erreurs Google Cloud
documentation.
Plus précisément, la surveillance des trajets nécessite de fournir
à partir d'un jeton d'accès. 401 UNAUTHENTICATED est déclenché en l'absence d'authentification valide
les identifiants, comme le jeton, a expiré.403 PERMISSION_DENIED est déclenché si le
l'appelant n'a pas l'autorisation d'appeler une API spécifique (par exemple, un utilisateur avec
"updateTrip" tente d'appeler "updateTrip"), ou la requête n'a pas de "vehicle_id/trip_id" valide
dans le jeton JWT.
Pour en savoir plus, consultez la page Consumer SDK Error Manipulation :
Personnalisation de l'interface utilisateur
Obtenir et définir des options d'interface utilisateur de polyligne personnalisées
L'exemple suivant montre comment définir des options d'interface utilisateur personnalisées pour les polylignes.
Swift
/** MapViewController.swift */
func updatePolylineUIOptions() {
// The polyline type that you would like to set custom UI options for.
let customizablePolylineType = GMTCPolylineType.activeRoute
let polylineStyleOptions = GMTCMutablePolylineStyleOptions()
polylineStyleOptions.strokeWidth = 8.0
polylineStyleOptions.strokeColor = .blue
polylineStyleOptions.isVisible = true
polylineStyleOptions.zIndex = 1000
polylineStyleOptions.isGeodesic = true
let coordinator = self.mapView.consumerMapStyleCoordinator
coordinator.setPolylineStyleOptions(polylineStyleOptions, polylineType:customizablePolylineType)
}
Objective-C
/** MapViewController.m */
- (void)updatePolylineUIOptions {
// The polyline type that you would like to set custom UI options for.
GMTCPolylineType customizablePolylineType = GMTCPolylineTypeActiveRoute;
GMTCMutablePolylineStyleOptions *polylineStyleOptions =
[[GMTCMutablePolylineStyleOptions alloc] init];
polylineStyleOptions.strokeWidth = 8.0;
polylineStyleOptions.strokeColor = [UIColor blueColor];
polylineStyleOptions.isVisible = YES;
polylineStyleOptions.zIndex = 1000;
polylineStyleOptions.isGeodesic = YES;
[[_mapView consumerMapStyleCoordinator] setPolylineStyleOptions:polylineStyleOptions
polylineType:customizablePolylineType];
}
Obtenir et définir des options d'UI personnalisées pour les repères
L'exemple suivant montre comment définir des options d'interface utilisateur personnalisées pour les repères.
Swift
/** MapViewController.swift */
func updateMarkerUIOptions() {
let customizableMarkerType = GMTCCustomizableMarkerType.tripVehicle
let markerStyleOptions = GMTCMutableMarkerStyleOptions()
markerStyleOptions.groundAnchor = groundAnchor
markerStyleOptions.isVisible = true
markerStyleOptions.icon = icon
markerStyleOptions.zIndex = 100
markerStyleOptions.isFlat = false
let coordinator = self.mapView.consumerMapStyleCoordinator
coordinator.setMarkerStyleOptions(markerStyleOptions, markerType: customizableMarkerType)
}
Objective-C
/** MapViewController.m */
- (void)updateMarkerUIOptions {
// The marker type that you would like to set custom UI options for.
GMTCCustomizableMarkerType customizableMarkerType = GMTCCustomizableMarkerTypeTripVehicle;
GMTCMutableMarkerStyleOptions *markerStyleOptions =
[[GMTCMutableMarkerStyleOptions alloc] init];
markerStyleOptions.groundAnchor = groundAnchor;
markerStyleOptions.isVisible = YES;
markerStyleOptions.icon = icon;
markerStyleOptions.zIndex = 100;
markerStyleOptions.isFlat = NO;
[[_mapView consumerMapStyleCoordinator] setMarkerStyleOptions:markerStyleOptions markerType:customizableMarkerType];
}
Régler le zoom de la caméra
L'option Ma position bouton dans le SDK Maps pour iOS centre l'appareil photo sur la position de l'appareil.
Si une session de partage de parcours est active, vous pouvez centrer la caméra sur se concentrer sur le parcours plutôt que uniquement sur la localisation de l'appareil.
Le SDK grand public fournit une fonctionnalité d'appareil photo automatique est activée par défaut. La caméra zoome pour se concentrer sur l'itinéraire et le point de cheminement suivant.
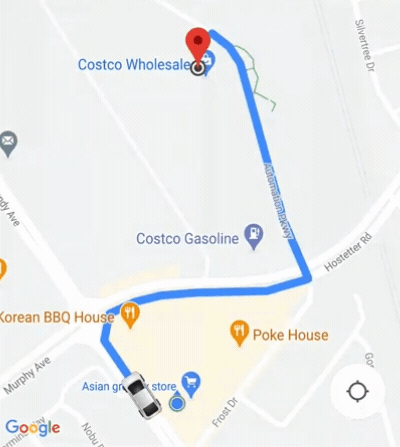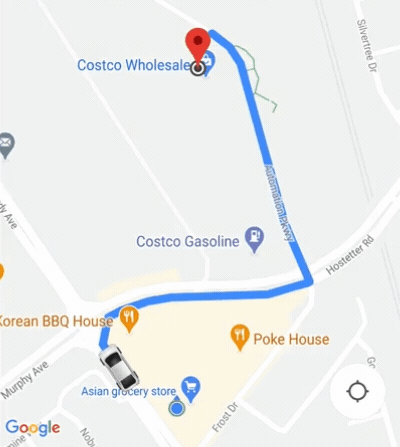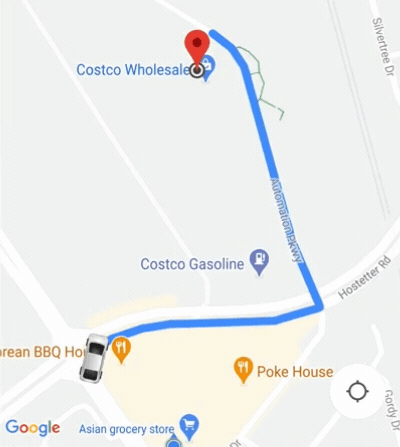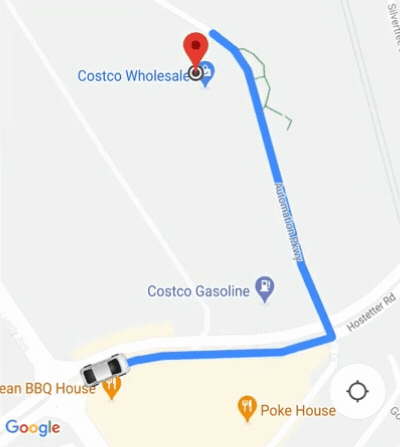
Si vous avez besoin de mieux contrôler le comportement de la caméra, vous pouvez activer ou désactiver
la fonctionnalité d'appareil photo automatique
isAllowCameraAutoUpdate
.
Pour plus de personnalisations de l'appareil photo, consultez Déplacement du SDK Maps pour iOS caméra.

