Présentation
L'association simplifiée Google Sign-In basée sur OAuth ajoute Google Sign-In à l'association OAuth. Cela offre une expérience d'association fluide aux utilisateurs Google et permet également de créer un compte, ce qui permet à l'utilisateur de créer un compte sur votre service à l'aide de son compte Google.
Pour associer des comptes avec OAuth et la connexion Google, procédez comme suit:
- Demandez d'abord à l'utilisateur d'autoriser l'accès à son profil Google.
- Utilisez les informations de son profil pour vérifier si le compte utilisateur existe.
- Pour les utilisateurs existants, associez les comptes.
- Si vous ne trouvez pas de correspondance pour l'utilisateur Google dans votre système d'authentification, validez le jeton d'ID reçu de Google. Vous pouvez ensuite créer un utilisateur en fonction des informations de profil contenues dans le jeton d'ID.
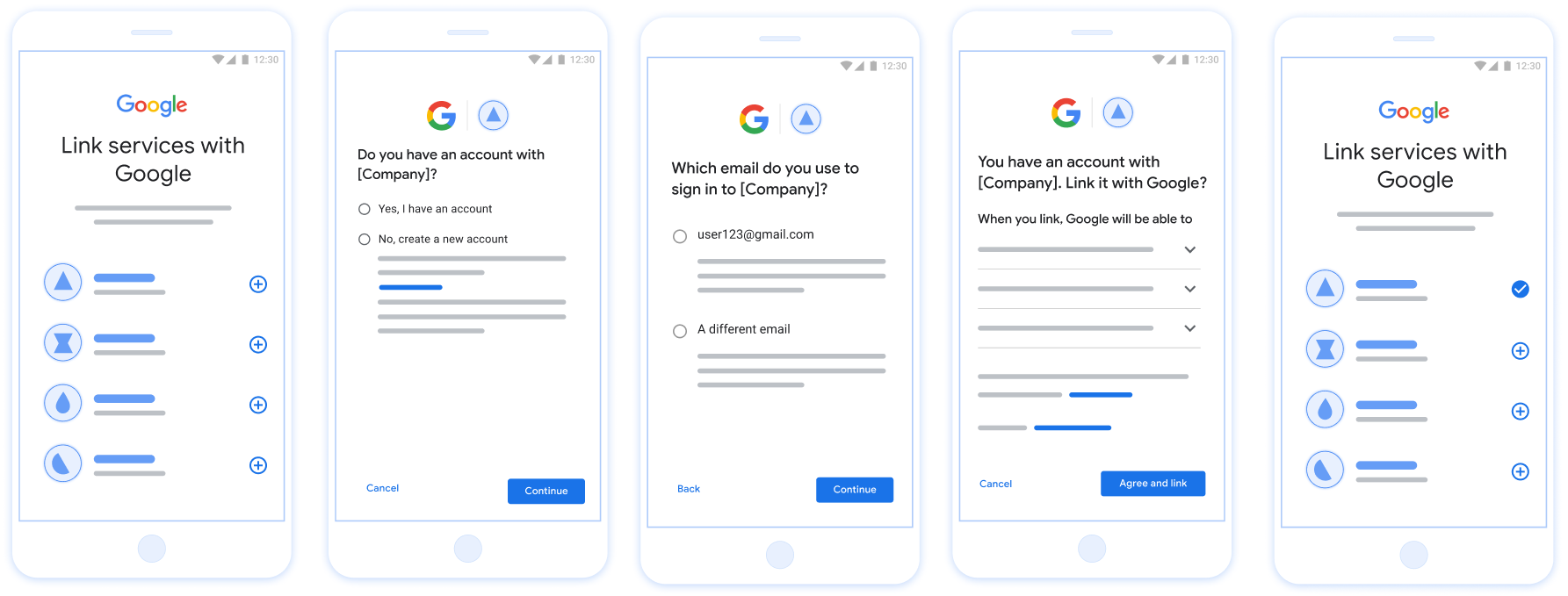
Figure 1 : Association de comptes sur le téléphone d'un utilisateur avec l'association simplifiée
Exigences concernant l'association simplifiée
- Implémentez le flux d'association OAuth Web de base. Votre service doit prendre en charge les points de terminaison d'autorisation et d'échange de jetons conformes à OAuth 2.0.
- Votre point de terminaison d'échange de jetons doit prendre en charge les assertions JSON Web Token (JWT) et implémenter les intents
check,createetget.
Implémenter votre serveur OAuth
Votre point de terminaison d'échange de jetons doit prendre en charge les intents check, create et get. Vous trouverez ci-dessous les étapes effectuées lors du flux d'association de comptes et les moments où les différents intents sont appelés:
- L'utilisateur dispose-t-il d'un compte dans votre système d'authentification ? (L'utilisateur décide en sélectionnant "OUI" ou "NON".)
- OUI : L'utilisateur utilise-t-il l'adresse e-mail associée à son compte Google pour se connecter à votre plate-forme ? (L'utilisateur décide en sélectionnant "OUI" ou "NON".)
- OUI : L'utilisateur dispose-t-il d'un compte correspondant dans votre système d'authentification ? (
check intentest appelé pour confirmation)- OUI :
get intentest appelé et le compte est associé si l'intent get renvoie un résultat positif. - NON : Créer un compte ? (L'utilisateur décide en sélectionnant "OUI" ou "NON".)
- OUI :
create intentest appelé et le compte est associé si l'intent de création renvoie un résultat positif. - NON : Le flux OAuth Web est déclenché, l'utilisateur est redirigé vers son navigateur et a la possibilité d'associer un autre e-mail.
- OUI :
- OUI :
- NON : le flux OAuth Web est déclenché, l'utilisateur est redirigé vers son navigateur et a la possibilité d'associer un autre compte de messagerie.
- OUI : L'utilisateur dispose-t-il d'un compte correspondant dans votre système d'authentification ? (
- NON : l'utilisateur dispose-t-il d'un compte correspondant dans votre système d'authentification ? (
check intentest appelé pour confirmation)- OUI :
get intentest appelé et le compte est associé si l'intent get renvoie un résultat positif. - NON :
create intentest appelé et le compte est associé si l'intent de création renvoie un résultat positif.
- OUI :
- OUI : L'utilisateur utilise-t-il l'adresse e-mail associée à son compte Google pour se connecter à votre plate-forme ? (L'utilisateur décide en sélectionnant "OUI" ou "NON".)
Rechercher un compte utilisateur existant (vérifier l'intent)
Une fois que l'utilisateur a autorisé l'accès à son profil Google, Google lui envoie une requête contenant une assertion signée de l'identité de l'utilisateur Google. La contient des informations comme l'ID du compte Google de l'utilisateur, votre nom et votre adresse e-mail. Le point de terminaison d'échange de jetons configuré pour votre le projet traite cette demande.
Si le compte Google correspondant est déjà présent dans votre authentification
votre point de terminaison d'échange de jetons renvoie account_found=true. Si le
Le compte Google ne correspond à aucun utilisateur existant, le point de terminaison de votre échange de jetons
renvoie une erreur HTTP 404 Not Found avec account_found=false.
La demande se présente sous la forme suivante:
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded grant_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer&intent=check&assertion=JWT&scope=SCOPES&client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET
Le point de terminaison de votre échange de jetons doit pouvoir gérer les paramètres suivants:
| Paramètres du point de terminaison du jeton | |
|---|---|
intent |
Pour ces requêtes, la valeur de ce paramètre est
check |
grant_type |
Type de jeton échangé. Pour ces requêtes,
a pour valeur urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer. |
assertion |
Jeton Web JSON (JWT, JSON Web Token) qui fournit une assertion signée du jeton Google l'identité de l'utilisateur. Le jeton JWT contient des informations qui incluent le jeton ID, nom et adresse e-mail du compte Google. |
client_id |
ID client que vous avez attribué à Google. |
client_secret |
Code secret du client que vous avez attribué à Google. |
Pour répondre aux requêtes d'intent check, le point de terminaison de votre échange de jetons doit procéder comme suit:
- Validez et décodez l'assertion JWT.
- Vérifiez si le compte Google est déjà présent dans votre système d'authentification.
Valider et décoder l'assertion JWT
Vous pouvez valider et décoder l'assertion JWT à l'aide d'un Bibliothèque de décodage JWT pour votre langage. Utilisez Clés publiques de Google, disponibles JWK ou formats PEM, à vérifier la signature du jeton.
Une fois décodée, l'assertion JWT ressemble à l'exemple suivant:
{ "sub": "1234567890", // The unique ID of the user's Google Account "iss": "https://accounts.google.com", // The assertion's issuer "aud": "123-abc.apps.googleusercontent.com", // Your server's client ID "iat": 233366400, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's creation time "exp": 233370000, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's expiration time "name": "Jan Jansen", "given_name": "Jan", "family_name": "Jansen", "email": "jan@gmail.com", // If present, the user's email address "email_verified": true, // true, if Google has verified the email address "hd": "example.com", // If present, the host domain of the user's GSuite email address // If present, a URL to user's profile picture "picture": "https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/a-/AOh14GjlTnZKHAeb94A-FmEbwZv7uJD986VOF1mJGb2YYQ", "locale": "en_US" // User's locale, from browser or phone settings }
En plus de vérifier la signature du jeton, vérifiez que l'assertion
(champ iss) est https://accounts.google.com, que l'audience
(champ aud) correspond à l'ID client qui vous a été attribué et que le jeton n'a pas expiré.
(champ exp).
À l'aide des champs email, email_verified et hd, vous pouvez déterminer
Google héberge les adresses e-mail et fait autorité pour celles-ci. Dans les cas où Google
faisant autorité, l'utilisateur est actuellement connu comme étant le titulaire légitime du compte
et vous pouvez ignorer le mot de passe
ou d'autres méthodes d'authentification. Sinon, ces méthodes
pour valider le compte avant de l'associer.
Cas dans lesquels Google fait autorité:
emailcomporte le suffixe@gmail.com. Il s'agit d'un compte Gmail.email_verifiedest "true" ethdest défini. Il s'agit d'un compte G Suite.
Les utilisateurs peuvent créer un compte Google sans utiliser Gmail ni G Suite. Quand ?
email ne contient pas de suffixe @gmail.com et hd est absent. Google ne l'est pas.
faisant autorité et un mot de passe ou d'autres
méthodes d'authentification sont recommandés pour
l'utilisateur. email_verified peut également être défini sur "true", car Google a initialement validé
utilisateur lors de la création du compte Google, quelle que soit la propriété du tiers
compte de messagerie peut avoir changé depuis.
Vérifier si le compte Google est déjà présent dans votre système d'authentification
Vérifiez si l'une des conditions suivantes est remplie:
- L'ID de compte Google, qui se trouve dans le champ
subde l'assertion, se trouve dans votre compte utilisateur base de données. - L'adresse e-mail indiquée dans l'assertion correspond à un utilisateur de votre base de données utilisateur.
Si l'une des conditions est vraie, l'utilisateur s'est déjà inscrit. Dans ce cas, renvoyer une réponse semblable à celle-ci:
HTTP/1.1 200 Success
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
{
"account_found":"true",
}
Si ni l'ID de compte Google, ni l'adresse e-mail spécifiée dans le champ
correspond à un utilisateur de votre base de données, l'utilisateur ne s'est pas encore inscrit. Dans
Dans ce cas, le point de terminaison de votre échange de jetons doit renvoyer une erreur HTTP 404
qui spécifie "account_found": "false", comme dans l'exemple suivant:
HTTP/1.1 404 Not found
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
{
"account_found":"false",
}
Gérer l'association automatique (obtenir l'intention)
Une fois que l'utilisateur a autorisé l'accès à son profil Google, Google lui envoie une requête contenant une assertion signée de l'identité de l'utilisateur Google. La contient des informations comme l'ID du compte Google de l'utilisateur, votre nom et votre adresse e-mail. Le point de terminaison d'échange de jetons configuré pour votre le projet traite cette demande.
Si le compte Google correspondant est déjà présent dans votre authentification
votre point de terminaison d'échange de jetons renvoie un jeton pour l'utilisateur. Si le
Le compte Google ne correspond à aucun utilisateur existant, le point de terminaison de votre échange de jetons
renvoie une erreur linking_error et une valeur login_hint facultative.
La demande se présente sous la forme suivante:
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded grant_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer&intent=get&assertion=JWT&scope=SCOPES&client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET
Le point de terminaison de votre échange de jetons doit pouvoir gérer les paramètres suivants:
| Paramètres du point de terminaison du jeton | |
|---|---|
intent |
Pour ces requêtes, la valeur de ce paramètre est get. |
grant_type |
Type de jeton échangé. Pour ces requêtes,
a pour valeur urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer. |
assertion |
Jeton Web JSON (JWT, JSON Web Token) qui fournit une assertion signée du jeton Google l'identité de l'utilisateur. Le jeton JWT contient des informations qui incluent le jeton ID, nom et adresse e-mail du compte Google. |
scope |
Facultatif:toutes les habilitations que vous avez configurées pour les demandes utilisateurs. |
client_id |
ID client que vous avez attribué à Google. |
client_secret |
Code secret du client que vous avez attribué à Google. |
Pour répondre aux requêtes d'intent get, le point de terminaison de votre échange de jetons doit procéder comme suit:
- Validez et décodez l'assertion JWT.
- Vérifiez si le compte Google est déjà présent dans votre système d'authentification.
Valider et décoder l'assertion JWT
Vous pouvez valider et décoder l'assertion JWT à l'aide d'un Bibliothèque de décodage JWT pour votre langage. Utilisez Clés publiques de Google, disponibles JWK ou formats PEM, à vérifier la signature du jeton.
Une fois décodée, l'assertion JWT ressemble à l'exemple suivant:
{ "sub": "1234567890", // The unique ID of the user's Google Account "iss": "https://accounts.google.com", // The assertion's issuer "aud": "123-abc.apps.googleusercontent.com", // Your server's client ID "iat": 233366400, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's creation time "exp": 233370000, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's expiration time "name": "Jan Jansen", "given_name": "Jan", "family_name": "Jansen", "email": "jan@gmail.com", // If present, the user's email address "email_verified": true, // true, if Google has verified the email address "hd": "example.com", // If present, the host domain of the user's GSuite email address // If present, a URL to user's profile picture "picture": "https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/a-/AOh14GjlTnZKHAeb94A-FmEbwZv7uJD986VOF1mJGb2YYQ", "locale": "en_US" // User's locale, from browser or phone settings }
En plus de vérifier la signature du jeton, vérifiez que l'assertion
(champ iss) est https://accounts.google.com, que l'audience
(champ aud) correspond à l'ID client qui vous a été attribué et que le jeton n'a pas expiré.
(champ exp).
À l'aide des champs email, email_verified et hd, vous pouvez déterminer
Google héberge les adresses e-mail et fait autorité pour celles-ci. Dans les cas où Google
faisant autorité, l'utilisateur est actuellement connu comme étant le titulaire légitime du compte
et vous pouvez ignorer le mot de passe
ou d'autres méthodes d'authentification. Sinon, ces méthodes
pour valider le compte avant de l'associer.
Cas dans lesquels Google fait autorité:
emailcomporte le suffixe@gmail.com. Il s'agit d'un compte Gmail.email_verifiedest "true" ethdest défini. Il s'agit d'un compte G Suite.
Les utilisateurs peuvent créer un compte Google sans utiliser Gmail ni G Suite. Quand ?
email ne contient pas de suffixe @gmail.com et hd est absent. Google ne l'est pas.
faisant autorité et un mot de passe ou d'autres
méthodes d'authentification sont recommandés pour
l'utilisateur. email_verified peut également être défini sur "true", car Google a initialement validé
utilisateur lors de la création du compte Google, quelle que soit la propriété du tiers
compte de messagerie peut avoir changé depuis.
Vérifier si le compte Google est déjà présent dans votre système d'authentification
Vérifiez si l'une des conditions suivantes est remplie:
- L'ID de compte Google, qui se trouve dans le champ
subde l'assertion, se trouve dans votre compte utilisateur base de données. - L'adresse e-mail indiquée dans l'assertion correspond à un utilisateur de votre base de données utilisateur.
Si un compte est trouvé pour l'utilisateur, émettez un jeton d'accès et renvoyez les valeurs dans un objet JSON dans le corps de votre réponse HTTPS, comme dans l'exemple suivant:
{ "token_type": "Bearer", "access_token": "ACCESS_TOKEN", "refresh_token": "REFRESH_TOKEN", "expires_in": SECONDS_TO_EXPIRATION }
Dans certains cas, l'association de comptes basée sur un jeton d'ID peut échouer pour l'utilisateur. Si
le fait pour une raison quelconque, votre point de terminaison d'échange de jetons doit répondre
401 spécifiant error=linking_error, comme le montre l'exemple suivant:
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
{
"error":"linking_error",
"login_hint":"foo@bar.com"
}
Lorsque Google reçoit une réponse d'erreur 401 avec linking_error, il envoie
l'utilisateur à votre point de terminaison d'autorisation avec login_hint comme paramètre. La
L'utilisateur effectue l'association du compte à l'aide du flux d'association OAuth dans son navigateur.
Gérer la création de compte via Google Sign-In (créer un intent)
Lorsqu'un utilisateur doit créer un compte sur votre service, Google lui envoie une demande
au point de terminaison de votre échange de jetons qui spécifie intent=create.
La demande se présente sous la forme suivante:
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded response_type=token&grant_type=urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer&scope=SCOPES&intent=create&assertion=JWT&client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET
Le point de terminaison de votre échange de jetons doit pouvoir gérer les paramètres suivants:
| Paramètres du point de terminaison du jeton | |
|---|---|
intent |
Pour ces requêtes, la valeur de ce paramètre est create. |
grant_type |
Type de jeton échangé. Pour ces requêtes,
a pour valeur urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:jwt-bearer. |
assertion |
Jeton Web JSON (JWT, JSON Web Token) qui fournit une assertion signée du jeton Google l'identité de l'utilisateur. Le jeton JWT contient des informations qui incluent le jeton ID, nom et adresse e-mail du compte Google. |
client_id |
ID client que vous avez attribué à Google. |
client_secret |
Code secret du client que vous avez attribué à Google. |
Le JWT du paramètre assertion contient l'ID du compte Google de l'utilisateur,
et l'adresse e-mail, que vous pourrez utiliser pour créer un nouveau compte sur votre
Google Cloud.
Pour répondre aux requêtes d'intent create, le point de terminaison de votre échange de jetons doit procéder comme suit:
- Validez et décodez l'assertion JWT.
- Validez les informations sur l'utilisateur et créez un compte.
Valider et décoder l'assertion JWT
Vous pouvez valider et décoder l'assertion JWT à l'aide d'un Bibliothèque de décodage JWT pour votre langage. Utilisez Clés publiques de Google, disponibles JWK ou formats PEM, à vérifier la signature du jeton.
Une fois décodée, l'assertion JWT ressemble à l'exemple suivant:
{ "sub": "1234567890", // The unique ID of the user's Google Account "iss": "https://accounts.google.com", // The assertion's issuer "aud": "123-abc.apps.googleusercontent.com", // Your server's client ID "iat": 233366400, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's creation time "exp": 233370000, // Unix timestamp of the assertion's expiration time "name": "Jan Jansen", "given_name": "Jan", "family_name": "Jansen", "email": "jan@gmail.com", // If present, the user's email address "email_verified": true, // true, if Google has verified the email address "hd": "example.com", // If present, the host domain of the user's GSuite email address // If present, a URL to user's profile picture "picture": "https://lh3.googleusercontent.com/a-/AOh14GjlTnZKHAeb94A-FmEbwZv7uJD986VOF1mJGb2YYQ", "locale": "en_US" // User's locale, from browser or phone settings }
En plus de vérifier la signature du jeton, vérifiez que l'assertion
(champ iss) est https://accounts.google.com, que l'audience
(champ aud) correspond à l'ID client qui vous a été attribué et que le jeton n'a pas expiré.
(champ exp).
À l'aide des champs email, email_verified et hd, vous pouvez déterminer
Google héberge les adresses e-mail et fait autorité pour celles-ci. Dans les cas où Google
faisant autorité, l'utilisateur est actuellement connu comme étant le titulaire légitime du compte
et vous pouvez ignorer le mot de passe
ou d'autres méthodes d'authentification. Sinon, ces méthodes
pour valider le compte avant de l'associer.
Cas dans lesquels Google fait autorité:
emailcomporte le suffixe@gmail.com. Il s'agit d'un compte Gmail.email_verifiedest "true" ethdest défini. Il s'agit d'un compte G Suite.
Les utilisateurs peuvent créer un compte Google sans utiliser Gmail ni G Suite. Quand ?
email ne contient pas de suffixe @gmail.com et hd est absent. Google ne l'est pas.
faisant autorité et un mot de passe ou d'autres
méthodes d'authentification sont recommandés pour
l'utilisateur. email_verified peut également être défini sur "true", car Google a initialement validé
utilisateur lors de la création du compte Google, quelle que soit la propriété du tiers
compte de messagerie peut avoir changé depuis.
Valider les informations sur l'utilisateur et créer un compte
Vérifiez si l'une des conditions suivantes est remplie:
- L'ID de compte Google, qui se trouve dans le champ
subde l'assertion, se trouve dans votre compte utilisateur base de données. - L'adresse e-mail indiquée dans l'assertion correspond à un utilisateur de votre base de données utilisateur.
Si l'une des conditions est vraie, invitez l'utilisateur à associer son compte existant
avec son compte Google. Pour ce faire, répondez à la requête avec une erreur HTTP 401.
qui spécifie error=linking_error et attribue l'adresse e-mail de l'utilisateur comme
login_hint Voici un exemple de réponse :
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
{
"error":"linking_error",
"login_hint":"foo@bar.com"
}
Lorsque Google reçoit une réponse d'erreur 401 avec linking_error, il envoie
l'utilisateur à votre point de terminaison d'autorisation avec login_hint comme paramètre. La
L'utilisateur effectue l'association du compte à l'aide du flux d'association OAuth dans son navigateur.
Si aucune condition n'est vraie, créez un nouveau compte d'utilisateur avec les informations fournies dans le JWT. En règle générale, aucun mot de passe n'est défini pour les nouveaux comptes. Il est recommandé d'ajouter Google Sign-In aux autres plates-formes pour permettre aux utilisateurs vous connecter à Google sur toutes les surfaces de votre application. Vous pouvez également Vous pouvez envoyer à l'utilisateur un lien qui lancera le processus de récupération de mot de passe pour lui permettre pour définir un mot de passe afin de se connecter sur d'autres plates-formes.
Une fois la création terminée, émettez un jeton d'accès et qui renvoient les valeurs dans un objet JSON le corps de votre réponse HTTPS, comme dans l'exemple suivant:
{ "token_type": "Bearer", "access_token": "ACCESS_TOKEN", "refresh_token": "REFRESH_TOKEN", "expires_in": SECONDS_TO_EXPIRATION }
Obtenir votre ID client pour les API Google
Vous devrez fournir votre ID client Google API lors de l'enregistrement de l'association de comptes.
Pour obtenir votre ID client d'API à l'aide du projet que vous avez créé lors de la procédure d'association OAuth. Pour ce faire, procédez comme suit :
Créez ou sélectionnez un projet Google APIs.
Si votre projet ne dispose pas d'ID client pour le type d'application Web, cliquez sur Créer un client pour en créer un. Veillez à inclure le domaine de votre site dans la zone Origines JavaScript autorisées. Lorsque vous effectuez des tests ou un développement locaux, vous devez ajouter
http://localhostethttp://localhost:<port_number>au champ Origines JavaScript autorisées.
Valider votre implémentation
Vous pouvez valider votre implémentation à l'aide de l'outil OAuth 2.0 Playground.
Dans l'outil, procédez comme suit:
- Cliquez sur Configuration pour ouvrir la fenêtre de configuration OAuth 2.0.
- Dans le champ OAuth flow (Flux OAuth), sélectionnez Client-side (Côté client).
- Dans le champ Points de terminaison OAuth, sélectionnez Personnalisé.
- Indiquez votre point de terminaison OAuth 2.0 et l'ID client que vous avez attribué à Google dans les champs correspondants.
- Dans la section Étape 1, ne sélectionnez aucun champ d'application Google. Laissez plutôt ce champ vide ou saisissez une portée valide pour votre serveur (ou une chaîne arbitraire si vous n'utilisez pas de portées OAuth). Lorsque vous avez terminé, cliquez sur Autoriser les API.
- Dans les sections Étape 2 et Étape 3, suivez le flux OAuth 2.0 et vérifiez que chaque étape fonctionne comme prévu.
Vous pouvez valider votre implémentation à l'aide de l'outil Démo d'association de comptes Google.
Dans l'outil, procédez comme suit:
- Cliquez sur le bouton Se connecter avec Google.
- Sélectionnez le compte que vous souhaitez associer.
- Saisissez l'ID du service.
- Saisissez éventuellement un ou plusieurs champs d'application pour lesquels vous demanderez l'accès.
- Cliquez sur Démarrer la démo.
- Lorsque vous y êtes invité, confirmez que vous pouvez accepter ou refuser la demande d'association.
- Vérifiez que vous êtes redirigé vers votre plate-forme.