帳戶連結會使用業界標準的 OAuth 2.0 隱含和授權碼流程。您的服務必須支援符合 OAuth 2.0 標準的授權和權杖交換端點。
在隱含流程中,Google 會在使用者的瀏覽器中開啟授權端點。成功登入後,會將長期存取權杖傳回 Google。這個存取權杖現在已納入 Google 發出的每項要求。
在授權碼流程中,您需要兩個端點:
授權端點,會為尚未登入的使用者顯示登入 UI。授權端點也會建立短效授權碼,記錄使用者對所要求存取權的同意聲明。
權杖交換端點,負責兩種交換:
- 交換授權碼用於長期更新權杖和短期存取權杖。使用者進行帳戶連結流程時,就會發生這個交換。
- 這個外掛程式能使用長期更新權杖做為短期存取權杖。 如果 Google 需要新的存取權存證,因為舊的存證已過期,就會發生此交換。
選擇 OAuth 2.0 流程
雖然隱含流程的實作方式較簡單,但 Google 建議隱含流程發出的存取權杖永遠不會過期。這是因為權杖過期後,系統必須要求使用者再次連結帳戶。如果您基於安全性考量而需要代碼到期,強烈建議您改用授權程式碼流程。
設計指南
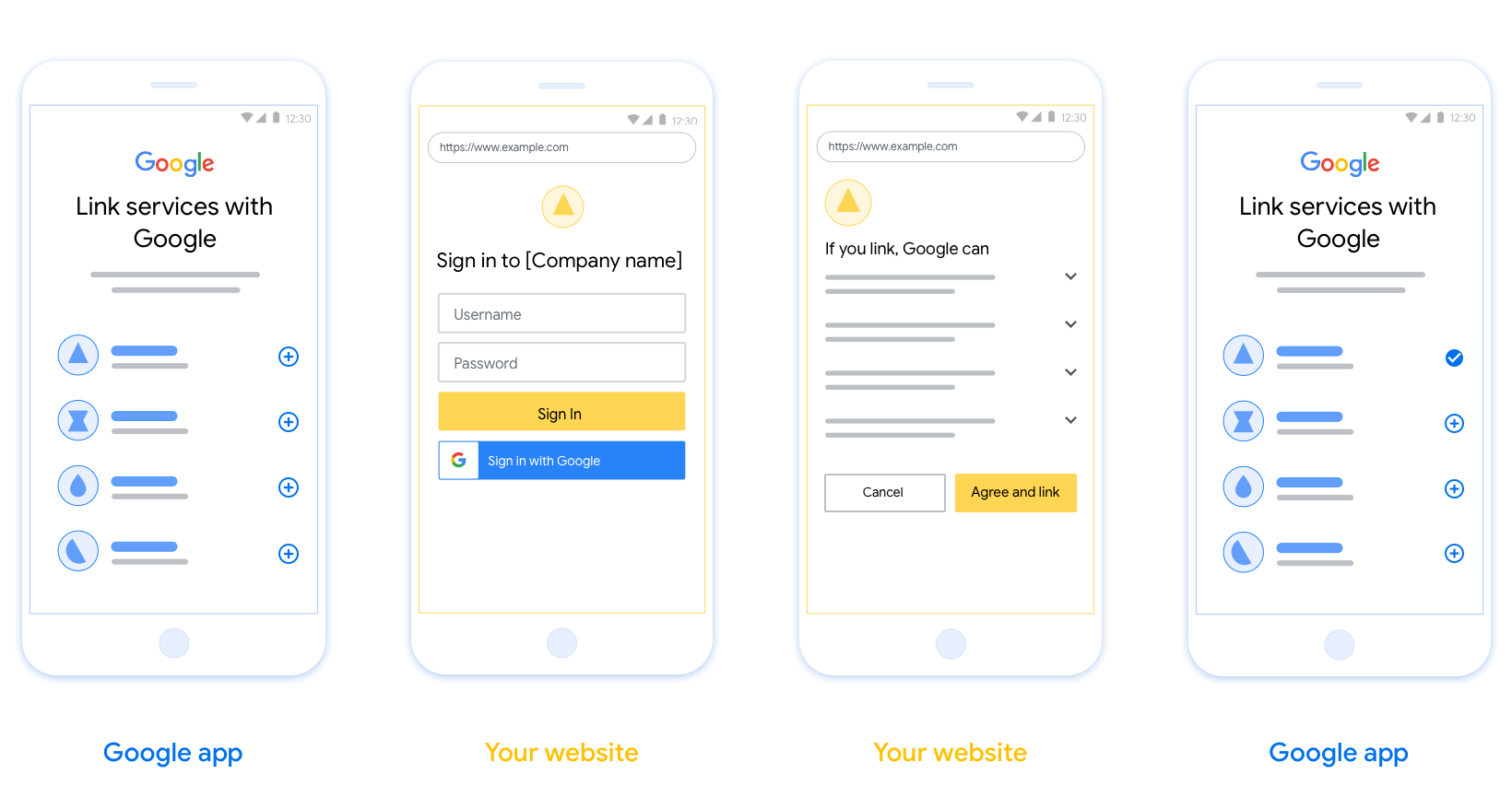
本節說明針對 OAuth 連結流程所託管使用者畫面的設計需求和建議。Google 的應用程式呼叫後,您的平台會向使用者顯示登入 Google 頁面和帳戶連結同意畫面。使用者同意連結帳戶後,系統會將他們導向 Google 的應用程式。
需求條件
- 您必須說明使用者的帳戶將連結至 Google,而不是 Google Home 或 Google 助理等特定 Google 產品。
建議
建議您採取以下做法:
顯示《Google 隱私權政策》。在同意畫面加入 Google 隱私權政策連結。
要共用的資料。使用簡潔明瞭的表達方式,向使用者說明 Google 需要他們的哪些資料,以及原因。
明確的行動號召。在同意聲明畫面上明確列出行動號召,例如「同意並連結」。這是因為使用者需要瞭解自己必須與 Google 分享哪些資料,才能連結帳戶。
可取消訂閱。如果使用者選擇不連結,請提供返回或取消的選項。
清除登入程序。請確認使用者有明確的方法登入 Google 帳戶,例如使用者名稱和密碼欄位,或使用 Google 帳戶登入。
可取消連結。提供使用者解除連結的機制,例如平台上帳戶設定的網址。或者,您也可以加入 Google 帳戶的連結,讓使用者能管理已連結帳戶。
變更使用者帳戶的功能。建議使用者切換帳戶的方法。如果使用者傾向擁有多個帳戶,這項功能就特別實用。
- 如果使用者必須關閉同意畫面才能切換帳戶,請將可復原的錯誤傳送給 Google,方便使用者透過 OAuth 連結和隱含流程登入所需帳戶。
加入標誌。在同意畫面上顯示公司標誌。 請依照您的樣式規範放置標誌。如果您也想顯示 Google 的標誌,請參閱標誌和商標。
Create the project
To create your project to use account linking:
- Go to the Google API Console.
- Click Create project.
- Enter a name or accept the generated suggestion.
- Confirm or edit any remaining fields.
- Click Create.
To view your project ID:
- Go to the Google API Console.
- Find your project in the table on the landing page. The project ID appears in the ID column.
Configure your OAuth Consent Screen
The Google Account Linking process includes a consent screen which tells users the application requesting access to their data, what kind of data they are asking for and the terms that apply. You will need to configure your OAuth consent screen before generating a Google API client ID.
- Open the OAuth consent screen page of the Google APIs console.
- If prompted, select the project you just created.
On the "OAuth consent screen" page, fill out the form and click the “Save” button.
Application name: The name of the application asking for consent. The name should accurately reflect your application and be consistent with the application name users see elsewhere. The application name will be shown on the Account Linking consent screen.
Application logo: An image on the consent screen that will help users recognize your app. The logo is shown on Account linking consent screen and on account settings
Support email: For users to contact you with questions about their consent.
Scopes for Google APIs: Scopes allow your application to access your user's private Google data. For the Google Account Linking use case, default scope (email, profile, openid) is sufficient, you don’t need to add any sensitive scopes. It is generally a best practice to request scopes incrementally, at the time access is required, rather than up front. Learn more.
Authorized domains: To protect you and your users, Google only allows applications that authenticate using OAuth to use Authorized Domains. Your applications' links must be hosted on Authorized Domains. Learn more.
Application Homepage link: Home page for your application. Must be hosted on an Authorized Domain.
Application Privacy Policy link: Shown on Google Account Linking consent screen. Must be hosted on an Authorized Domain.
Application Terms of Service link (Optional): Must be hosted on an Authorized Domain.
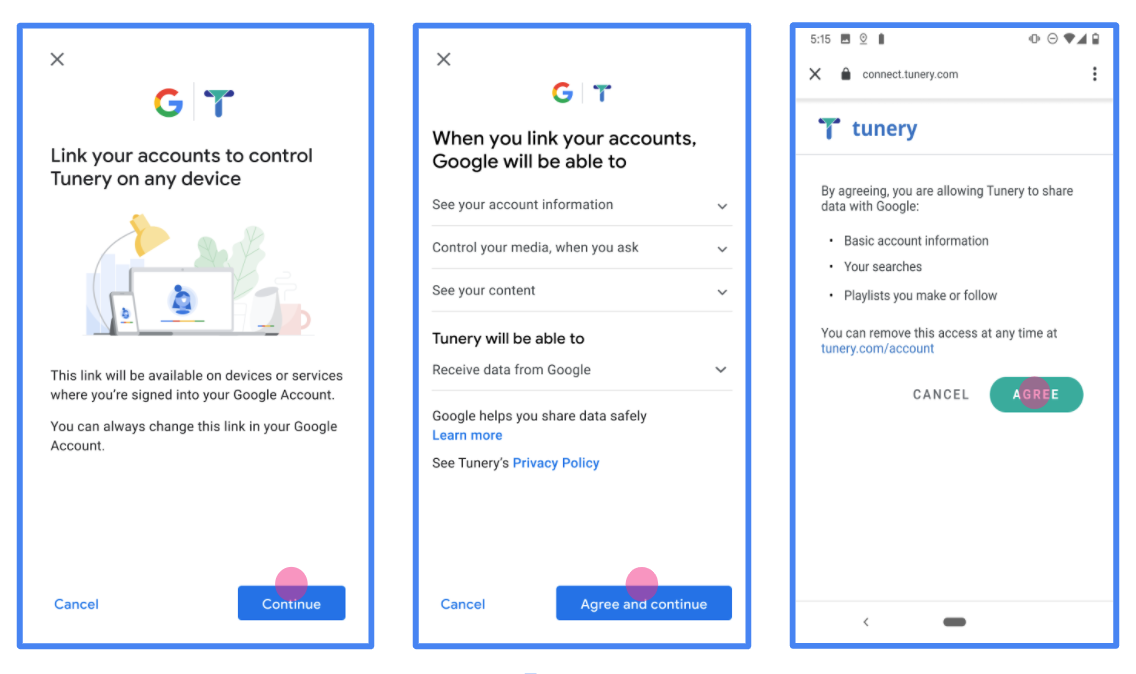
Figure 1. Google Account Linking Consent Screen for a fictitious Application, Tunery
Check "Verification Status", if your application needs verification then click the "Submit For Verification" button to submit your application for verification. Refer to OAuth verification requirements for details.
實作 OAuth 伺服器
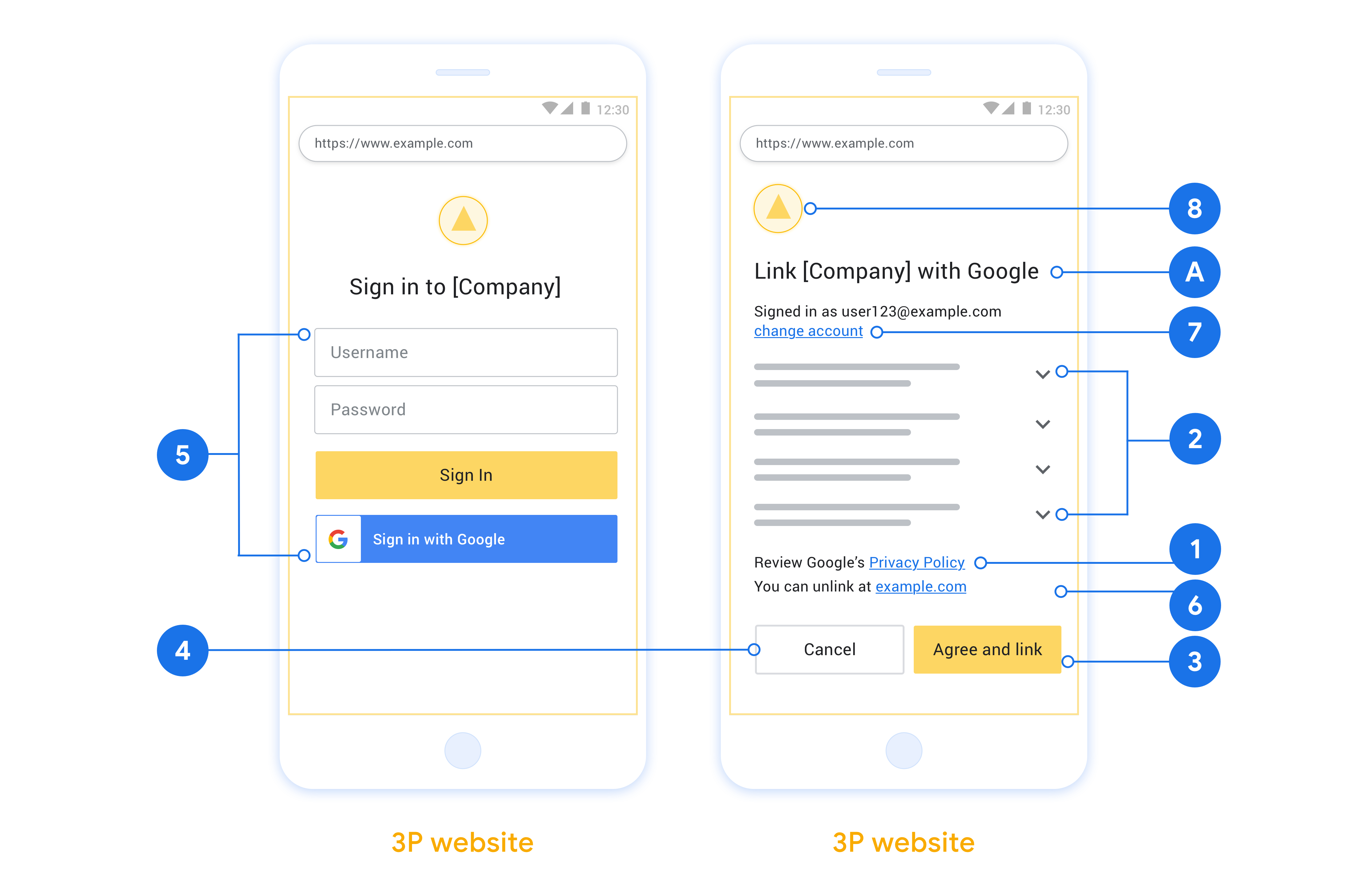
授權碼流程的 OAuth 2.0 伺服器實作包含 服務透過 HTTPS 提供第一個端點 是授權端點,負責尋找或取得 徵得使用者同意並授予資料存取權授權端點會顯示 登入使用者介面,供尚未登入的使用者查看,且將同意 所要求的存取權第二個端點是權杖交換端點 用於取得加密字串 (稱為「權杖」),藉此授權使用者 存取您的服務。
當 Google 應用程式需要呼叫服務的其中一個 API 時,Google 會使用 這些端點都會一起取得權限,以便使用者呼叫這些 API 管理。
由 Google 發起的 OAuth 2.0 授權碼流程工作階段, 下列流程:
- Google 會在使用者的瀏覽器中開啟授權端點。如果流程 透過純語音裝置啟動動作,則 Google 將 到手機上
- 使用者登入後 (如果尚未登入),並將權限授予 Google 透過您的 API 存取他們的資料 (如果尚未授予權限)。
- 您的服務會建立授權碼,並傳回 Google。待辦 因此,請透過授權碼將使用者的瀏覽器重新導向回 Google 附加在要求中
- Google 將授權碼傳送至權杖交換端點 驗證程式碼的真實性,並傳回存取權杖和 更新權杖。存取權杖是服務 以憑證存取 API。更新權杖存在長期 憑證,可供 Google 儲存,用於取得新的存取權杖 過期。
- 使用者完成帳戶連結流程後, 來自 Google 的要求會包含存取權杖。
處理授權要求
使用 OAuth 2.0 授權碼執行帳戶連結時 流程時,Google 會透過以下要求將使用者傳送到您的授權端點 包含下列參數:
| 授權端點參數 | |
|---|---|
client_id |
您指派給 Google 的用戶端 ID。 |
redirect_uri |
您傳送回應到這項要求的網址。 |
state |
傳回給 Google 的記帳金額,值維持不變 重新導向 URI |
scope |
選用:一組以空格分隔的範圍字串,指定 也就是 Google 要求授權的資料 |
response_type |
要在回應中傳回的值類型。針對 OAuth 2.0
授權碼流程,回應類型一律為 code。
|
user_locale |
中的 Google 帳戶語言設定 RFC5646 格式,用來將內容翻譯成使用者偏好的語言。 |
舉例來說,如果您的授權端點位於
https://myservice.example.com/auth,要求可能如下所示:
GET https://myservice.example.com/auth?client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&redirect_uri=REDIRECT_URI&state=STATE_STRING&scope=REQUESTED_SCOPES&response_type=code&user_locale=LOCALE
如要讓授權端點處理登入要求,請按照下列步驟操作: 步驟:
- 確認
client_id與您指派給 Google 的用戶端 ID 相符,且redirect_uri與 Google 為您的服務提供的重新導向網址相符。這些檢查至關重要 存取非預期或設定錯誤的用戶端應用程式。如果跨平台支援 OAuth 2.0 流程,也可以確認response_type是code。 - 檢查使用者是否已登入您的服務。如果使用者未登入, 完成服務的登入或註冊流程。
- 產生授權代碼,讓 Google 用來存取您的 API。 授權碼可以是任何字串值,但必須不重複 代表使用者、該權杖所屬的用戶端,以及代碼的到期時間 而且您無法憑空猜測您通常會核發授權 驗證碼會在大約 10 分鐘後失效
- 請確認
redirect_uri參數指定的網址包含 以下表單:https://oauth-redirect.googleusercontent.com/r/YOUR_PROJECT_ID https://oauth-redirect-sandbox.googleusercontent.com/r/YOUR_PROJECT_ID
- 將使用者的瀏覽器重新導向至
redirect_uri參數。附上 產生的原始值,以及您在重新導向時 方法是附加code和state參數。以下是 結果網址的範例:https://oauth-redirect.googleusercontent.com/r/YOUR_PROJECT_ID?code=AUTHORIZATION_CODE&state=STATE_STRING
處理權杖交換要求
服務的權杖交換端點負責兩種權杖 廣告交易平台:
- 交換存取權杖和更新權杖的授權碼
- 交換存取權杖的更新權杖
權杖交換要求包含下列參數:
| 權杖交換端點參數 | |
|---|---|
client_id |
用來識別要求來源為 Google 的字串。此字串必須 在您的系統中註冊為 Google 專屬識別碼。 |
client_secret |
您向 Google 註冊的服務專用密鑰。 |
grant_type |
要交換的權杖類型。這可以是
authorization_code 或 refresh_token。 |
code |
如果 grant_type=authorization_code,這個參數是
Google 從登入或權杖交換收到驗證碼
端點 |
redirect_uri |
如果 grant_type=authorization_code,這個參數是
用於初始授權要求的網址。 |
refresh_token |
如果 grant_type=refresh_token,這個參數是
Google 從您的權杖交換端點收到更新權杖。 |
交換存取權杖和更新權杖的授權碼
使用者登入,且您的授權端點傳回 授權代碼傳送給 Google,Google 會向你的權杖交換要求傳送要求 來交換存取權杖的授權碼 產生下一個符記
在這些要求中,grant_type 的值為 authorization_code,
code 的值是您先前授予的授權碼
Google。以下為
存取權杖和更新權杖的授權碼:
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET&grant_type=authorization_code&code=AUTHORIZATION_CODE&redirect_uri=REDIRECT_URI
如要交換存取權杖和更新權杖的授權碼,您的
權杖交換端點會執行下列命令來回應 POST 要求:
步驟:
- 驗證
client_id會將要求來源識別為已授權的要求 ,且client_secret符合預期值。 - 請檢查授權碼是否有效且未過期,且 要求中指定的用戶端 ID 與 授權碼。
- 確認
redirect_uri參數指定的網址相同 設為初始授權要求使用的值。 - 如果您無法驗證上述所有條件,請傳回 HTTP
400 「Bad Request」錯誤,內文為
{"error": "invalid_grant"}。 - 否則,請使用授權碼中的使用者 ID 產生重新整理 權杖和存取權杖這些符記可以是任何字串值,但 必須明確代表憑證所屬的用戶端、 另一個使用者如果是存取權杖,也請記下 權杖,通常是在您核發權杖後 1 小時。 重新整理權杖沒有期限。
- 在 HTTPS 回應的內文中傳回下列 JSON 物件:
{ "token_type": "Bearer", "access_token": "ACCESS_TOKEN", "refresh_token": "REFRESH_TOKEN", "expires_in": SECONDS_TO_EXPIRATION }
Google 會儲存使用者和記錄的存取權杖和更新權杖 存取權杖的到期時間存取權杖到期時,Google 會使用 更新憑證,從權杖交換端點取得新的存取權杖。
交換存取權杖的更新權杖
存取權杖到期時,Google 會傳送要求至您的權杖交換 更新憑證,藉此將更新憑證交換給新的存取權杖。
在這些要求的 grant_type 值為 refresh_token,其值為
refresh_token 是您先前授予的更新權杖值
Google。以下是交換更新權杖的要求範例
定義存取權杖:
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET&grant_type=refresh_token&refresh_token=REFRESH_TOKEN
如要將更新權杖換成存取權杖,權杖交換端點
執行下列步驟來回應 POST 要求:
- 驗證
client_id會將要求來源指定為 Google。client_secret與預期值相符 - 驗證更新權杖是否有效,以及 此請求會與更新權杖關聯的用戶端 ID 相符。
- 如果您無法驗證上述所有條件,請傳回 HTTP 400
「Bad Request」錯誤,以
{"error": "invalid_grant"}為主體。 - 否則,請使用更新權杖的使用者 ID 產生存取權 產生下一個符記這些權杖可以是任何字串值,但必須不重複 代表使用者和用戶端,不得 容易猜測的字詞如果是存取權杖,也請記錄權杖的到期時間 通常在核發權杖後一小時。
- 在 HTTPS 內文中傳回下列 JSON 物件
回應:
{ "token_type": "熊", "access_token": "ACCESS_TOKEN", 「expires_in」:SECONDS_TO_EXPIRATION }
處理使用者資訊要求
userinfo 端點是 OAuth 2.0 受保護的資源,可傳回已連結使用者的聲明。除了下列用途外,不一定要實作並代管 userinfo 端點:
成功從權杖端點擷取存取權杖後,Google 會向您的使用者資訊端點傳送要求,以擷取已連結使用者的基本個人資料。
| userinfo 端點要求標頭 | |
|---|---|
Authorization header |
Bearer 類型的存取權杖。 |
舉例來說,如果您的 userinfo 端點位於
https://myservice.example.com/userinfo,要求可能如下所示:
GET /userinfo HTTP/1.1 Host: myservice.example.com Authorization: Bearer ACCESS_TOKEN
為了讓 userinfo 端點處理要求,請按照下列步驟操作:
- 從授權標頭擷取存取權杖,然後為與存取權杖相關聯的使用者傳回資訊。
- 如果存取權杖無效,請使用
WWW-Authenticate回應標頭傳回 HTTP 401 Unauthorized 錯誤。以下是 userinfo 錯誤回應的範例:HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized WWW-Authenticate: error="invalid_token", error_description="The Access Token expired"
如果存取權杖有效,則傳回並傳回 HTTP 200 回應,且 HTTPS 內文含有下列 JSON 物件 回應:
{ "sub": "USER_UUID", "email": "EMAIL_ADDRESS", "given_name": "FIRST_NAME", "family_name": "LAST_NAME", "name": "FULL_NAME", "picture": "PROFILE_PICTURE", }userinfo 端點回應 sub用來在系統中識別使用者的專屬 ID。 email使用者的電子郵件地址。 given_name選填:使用者的名字。 family_name選填:使用者的姓氏。 name選填:使用者全名。 picture選用:使用者的個人資料相片。
驗證實作
您可以使用 OAuth 2.0 Playground 工具驗證實作結果。
請在工具中按照下列步驟操作:
- 點選「Configuration」圖示 ,開啟 OAuth 2.0 設定視窗。
- 在「OAuth 流程」欄位中,選取「用戶端」。
- 在「OAuth 端點」欄位中,選取「自訂」。
- 在對應的欄位中指定 OAuth 2.0 端點,以及您指派給 Google 的用戶端 ID。
- 在「步驟 1」部分中,請勿選取任何 Google 範圍。請改為將這個欄位留空,或輸入有效的伺服器範圍 (如果您不使用 OAuth 範圍,則輸入任意字串)。完成後,按一下「授權 API」。
- 在「步驟 2」和「步驟 3」部分,請完成 OAuth 2.0 流程,並確認每個步驟都能正常運作。
您可以使用 Google 帳戶連結示範工具驗證實作成果。
在工具中執行下列步驟:
- 按一下「使用 Google 帳戶登入」按鈕。
- 選擇要連結的帳戶。
- 輸入服務 ID。
- 您可以選擇輸入一或多個要申請存取權的範圍。
- 按一下「開始試用」。
- 系統顯示提示時,請確認您可以同意或拒絕連結要求。
- 確認系統是否會將你重新導向至平台。