Các tài khoản được liên kết bằng các quy trình ngầm ẩn và mã uỷ quyền OAuth 2.0 theo tiêu chuẩn ngành. Dịch vụ của bạn phải hỗ trợ các điểm cuối uỷ quyền và trao đổi mã thông báo tuân thủ OAuth 2.0.
Trong luồng ngầm ẩn, Google sẽ mở điểm cuối uỷ quyền của bạn trong trình duyệt của người dùng. Sau khi đăng nhập thành công, bạn sẽ trả về một mã thông báo truy cập có thời hạn dài cho Google. Mã truy cập này hiện được đưa vào mọi yêu cầu do Google gửi.
Trong quy trình mã uỷ quyền, bạn cần có hai điểm cuối:
Điểm cuối uỷ quyền hiển thị giao diện người dùng đăng nhập cho những người dùng chưa đăng nhập. Điểm cuối uỷ quyền cũng tạo một mã uỷ quyền ngắn hạn để ghi lại sự đồng ý của người dùng đối với quyền truy cập đã yêu cầu.
Điểm cuối trao đổi mã thông báo chịu trách nhiệm cho hai loại giao dịch:
- Trao đổi mã uỷ quyền lấy mã làm mới dài hạn và mã truy cập ngắn hạn. Quá trình trao đổi này diễn ra khi người dùng thực hiện quy trình liên kết tài khoản.
- Trao đổi mã làm mới dài hạn cho mã truy cập ngắn hạn. Quá trình trao đổi này xảy ra khi Google cần một mã thông báo truy cập mới vì mã thông báo cũ đã hết hạn.
Chọn quy trình OAuth 2.0
Mặc dù quy trình ngầm ẩn dễ triển khai hơn, nhưng bạn nên đảm bảo rằng mã truy cập do luồng ngầm ẩn cấp không bao giờ hết hạn. Điều này là do người dùng buộc phải liên kết lại tài khoản của họ sau khi mã thông báo hết hạn bằng luồng ngầm ẩn. Nếu cần hết hạn mã thông báo vì lý do bảo mật, bạn nên sử dụng quy trình mã uỷ quyền.
Hướng dẫn thiết kế
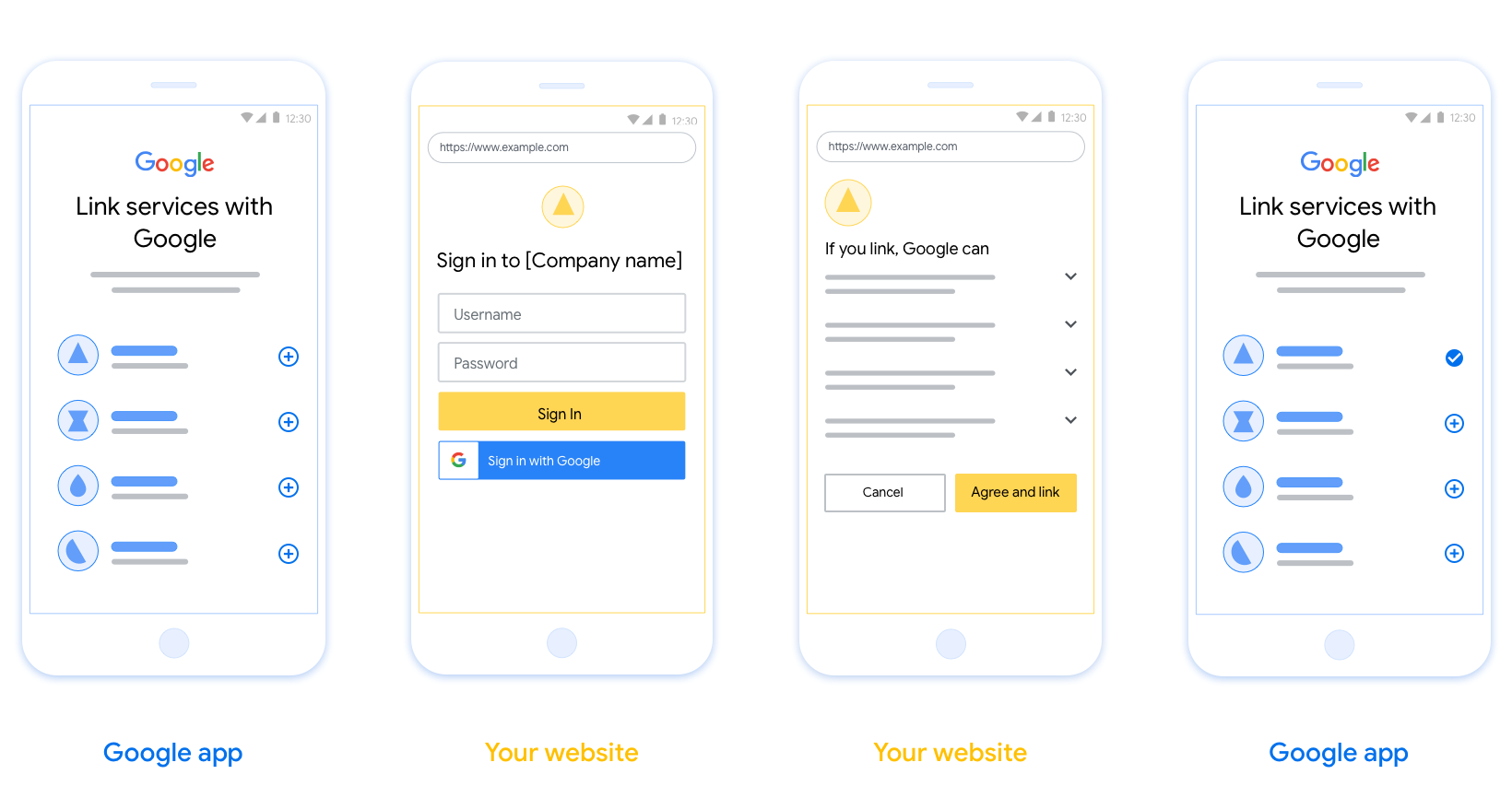
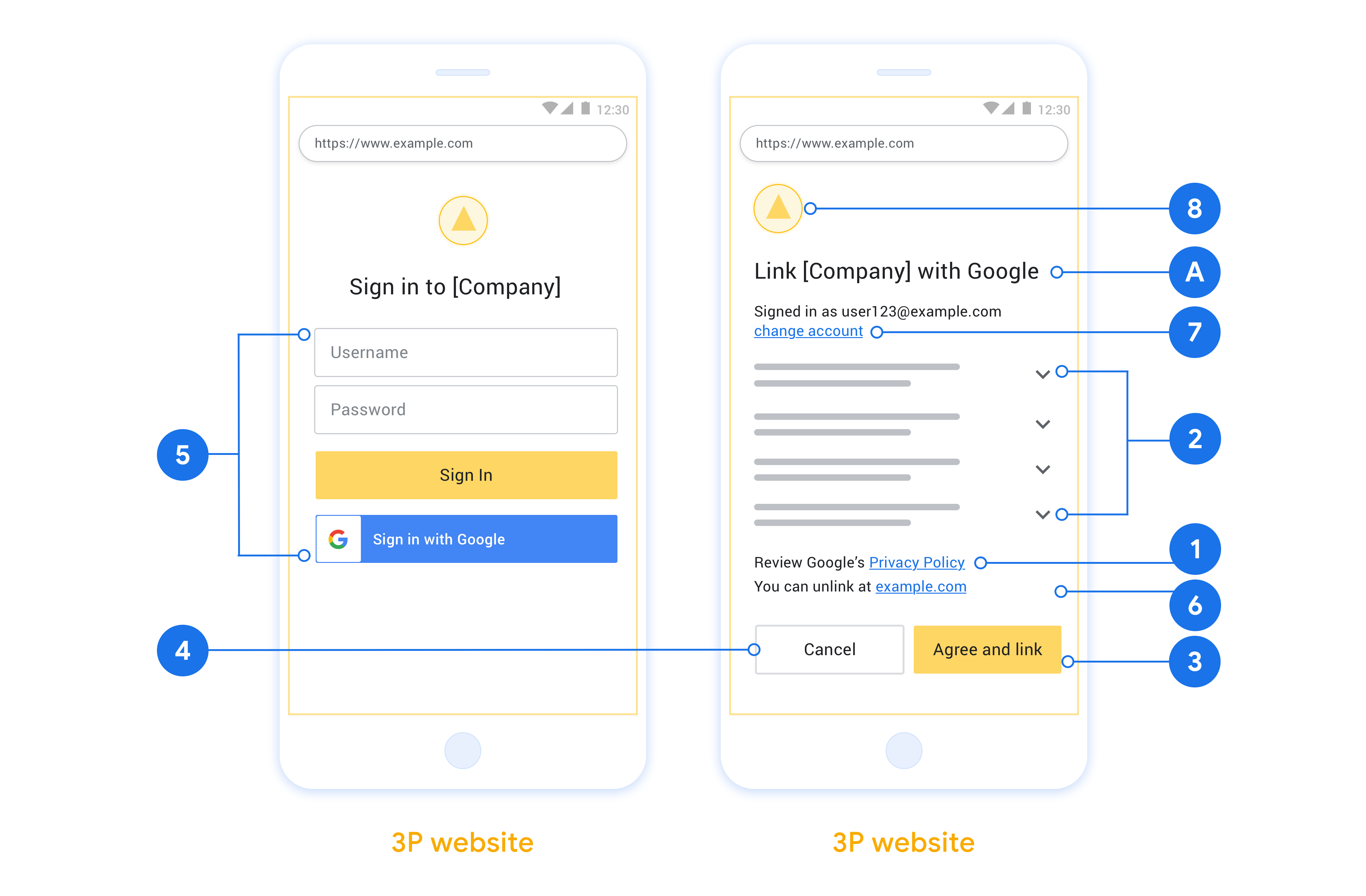
Phần này mô tả các yêu cầu và đề xuất về thiết kế đối với màn hình người dùng mà bạn lưu trữ cho các quy trình liên kết OAuth. Sau khi được ứng dụng của Google gọi, nền tảng của bạn sẽ hiển thị trang đăng nhập vào Google và màn hình đồng ý liên kết tài khoản cho người dùng. Người dùng được chuyển hướng trở lại ứng dụng của Google sau khi đồng ý liên kết tài khoản.
Yêu cầu
- Bạn phải thông báo rằng tài khoản của người dùng sẽ được liên kết với Google, chứ không phải một sản phẩm cụ thể của Google như Google Home hoặc Trợ lý Google.
Đề xuất
Bạn nên thực hiện những điều sau:
Hiển thị Chính sách quyền riêng tư của Google. Đưa một đường liên kết đến Chính sách quyền riêng tư của Google trên màn hình xin phép.
Dữ liệu sẽ được chia sẻ. Sử dụng ngôn từ rõ ràng và súc tích để cho người dùng biết Google yêu cầu dữ liệu nào của họ và lý do tại sao.
Lời kêu gọi hành động rõ ràng. Đưa ra lời kêu gọi hành động rõ ràng trên màn hình xin phép, chẳng hạn như “Đồng ý và liên kết”. Điều này là vì người dùng cần biết dữ liệu nào họ cần phải chia sẻ với Google để liên kết tài khoản của họ.
Khả năng huỷ. Cung cấp cách để người dùng quay lại hoặc huỷ nếu họ chọn không liên kết.
Quy trình đăng nhập rõ ràng. Đảm bảo rằng người dùng có phương thức rõ ràng để đăng nhập vào Tài khoản Google của họ, chẳng hạn như các trường cho tên người dùng và mật khẩu hoặc Đăng nhập bằng Google.
Có thể huỷ liên kết. Cung cấp cơ chế để người dùng huỷ liên kết, chẳng hạn như một URL đến phần cài đặt tài khoản của họ trên nền tảng của bạn. Ngoài ra, bạn có thể thêm một đường liên kết đến Tài khoản Google để người dùng có thể quản lý tài khoản được liên kết của họ.
Khả năng thay đổi tài khoản người dùng. Đề xuất một phương thức để người dùng chuyển đổi(các) tài khoản của họ. Điều này đặc biệt có lợi nếu người dùng có xu hướng sử dụng nhiều tài khoản.
- Nếu người dùng phải đóng màn hình đồng ý để chuyển đổi tài khoản, hãy gửi lỗi có thể khôi phục cho Google để người dùng có thể đăng nhập vào tài khoản mong muốn bằng tính năng liên kết OAuth và quy trình ngầm ẩn.
Thêm biểu trưng của bạn. Hiển thị biểu trưng của công ty bạn trên màn hình xin phép. Sử dụng nguyên tắc thiết kế để đặt biểu trưng. Nếu bạn cũng muốn hiển thị biểu trưng của Google, hãy xem phần Biểu trưng và nhãn hiệu.
Tạo dự án
Cách tạo dự án để sử dụng tính năng liên kết tài khoản:
- Nhấp vào Tạo dự án.
- Nhập tên hoặc chấp nhận tên được đề xuất.
- Xác nhận hoặc chỉnh sửa mọi trường còn lại.
- Nhấp vào Tạo.
Cách xem mã dự án:
- Tìm dự án của bạn trong bảng trên trang đích. Mã dự án xuất hiện trong cột Mã.
Định cấu hình màn hình đồng ý OAuth
Quy trình Liên kết với Tài khoản Google bao gồm một màn hình yêu cầu sự đồng ý cho người dùng biết ứng dụng đang yêu cầu quyền truy cập vào dữ liệu của họ, loại dữ liệu mà ứng dụng đang yêu cầu và các điều khoản áp dụng. Bạn cần định cấu hình màn hình đồng ý OAuth trước khi tạo mã ứng dụng Google API.
- Mở trang màn hình đồng ý OAuth của Google API Console.
- Nếu được nhắc, hãy chọn dự án mà bạn vừa tạo.
Trên trang "Màn hình xin phép bằng OAuth", hãy điền thông tin vào biểu mẫu rồi nhấp vào nút "Lưu".
Tên ứng dụng: Tên của ứng dụng yêu cầu sự đồng ý. Tên này phải phản ánh chính xác ứng dụng của bạn và nhất quán với tên ứng dụng mà người dùng thấy ở những nơi khác. Tên ứng dụng sẽ xuất hiện trên màn hình đồng ý Liên kết tài khoản.
Biểu trưng ứng dụng: Một hình ảnh trên màn hình đồng ý giúp người dùng nhận ra ứng dụng của bạn. Biểu trưng này xuất hiện trên màn hình đồng ý liên kết tài khoản và trên chế độ cài đặt tài khoản
Email hỗ trợ: Để người dùng liên hệ với bạn khi có thắc mắc về sự đồng ý của họ.
Phạm vi cho các API của Google: Phạm vi cho phép ứng dụng của bạn truy cập vào dữ liệu riêng tư của người dùng trên Google. Đối với trường hợp sử dụng Liên kết với Tài khoản Google, phạm vi mặc định (email, hồ sơ, openid) là đủ, bạn không cần thêm bất kỳ phạm vi nhạy cảm nào. Thông thường, bạn nên yêu cầu các phạm vi theo từng bước, tại thời điểm cần truy cập, thay vì yêu cầu trước. Tìm hiểu thêm.
Miền được uỷ quyền: Để bảo vệ bạn và người dùng, Google chỉ cho phép những ứng dụng xác thực bằng OAuth sử dụng Miền được uỷ quyền. Đường liên kết đến các ứng dụng của bạn phải được lưu trữ trên Miền được uỷ quyền. Tìm hiểu thêm.
Đường liên kết đến trang chủ của ứng dụng: Trang chủ của ứng dụng. Phải được lưu trữ trên một Miền được uỷ quyền.
Đường liên kết đến Chính sách quyền riêng tư của ứng dụng: Xuất hiện trên màn hình xin phép Liên kết với Tài khoản Google. Phải được lưu trữ trên một Miền được uỷ quyền.
Đường liên kết đến Điều khoản dịch vụ của ứng dụng (Không bắt buộc): Phải được lưu trữ trên một Miền được uỷ quyền.
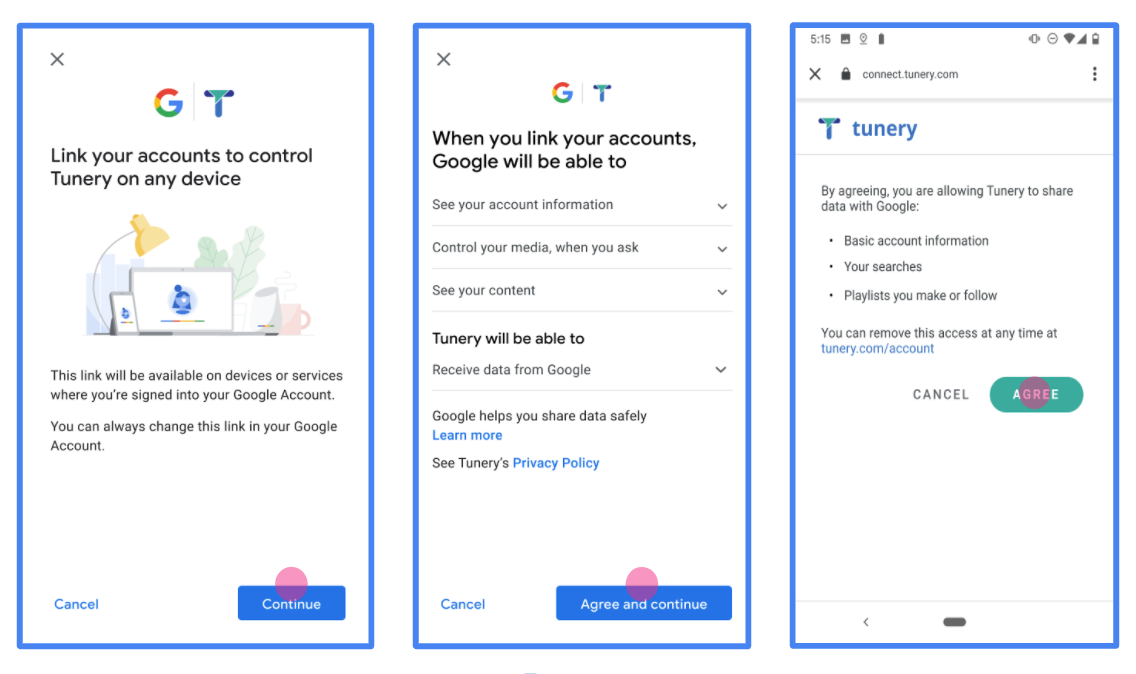
Hình 1 Màn hình đồng ý liên kết Tài khoản Google cho một Ứng dụng giả tưởng, Tunery
Kiểm tra "Trạng thái xác minh". Nếu ứng dụng của bạn cần xác minh, hãy nhấp vào nút "Gửi để xác minh" để gửi ứng dụng của bạn đi xác minh. Hãy tham khảo các yêu cầu xác minh OAuth để biết thông tin chi tiết.
Triển khai máy chủ OAuth
Quá trình triển khai máy chủ OAuth 2.0 của quy trình mã uỷ quyền bao gồm hai điểm cuối mà dịch vụ của bạn cung cấp qua HTTPS. Điểm cuối đầu tiên là điểm cuối uỷ quyền, chịu trách nhiệm tìm hoặc lấy sự đồng ý của người dùng về quyền truy cập dữ liệu. Điểm cuối uỷ quyền đưa ra giao diện người dùng đăng nhập cho những người dùng chưa đăng nhập và ghi lại sự đồng ý đối với quyền truy cập được yêu cầu. Điểm cuối thứ hai là điểm cuối trao đổi mã thông báo, được dùng để lấy các chuỗi đã mã hoá (được gọi là mã thông báo) cho phép người dùng truy cập vào dịch vụ của bạn.
Khi ứng dụng của Google cần gọi một trong các API của dịch vụ, Google sẽ sử dụng các điểm cuối này cùng nhau để yêu cầu người dùng cho phép gọi các API này thay mặt cho công ty.
Phiên quy trình mã uỷ quyền OAuth 2.0 do Google khởi tạo có quy trình sau:
- Google sẽ mở điểm cuối uỷ quyền của bạn trong trình duyệt của người dùng. Nếu luồng bắt đầu trên một thiết bị chỉ dùng giọng nói cho một Hành động, thì Google sẽ chuyển thực thi trên điện thoại.
- Người dùng này đăng nhập (nếu chưa đăng nhập) và cấp cho Google quyền truy cập vào dữ liệu của họ bằng API của bạn nếu họ chưa cấp quyền.
- Dịch vụ của bạn sẽ tạo một mã uỷ quyền rồi trả lại mã này cho Google. Việc cần làm do đó, hãy chuyển hướng trình duyệt của người dùng trở lại Google bằng mã uỷ quyền được đính kèm vào yêu cầu.
- Google sẽ gửi mã uỷ quyền đến điểm cuối trao đổi mã thông báo của bạn. Điểm cuối này xác minh tính xác thực của mã và trả về mã truy cập cũng như mã làm mới. Mã truy cập là một mã ngắn hạn mà dịch vụ của bạn chấp nhận làm thông tin đăng nhập để truy cập các API. Mã làm mới là mã tồn tại trong một thời gian dài mã thông báo mà Google có thể lưu trữ và sử dụng để thu nạp mã truy cập mới khi hết hạn.
- Sau khi người dùng hoàn tất quy trình liên kết tài khoản, mỗi yêu cầu do Google gửi có chứa mã truy cập.
Xử lý yêu cầu uỷ quyền
Khi bạn cần liên kết tài khoản bằng mã uỷ quyền OAuth 2.0 quy trình này, Google sẽ chuyển người dùng đến điểm cuối uỷ quyền của bạn kèm theo yêu cầu bao gồm các thông số sau:
| Tham số điểm cuối ủy quyền | |
|---|---|
client_id |
Mã ứng dụng khách mà bạn đã chỉ định cho Google. |
redirect_uri |
URL mà bạn gửi phản hồi tới yêu cầu này. |
state |
Giá trị sổ sách được chuyển lại cho Google không thay đổi trong URI chuyển hướng. |
scope |
Không bắt buộc: Một tập hợp chuỗi phạm vi được phân tách bằng dấu cách chỉ định dữ liệu mà Google đang yêu cầu uỷ quyền. |
response_type |
Loại giá trị cần trả về trong phản hồi. Đối với OAuth 2.0
luồng mã uỷ quyền, loại phản hồi luôn là code.
|
user_locale |
Chế độ cài đặt ngôn ngữ trong Tài khoản Google trong RFC5646 định dạng này, được dùng để bản địa hoá nội dung của bạn sang ngôn ngữ ưu tiên của người dùng. |
Ví dụ: nếu điểm cuối uỷ quyền của bạn có tại
https://myservice.example.com/auth, một yêu cầu có thể có dạng như sau:
GET https://myservice.example.com/auth?client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&redirect_uri=REDIRECT_URI&state=STATE_STRING&scope=REQUESTED_SCOPES&response_type=code&user_locale=LOCALE
Để điểm cuối uỷ quyền của bạn có thể xử lý các yêu cầu đăng nhập, hãy làm như sau các bước:
- Xác minh rằng
client_idkhớp với Mã ứng dụng khách mà bạn đã chỉ định cho Google, vàredirect_urikhớp với URL chuyển hướng do Google cung cấp cho dịch vụ của bạn. Đây là những bước kiểm tra quan trọng để ngăn chặn việc cấp truy cập vào các ứng dụng khách ngoài ý muốn hoặc bị định cấu hình sai. Nếu bạn hỗ trợ nhiều Luồng OAuth 2.0, cũng xác nhận rằngresponse_typelàcode. - Kiểm tra xem người dùng đã đăng nhập vào dịch vụ của bạn chưa. Nếu người dùng chưa đăng nhập, hoàn tất quy trình đăng nhập hoặc đăng ký dịch vụ của bạn.
- Tạo mã uỷ quyền cho Google dùng để truy cập vào API của bạn. Mã uỷ quyền có thể là bất kỳ giá trị chuỗi nào, nhưng phải là duy nhất đại diện cho người dùng, máy khách và thời gian hết hạn của mã và thông tin đó không phải ai cũng đoán được. Bạn thường cấp phép các mã sẽ hết hạn sau khoảng 10 phút.
- Xác nhận rằng URL do tham số
redirect_urichỉ định có biểu mẫu sau:https://oauth-redirect.googleusercontent.com/r/YOUR_PROJECT_ID https://oauth-redirect-sandbox.googleusercontent.com/r/YOUR_PROJECT_ID
- Chuyển hướng trình duyệt của người dùng tới URL được chỉ định
Tham số
redirect_uri. Bao gồm mã uỷ quyền mà bạn vừa được tạo và giá trị trạng thái ban đầu, chưa sửa đổi khi bạn chuyển hướng bằng cách thêm các tham sốcodevàstate. Sau đây là một ví dụ về URL kết quả:https://oauth-redirect.googleusercontent.com/r/YOUR_PROJECT_ID?code=AUTHORIZATION_CODE&state=STATE_STRING
Xử lý các yêu cầu trao đổi mã thông báo
Điểm cuối trao đổi mã thông báo của dịch vụ của bạn chịu trách nhiệm về 2 loại mã thông báo sàn giao dịch:
- Trao đổi mã uỷ quyền để lấy mã truy cập và mã làm mới
- Mã làm mới trao đổi cho mã truy cập
Yêu cầu trao đổi mã thông báo bao gồm các tham số sau:
| Tham số điểm cuối trao đổi mã thông báo | |
|---|---|
client_id |
Một chuỗi xác định nguồn gốc của yêu cầu là Google. Chuỗi này phải được đăng ký trong hệ thống của bạn dưới dạng mã nhận dạng duy nhất của Google. |
client_secret |
Chuỗi bí mật mà bạn đã đăng ký với Google cho dịch vụ của bạn. |
grant_type |
Loại mã thông báo đang được trao đổi. Có một trong hai
authorization_code hoặc refresh_token. |
code |
Khi grant_type=authorization_code, tham số này sẽ là
mã Google nhận được từ thông tin đăng nhập của bạn hoặc từ trao đổi mã thông báo
điểm cuối. |
redirect_uri |
Khi grant_type=authorization_code, tham số này sẽ là
URL dùng trong yêu cầu uỷ quyền ban đầu. |
refresh_token |
Khi grant_type=refresh_token, tham số này sẽ là
mã làm mới mà Google nhận được từ điểm cuối trao đổi mã thông báo của bạn. |
Trao đổi mã uỷ quyền để lấy mã truy cập và mã làm mới
Sau khi người dùng đăng nhập và điểm cuối uỷ quyền của bạn trả về một thông báo ngắn hạn mã uỷ quyền cho Google, Google sẽ gửi yêu cầu đến sàn giao dịch mã thông báo của bạn điểm cuối để trao đổi mã uỷ quyền lấy mã truy cập và làm mới mã thông báo.
Đối với các yêu cầu này, giá trị của grant_type là authorization_code và
giá trị code là giá trị của mã uỷ quyền mà bạn đã cấp trước đó
cho Google. Sau đây là ví dụ về yêu cầu trao đổi
mã uỷ quyền cho mã truy cập và mã làm mới:
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET&grant_type=authorization_code&code=AUTHORIZATION_CODE&redirect_uri=REDIRECT_URI
Để đổi mã uỷ quyền lấy mã truy cập và mã làm mới,
điểm cuối trao đổi mã thông báo phản hồi các yêu cầu POST bằng cách thực thi lệnh sau
các bước:
- Xác minh rằng
client_idxác định nguồn gốc của yêu cầu là nguồn đã được uỷ quyền điểm gốc vàclient_secretkhớp với giá trị dự kiến. - Xác minh rằng mã uỷ quyền là hợp lệ và chưa hết hạn, đồng thời client ID được chỉ định trong yêu cầu khớp với ID ứng dụng khách được liên kết với mã uỷ quyền.
- Xác nhận rằng URL mà tham số
redirect_urichỉ định là giống hệt nhau thành giá trị được sử dụng trong yêu cầu uỷ quyền ban đầu. - Nếu bạn không thể xác minh tất cả các tiêu chí trên, hãy trả về một HTTP
400 Lỗi Yêu cầu không hợp lệ, trong đó
{"error": "invalid_grant"}là phần nội dung. - Nếu không, hãy sử dụng mã nhận dạng người dùng trong mã uỷ quyền để tạo quy trình làm mới và mã truy cập. Các mã thông báo này có thể là giá trị chuỗi bất kỳ, nhưng phải đại diện riêng cho người dùng và khách hàng mà mã thông báo dành cho họ, đồng thời không được dễ đoán. Đối với mã truy cập, hãy ghi lại cả thời gian hết hạn của mã thông báo. Thời gian này thường là một giờ sau khi bạn cấp mã thông báo. Mã làm mới không hết hạn.
- Trả về đối tượng JSON sau đây trong phần nội dung của phản hồi HTTPS:
{ "token_type": "Bearer", "access_token": "ACCESS_TOKEN", "refresh_token": "REFRESH_TOKEN", "expires_in": SECONDS_TO_EXPIRATION }
Google lưu trữ mã truy cập và mã làm mới cho người dùng và bản ghi mã truy cập đã hết hạn. Khi mã truy cập hết hạn, Google sẽ sử dụng mã làm mới để nhận mã truy cập mới từ điểm cuối trao đổi mã thông báo.
Mã làm mới trao đổi cho mã truy cập
Khi mã truy cập hết hạn, Google sẽ gửi yêu cầu đến sàn giao dịch mã thông báo của bạn để trao đổi mã làm mới lấy mã truy cập mới.
Đối với các yêu cầu này, giá trị của grant_type là refresh_token và giá trị
refresh_token là giá trị của mã làm mới mà bạn đã cấp trước đó
Google. Sau đây là ví dụ về yêu cầu trao đổi mã làm mới
đối với mã truy cập:
POST /token HTTP/1.1 Host: oauth2.example.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded client_id=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID&client_secret=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET&grant_type=refresh_token&refresh_token=REFRESH_TOKEN
Để đổi mã làm mới lấy mã truy cập, điểm cuối trao đổi mã thông báo của bạn
phản hồi các yêu cầu POST bằng cách thực thi các bước sau:
- Xác minh rằng
client_idxác định nguồn gốc của yêu cầu là Google, vàclient_secretkhớp với giá trị dự kiến. - Xác minh rằng mã làm mới là hợp lệ và mã ứng dụng khách được chỉ định trong yêu cầu khớp với mã ứng dụng khách liên kết với mã làm mới.
- Nếu bạn không thể xác minh tất cả các tiêu chí trên, hãy trả về HTTP 400
Lỗi Yêu cầu không hợp lệ, trong đó phần nội dung là
{"error": "invalid_grant"}. - Nếu không, hãy sử dụng mã nhận dạng người dùng từ mã làm mới để tạo quyền truy cập mã thông báo. Các mã thông báo này có thể là bất kỳ giá trị chuỗi nào, nhưng phải là duy nhất đại diện cho người dùng và khách hàng mà mã thông báo dành cho họ, đồng thời không được có thể đoán được. Đối với mã truy cập, hãy ghi lại thời gian hết hạn của mã thông báo, thường là một giờ sau khi bạn phát hành mã thông báo.
- Trả về đối tượng JSON sau trong phần nội dung của HTTPS
trả lời:
{ "token_type": "Người mang", "access_token": "ACCESS_TOKEN", "expiry_in" (hết hạn): SECONDS_TO_EXPIRATION }
Xử lý các yêu cầu thông tin người dùng
Điểm cuối userinfo là một tài nguyên được bảo vệ bằng OAuth 2.0. Tài nguyên này trả về các thông báo xác nhận quyền sở hữu về người dùng được liên kết. Việc triển khai và lưu trữ điểm cuối userinfo là không bắt buộc, ngoại trừ các trường hợp sử dụng sau:
- Đăng nhập vào tài khoản được liên kết bằng tính năng Google One Chạm.
- Gói thuê bao dễ dàng trên Android TV.
Sau khi đã truy xuất thành công mã truy cập từ điểm cuối của mã thông báo, Google sẽ gửi yêu cầu đến điểm cuối userinfo của bạn để truy xuất thông tin hồ sơ cơ bản về người dùng được liên kết.
| tiêu đề của yêu cầu điểm cuối userinfo | |
|---|---|
Authorization header |
Mã truy cập thuộc loại Bearer. |
Ví dụ: nếu điểm cuối userinfo của bạn có sẵn tại
https://myservice.example.com/userinfo, một yêu cầu có thể có dạng như sau:
GET /userinfo HTTP/1.1 Host: myservice.example.com Authorization: Bearer ACCESS_TOKEN
Để điểm cuối userinfo xử lý các yêu cầu, hãy làm theo các bước sau:
- Trích xuất mã truy cập từ tiêu đề Uỷ quyền và trả về thông tin cho người dùng được liên kết với mã truy cập.
- Nếu mã truy cập không hợp lệ, hãy trả về lỗi HTTP 401 unauthorized (Không được phép sử dụng tiêu đề phản hồi
WWW-Authenticate). Dưới đây là ví dụ về phản hồi khi xảy ra lỗi thông tin người dùng:HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized WWW-Authenticate: error="invalid_token", error_description="The Access Token expired"
Nếu mã truy cập hợp lệ, hãy trả về và phản hồi HTTP 200 kèm theo đối tượng JSON sau trong phần nội dung của HTTPS trả lời:
{ "sub": "USER_UUID", "email": "EMAIL_ADDRESS", "given_name": "FIRST_NAME", "family_name": "LAST_NAME", "name": "FULL_NAME", "picture": "PROFILE_PICTURE", }phản hồi của thiết bị đầu cuối userinfo subMã nhận dạng duy nhất giúp nhận dạng người dùng trong hệ thống của bạn. emailĐịa chỉ email của người dùng. given_nameKhông bắt buộc: Tên của người dùng. family_nameKhông bắt buộc: Họ của người dùng. nameKhông bắt buộc: Tên đầy đủ của người dùng. pictureKhông bắt buộc: Ảnh hồ sơ của người dùng.
Xác thực quá trình triển khai
Bạn có thể xác thực phương thức triển khai bằng cách sử dụng công cụ OAuth 2.0 Playground.
Trong công cụ này, hãy làm theo các bước sau:
- Nhấp vào biểu tượng Configuration (Cấu hình) để mở cửa sổ OAuth 2.0 Configuration (Cấu hình OAuth 2.0).
- Trong trường Quy trình OAuth, hãy chọn Phía máy khách.
- Trong trường OAuth Endpoints (Điểm cuối OAuth), hãy chọn Custom (Tuỳ chỉnh).
- Chỉ định điểm cuối OAuth 2.0 và mã ứng dụng khách mà bạn đã chỉ định cho Google trong các trường tương ứng.
- Trong phần Bước 1, đừng chọn bất kỳ phạm vi nào của Google. Thay vào đó, hãy để trống trường này hoặc nhập một phạm vi hợp lệ cho máy chủ của bạn (hoặc một chuỗi tuỳ ý nếu bạn không sử dụng phạm vi OAuth). Khi bạn hoàn tất, hãy nhấp vào Uỷ quyền cho API.
- Trong các mục Bước 2 và Bước 3, hãy thực hiện quy trình OAuth 2.0 và xác minh rằng mỗi bước hoạt động như dự kiến.
Bạn có thể xác thực việc triển khai của mình bằng cách sử dụng công cụ Bản minh hoạ về cách liên kết Tài khoản Google.
Trong công cụ này, hãy làm theo các bước sau:
- Nhấp vào nút Đăng nhập bằng Google.
- Chọn tài khoản mà bạn muốn liên kết.
- Nhập mã dịch vụ.
- Bạn có thể nhập một hoặc nhiều phạm vi mà bạn sẽ yêu cầu quyền truy cập.
- Nhấp vào Bắt đầu bản minh hoạ.
- Khi được nhắc, hãy xác nhận rằng bạn có thể đồng ý và từ chối yêu cầu liên kết.
- Xác nhận rằng bạn được chuyển hướng đến nền tảng của mình.