If your site uses third-party cookies, it's time to take action as we approach their deprecation. To facilitate testing, Chrome has restricted third-party cookies for 1% of users from January 4th, 2024. Chrome plans to ramp up third-party cookie restrictions to 100% of users from Q3 2024, subject to addressing any remaining competition concerns of the UK's Competition and Markets Authority.
Our goal with the Privacy Sandbox is to reduce cross-site tracking while still enabling the functionality that keeps online content and services freely accessible by everyone. Deprecating and removing third-party cookies encapsulates the challenge, as they enable critical functionality across sign-in, fraud protection, advertising, and generally the ability to embed rich, third-party content in your sites—but at the same time they're also the key enablers of cross-site tracking.
In our previous major milestone, we launched a range of APIs providing a privacy-focused alternative to today's status quo for use cases like identity, advertising, and fraud detection. With alternatives in place, we can now move on to begin phasing out third-party cookies.
In this Cookie Countdown series, we will take you through the timeline and immediate actions you can take to ensure your sites are prepared.
1% third-party cookie deprecation and Chrome-facilitated testing
On the privacysandbox.com timeline you can see two milestones in Q4 2023 and Q1 2024, as part of Chrome-facilitated testing modes. This testing is primarily for organizations testing the Privacy Sandbox relevance and measurement APIs, however as part of this we will be disabling third-party cookies for 1% of Chrome Stable users.
This means that from the start of 2024, you can expect to see an increased portion of Chrome users on your site with third-party cookies disabled even if you are not actively participating in the Chrome-facilitated testing. This testing period continues through to Q3 2024 when, after consultation with the CMA and subject to resolving any competition concerns, we plan to begin disabling third-party cookies for all Chrome users.
Prepare for the third-party cookie phase out
We've broken the process down into these key steps, with detail below, to ensure you're prepared for your site to run without third-party cookies:
- Audit your third-party cookie usage.
- Test for breakage.
- For cross-site cookies which store data on a per site basis, like an embed, consider
Partitionedwith CHIPS. - For cross-site cookies across a small group of meaningfully linked sites, consider Related Website Sets.
- For other third-party cookie use cases, migrate to the relevant web APIs.
1. Audit your third-party cookie usage
Third-party cookies can be identified by their SameSite=None value. You should search your code to look for instances where you set the SameSite attribute to this value. If you previously made changes to add SameSite=None to your cookies around 2020, then those changes may provide a good starting point.
Chrome DevTools
The Chrome DevTools Network panel shows cookies set and sent on requests. In the Application panel you can see the Cookies heading under Storage. You can browse the cookies stored for each site accessed as part of the page load. You can sort by the SameSite column to group all the None cookies.
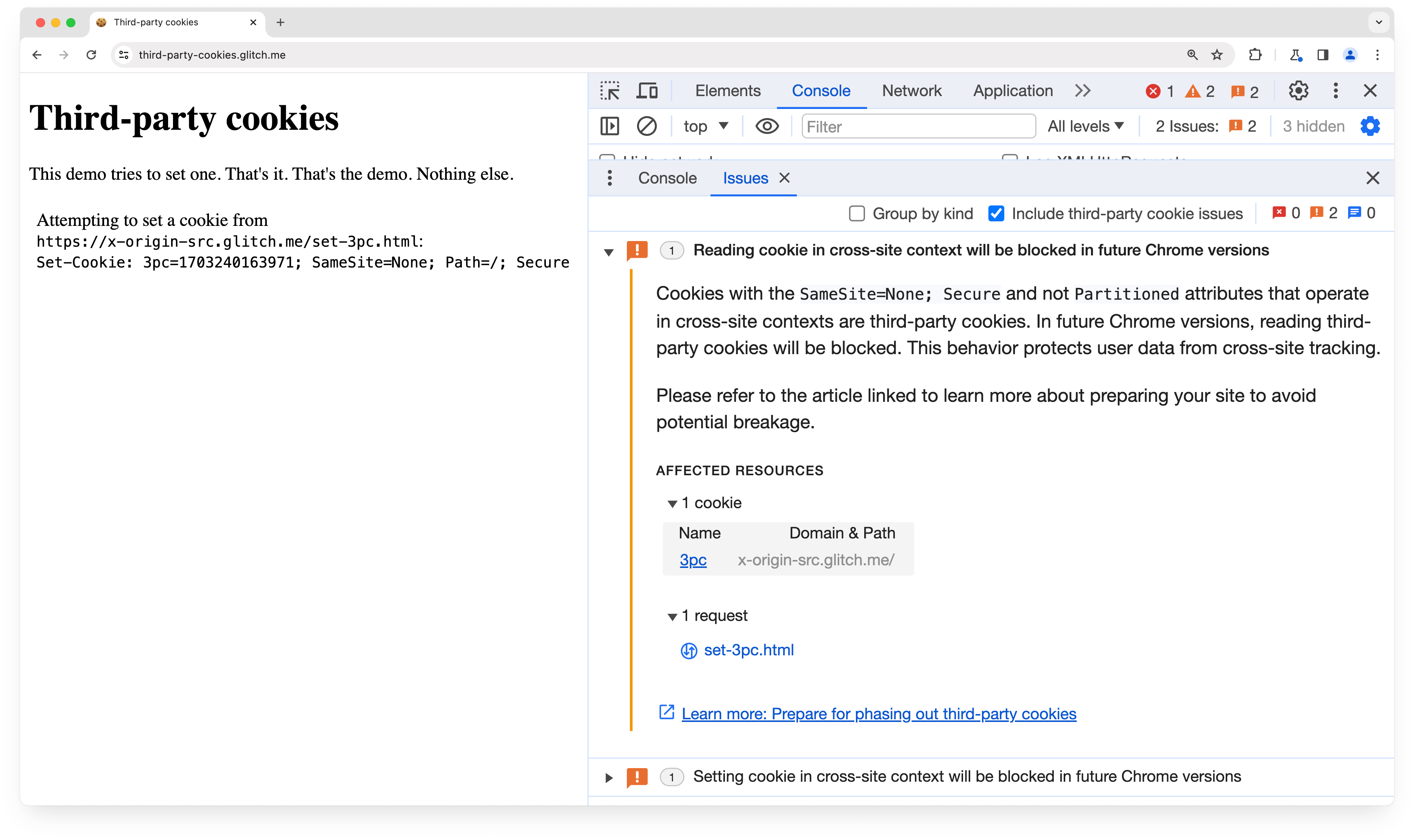
From Chrome 118, the DevTools Issues tab shows the breaking change issue, "Cookie sent in cross-site context will be blocked in future Chrome versions." The issue lists potentially affected cookies for the current page.
Privacy Sandbox Analysis Tool (PSAT)
We have also built the Privacy Sandbox Analysis Tool (PSAT), a DevTools extension to facilitate analysis of cookie usage during browsing sessions. This provides debugging pathways for cookies and Privacy Sandbox features, with access points to learn more about the Privacy Sandbox initiative.
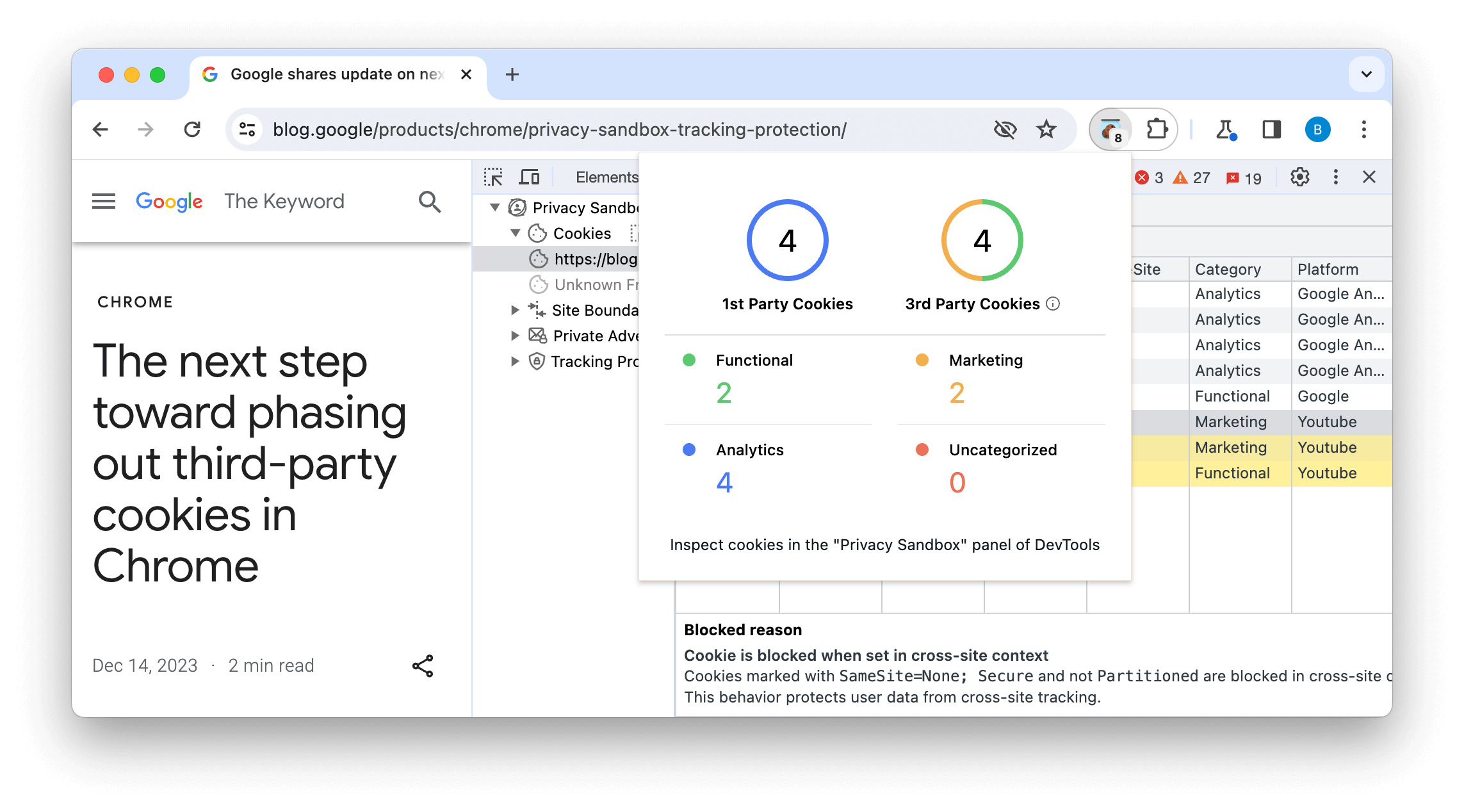
The extension complements DevTools with specialized capabilities for analyzing and debugging scenarios related to the deprecation of third-party cookies and adoption of new privacy-preserving alternatives.
You can download the extension from the Chrome Web Store or access the PSAT repository and wiki.
Check your third-parties using cookies
If you identify cookies set by third parties, you should check with those providers to see if they have plans for the third-party cookie phase out. For instance, you may need to upgrade a version of a library you are using, change a configuration option in the service, or take no action if the third party is handling the necessary changes themselves.
2. Test for breakage
You can launch Chrome using the --test-third-party-cookie-phaseout command-line flag or from Chrome 118, enable chrome://flags/#test-third-party-cookie-phaseout. This will set Chrome to block third-party cookies and ensure that new functionality and mitigations are active in order to best simulate the state after the phase out.
You can also try browsing with third-party cookies blocked via chrome://settings/cookies, but be aware that the flag ensures the new and updated functionality is also enabled. Blocking third-party cookies is a good approach to detect issues, but not necessarily validate you have fixed them.
If you maintain an active test suite for your sites, then you should do two side-by-side runs: one with Chrome on the usual settings and one with the same version of Chrome launched with the --test-third-party-cookie-phaseout flag. Any test failures in the second run and not in the first are good candidates to investigate for third-party cookie dependencies. Make sure you report the issues you find.
Once you have identified the cookies with issues and understand the use cases for them, you can work through the following options to pick the necessary solution.
3. Use Partitioned cookies with CHIPS
Where your third-party cookie is being used in a 1:1 embedded context with the top-level site, then you may consider using the Partitioned attribute as part of Cookies Having Independent Partitioned State (CHIPS) to allow cross-site access with a separate cookie used per site.
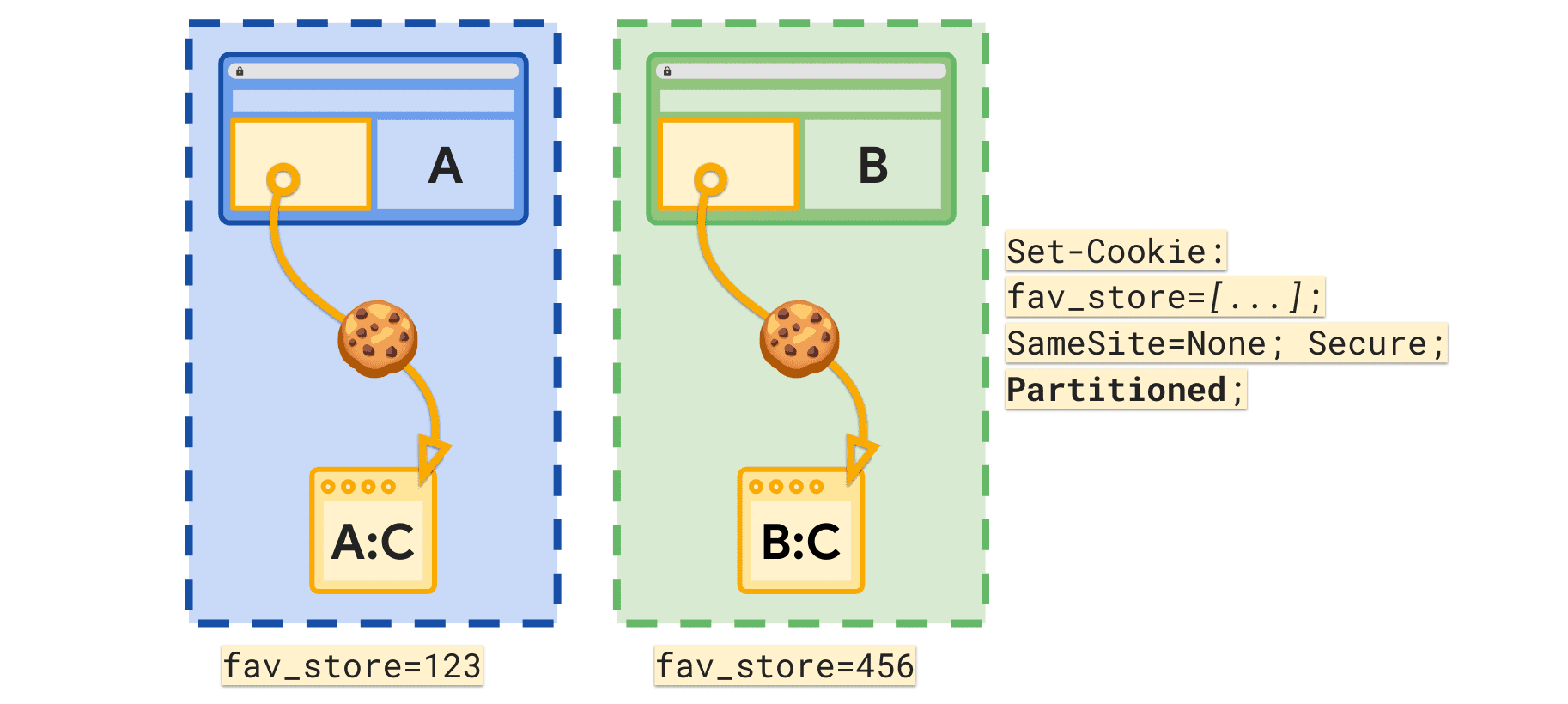
To implement CHIPS, you add the Partitioned attribute to your Set-Cookie header:
By setting Partitioned, the site opts in to storing the cookie in a separate cookie jar partitioned by top-level site. In the example above, the cookie comes from store-finder.site which hosts a map of stores that enables a user to save their favorite store. By using CHIPS, when brand-a.site embeds store-finder.site, the value of the fav_store cookie is 123. Then when brand-b.site also embeds store-finder.site they will set and send their own partitioned instance of the fav_store cookie, for example with value 456.
This means embedded services can still save state, but do not have shared cross-site storage that would allow cross-site tracking.
Potential use cases: third-party chat embeds, third-party map embeds, third-party payment embeds, subresource CDN load balancing, headless CMS providers, sandbox domains for serving untrusted user content, third-party CDNs using cookies for access control, third-party API calls that require cookies on requests, embedded ads with state scoped per publisher.
4. Use Storage Access API and Related Website Sets
Where your third-party cookie is only used across a small number of related sites, then you may consider using Related Website Sets (RWS) to allow cross-site access for that cookie within the context of those defined sites.
To implement RWS, you will need to define and submit the group of sites for the set. To ensure that the sites are meaningfully related, the policy for a valid set requires grouping those sites by: associated sites with a visible relation to each other (e.g. variants of a company's product offering), service domains (e.g. APIs, CDNs), or country-code domains (e.g. *.uk, *.jp).
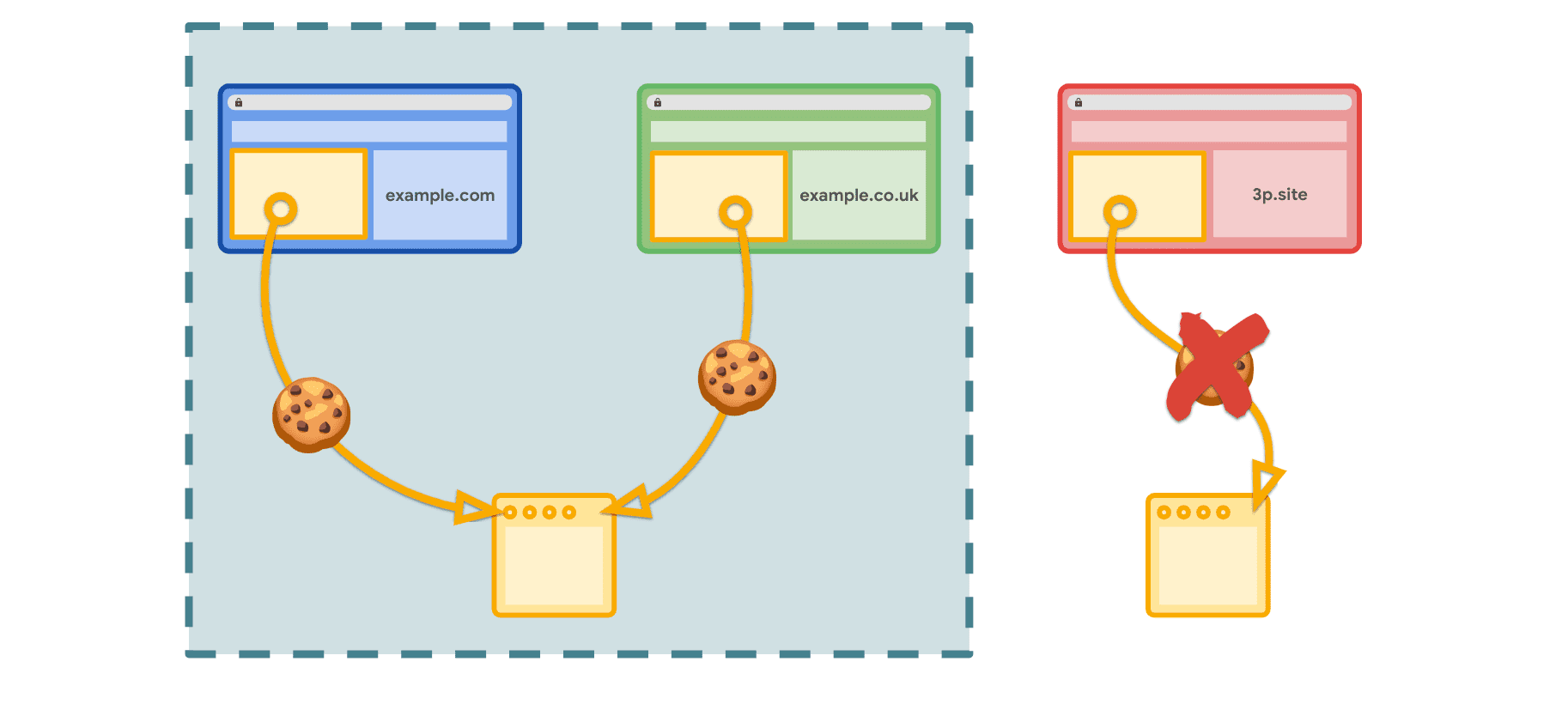
Sites can use the Storage Access API to either request cross-site cookie access using requestStorageAccess() or delegate access using requestStorageAccessFor(). When sites are within the same set, the browser will automatically grant access and cross-site cookies will be available.
This means that groups of related sites can still make use of cross-site cookies in a limited context, but do not risk sharing third-party cookies across unrelated sites in a way that would allow cross-site tracking.
Potential use cases: app-specific domains, brand-specific domains, country-specific domains, sandbox domains for serving untrusted user content, service domains for APIs, CDNs.
5. Migrate to the relevant web APIs
CHIPS and RWS enable specific types of cross-site cookie access while retaining user privacy, however the other use cases for third-party cookies must migrate to privacy-focused alternatives.
The Privacy Sandbox provides a range of purpose-built APIs for specific use cases without a need for third-party cookies:
- Federated Credential Management (FedCM) enables federated identity services allowing users to sign in to sites and services.
- Private State Tokens enable anti-fraud and anti-spam by exchanging limited, non-identifying information across sites.
- Topics enables interest-based advertising and content personalization.
- Protected Audience enables remarketing and custom audiences.
- Attribution Reporting enables measurement of ad impressions and conversions.
Additionally, Chrome supports the Storage Access API (SAA) for usage in iframes with user interaction. SAA is already supported across Edge, Firefox, and Safari. We believe it strikes a good balance to maintain user privacy while still enabling critical cross-site functionality with the benefit of cross-browser compatibility.
Note that the Storage Access API will surface a browser permission prompt to users. To provide an optimal user experience, we will only prompt the user if the site calling requestStorageAccess() has interacted with the embedded page and has previously visited the third-party site in a top-level context. A successful grant will allow cross-site cookie access for that site for 30 days. Potential use cases are authenticated cross-site embeds such as social network commenting widgets, payment providers, subscribed video services.
If you still have third-party cookie use cases that are not covered by these options, you should report the issue to us and consider if there are alternative implementations that do not depend on functionality that can enable cross-site tracking.
Enterprise support
Enterprise-managed Chrome always has unique requirements compared to general web usage and we will be ensuring that enterprise administrators have appropriate controls over the deprecation of third-party cookies in their browsers.
As with the majority of Chrome experiments, most enterprise end users will be excluded from the 1% third-party cookie deprecation automatically. For the few that may be affected, enterprise administrators can set the BlockThirdPartyCookies policy to false to opt out their managed browsers ahead of the experiment and allow time to make necessary changes to not rely on this policy or third-party cookies. You can read more in the Chrome Enterprise release notes.
We also intend to provide further reporting and tooling to help identify third-party cookie usage on enterprise sites. We have less visibility of enterprise browsers in Chrome's usage metrics which means it is especially important for enterprises to test for breakage and report issues to us.
Enterprise SaaS integrations will be able to use the third-party deprecation trial described below.
Request additional time with the third-party deprecation trial for non-advertising use cases
As with many previous deprecations on the web, we understand there are cases where sites need extra time to make the necessary changes. When it comes to privacy-related changes like this, we also have to balance that against the best interests of people using the web.
We plan to offer a deprecation trial to provide a way for sites or services used in a cross-site context to register for continued access to third-party cookies for a limited period of time.
We will share more details as plans progress, but we are starting with a few key principles:
- It will be a third-party deprecation trial allowing third-party embeds to opt in to temporarily continue using third-party cookies.
- Registering will require a review process to ensure the deprecation trial is only used for functions that greatly affect critical user journeys and registrations will be considered on a case by case basis.
- It will not interfere with the advertising testing planned for the start of 2024, as described by the CMA. As such, this means advertising use cases will not be considered for the deprecation trial.
Next step: We will publish an Intent to the blink-dev mailing list with further details this month and continue to update documentation here.
Preserving critical user experiences
Cross-site cookies have been a critical part of the web for over a quarter of a century. This makes any change, especially a breaking change, a complex process that requires a coordinated and incremental approach. While the additional cookie attributes and new privacy-focused APIs account for the majority of use cases, there are specific scenarios where we want to ensure we do not break the experience for people using those sites.
Primarily these are authentication or payment flows where a top-level site either opens a pop-up window or redirects to a third-party site for an operation and then returns to the top-level site, making use of a cookie either on that return journey or in the embedded context. We intend to provide a temporary set of heuristics to identify these scenarios and allow third-party cookies for a limited amount of time, giving sites a longer window to implement the necessary changes.
Next step: We will publish an Intent to the blink-dev mailing list with further details in this month and continue to update documentation here.
Reporting issues with third-party cookies and getting help
We want to ensure we are capturing the various scenarios where sites break without third-party cookies to ensure that we have provided guidance, tooling, and functionality to allow sites to migrate away from their third-party cookie dependencies. If your site or a service you depend on is breaking with third-party cookies disabled, you can submit it to our breakage tracker at goo.gle/report-3pc-broken.
If you have questions around the deprecation process and Chrome's plan, you can raise a new issue using the "third-party cookie deprecation" tag in our developer support repo.
