Check if third-party cookies are being used on your website or by third-party services that your site relies on.
Understand third-party cookie usage
Cookies sent in cross-site contexts such as iframes or subresource requests, are generally referred to as third-party cookies—even when they're not from a third party. Third-party cookies can be from a third party such as an analytics service or ad tech, but they can also be from a site or service of your own that has a domain that's different from the top-level page, such as an image server or a microsite.
Use cases for third-party cookies include:
- Embedded content shared from other sites, such as videos, maps, code samples, and social posts.
- Widgets for external services such as payments, calendars, booking, and reservation.
- Widgets such as social buttons or anti-fraud services.
- Remote
<img>or<script>resources that rely on cookies to be sent with a request (commonly used for tracking pixels and personalizing content).
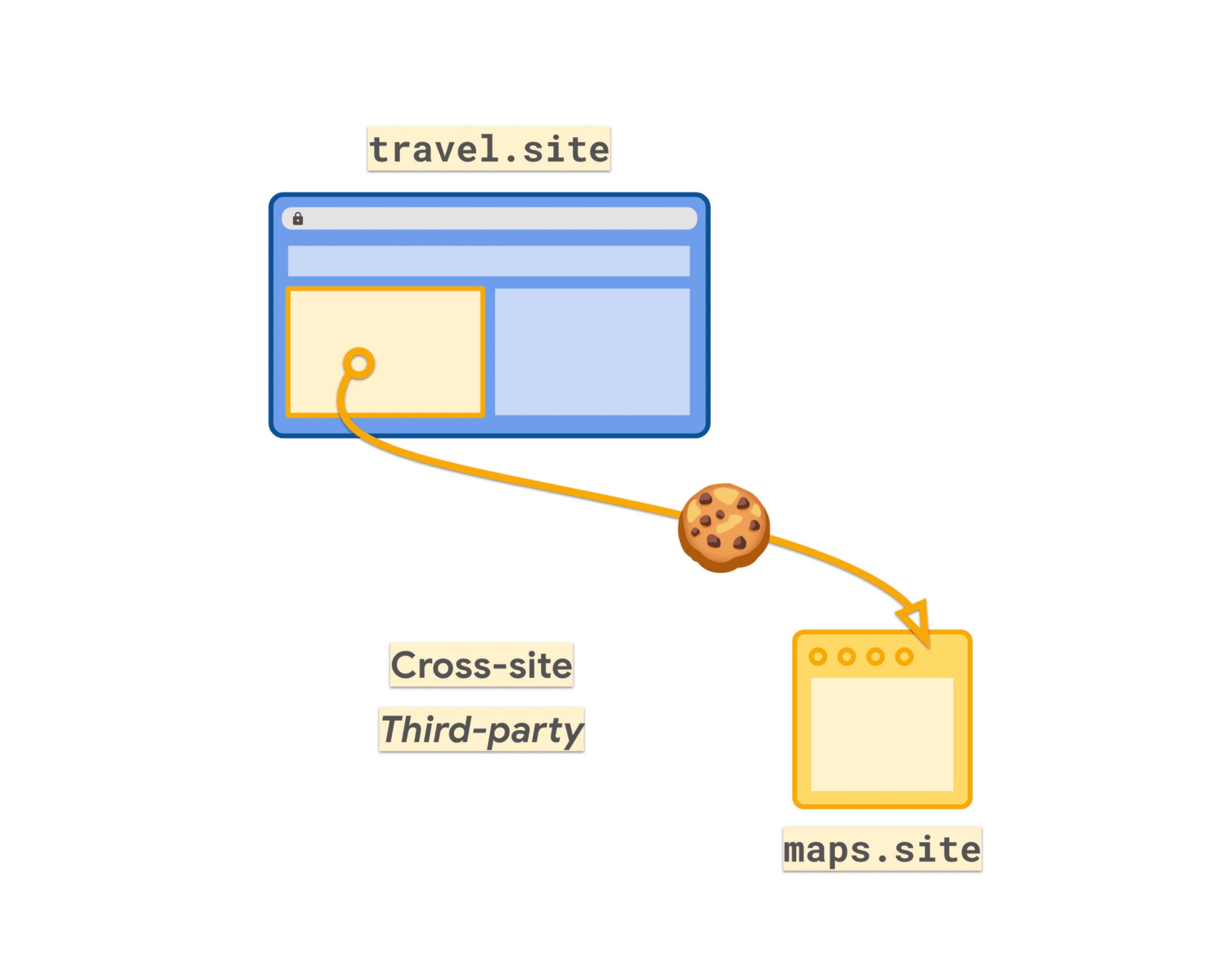
In 2019, browsers changed cookie behavior, restricting cookies to first-party access by default.
Any cookies used in cross-site contexts today must be set with SameSite=None
attribute.
Set-Cookie: cookie-name=value; SameSite=None; Secure
This means that third-party cookies can be identified by their SameSite=None attribute.
Audit your third-party cookie usage
You should search your code for instances where you set the SameSite cookie attribute to None. If you previously made changes to add SameSite=None to your cookies around 2020, then those changes may provide a good starting point.
If you find cookies marked as SameSite=None that don't seem to be used in a cross-site context, check if that's deliberate, as they may be used in a cross-site context elsewhere. Otherwise, SameSite=None may have been set inadvertently and you should remove any unnecessary SameSite=None usage.
Partitioned cookies—those set with the Partitioned attribute—will continue to be delivered even where third-party cookies are restricted on browsers that support this attribute.
Chrome DevTools
The Chrome DevTools Network panel shows cookies set and sent on requests. In the Application panel you can see the Cookies heading under Storage. You can browse the cookies stored for each site accessed as part of the page load. You can sort by the SameSite column to group all the None cookies.
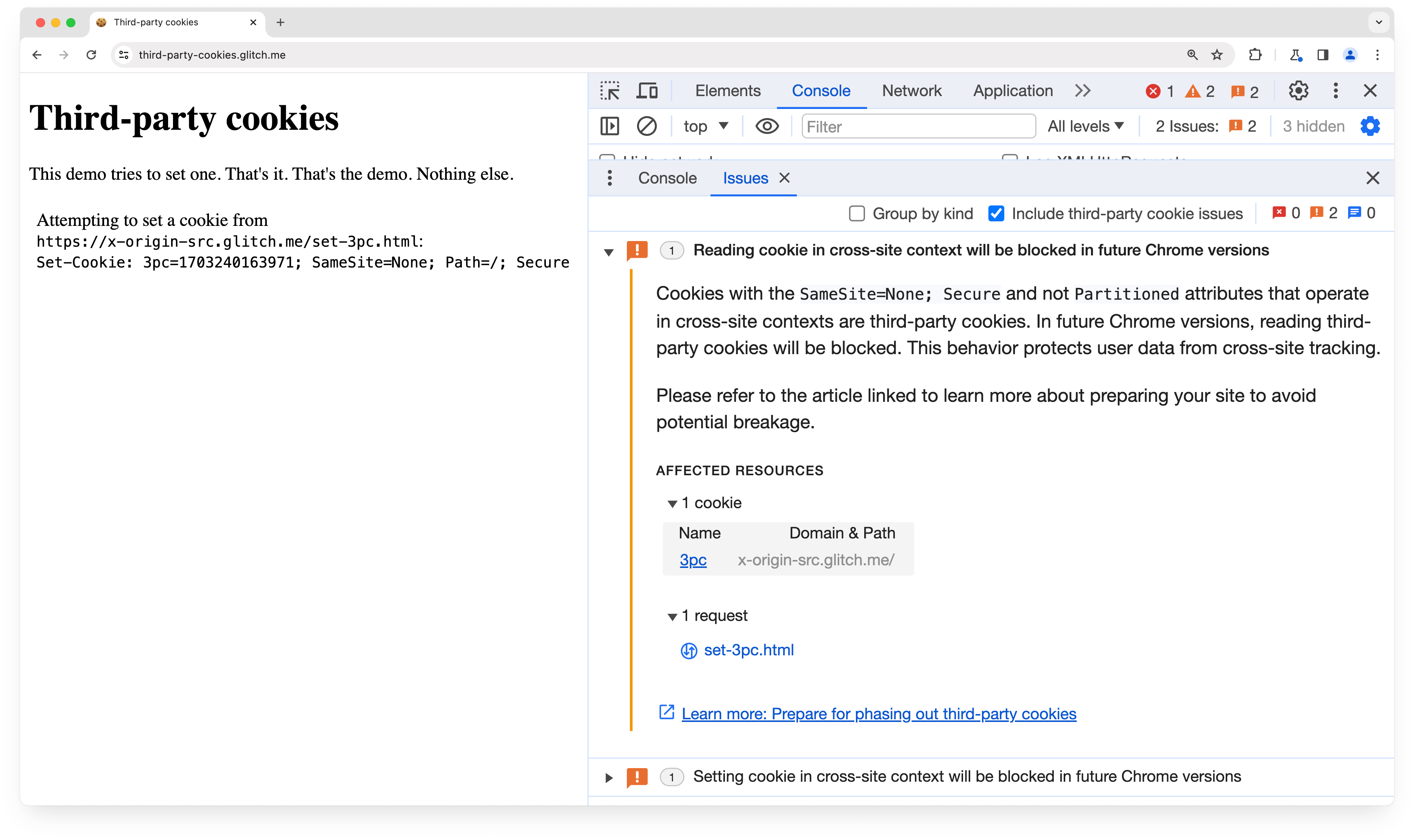
From Chrome 118, the DevTools Issues tab shows the breaking change issue, "Cookie sent in cross-site context will be blocked in future Chrome versions." The issue lists potentially affected cookies for the current page.
Privacy Sandbox Analysis Tool
We've also built the Privacy Sandbox Analysis Tool (PSAT), a DevTools extension to facilitate analysis of cookie usage during browsing sessions. This provides debugging pathways for cookies and Privacy Sandbox features, with access points to learn more about the Privacy Sandbox initiative.
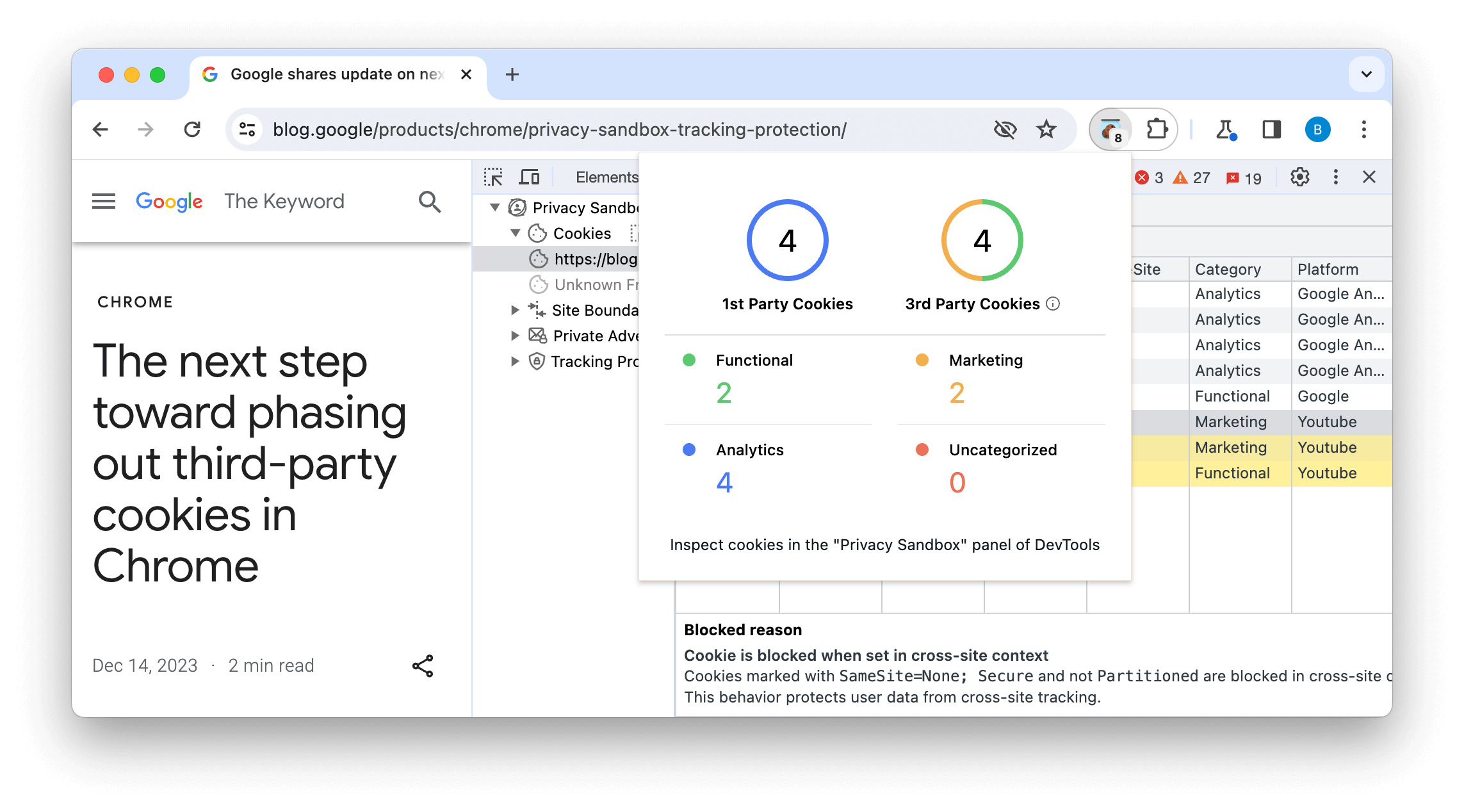
The extension complements DevTools with specialized capabilities for analyzing and debugging scenarios related to third-party cookie usage, and the adoption of new privacy-preserving alternatives.
You can download the extension from the Chrome Web Store or access the PSAT repository and wiki.
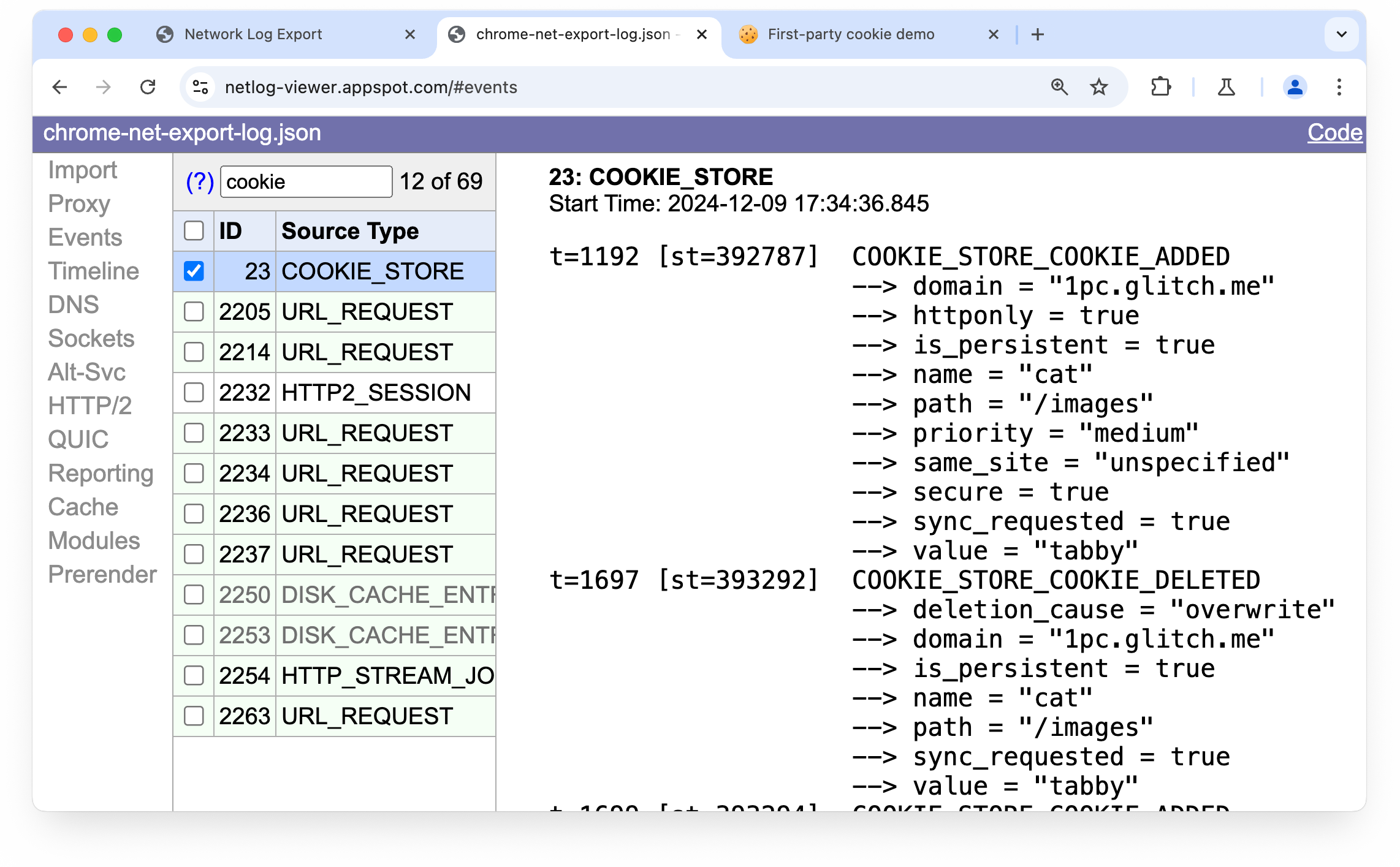
Chrome Network Log
Chrome makes it possible to record a log file of the browser's network-level events and state.
This can be useful for deep analysis of how and when cookies are set or blocked.
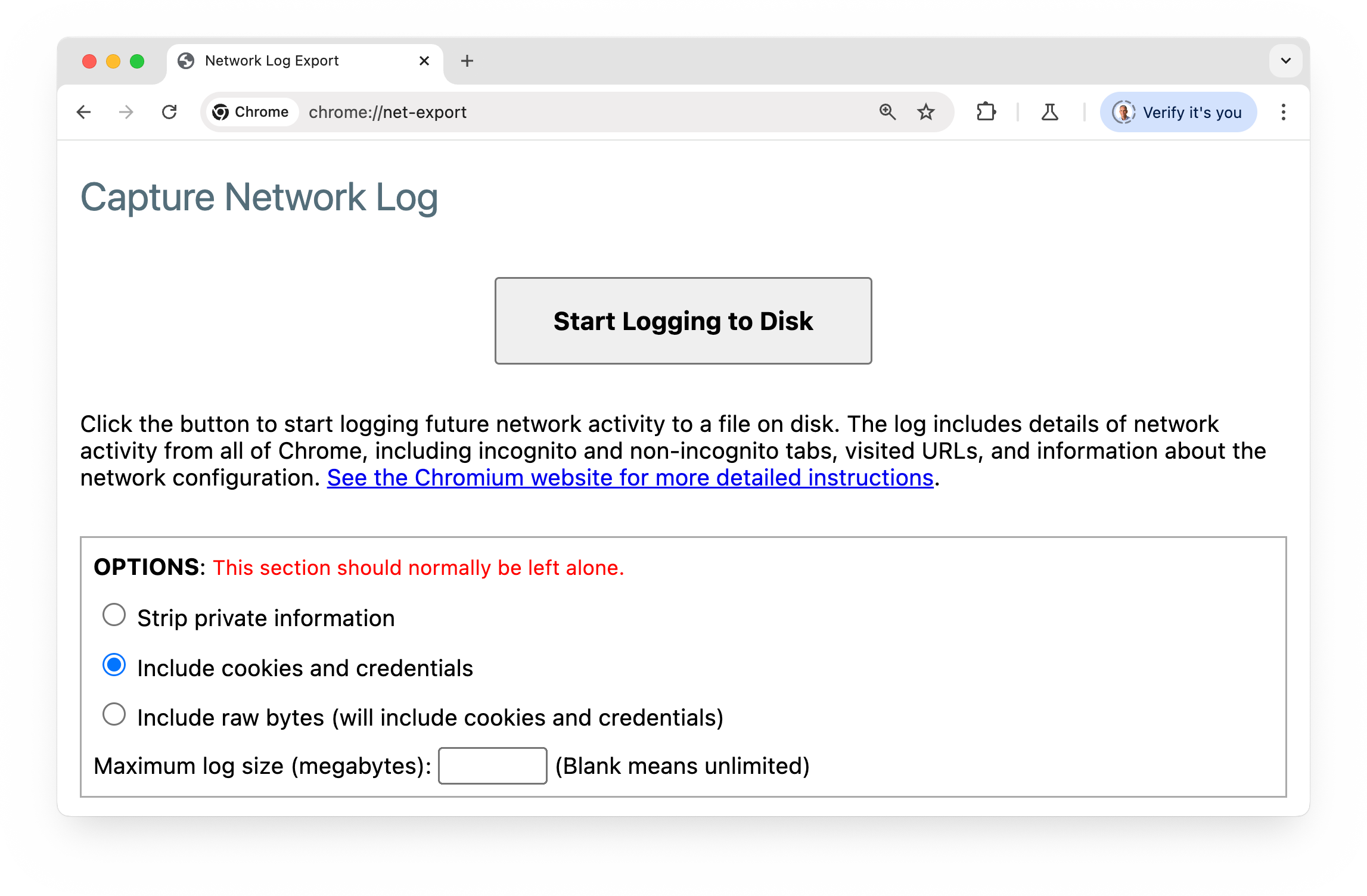
View cookie events:
- Open the
chrome://net-exportpage. - Click Start Logging to Disk.
- Click Stop Logging.
- Click Show File.
- Open the file in Network Log Viewer.
- Select Events (at left).
- Select items such as
COOKIE_STOREorURL_REQUEST. - View log output at right. (You may need to drag the divider to the left to see the content.)
Find out more: Using a NetLog dump.
Check in with your third-party service providers
If you identify cookies set by third parties, you should check with those providers to see if they plan to move away from setting cross-site cookies. You may need to upgrade a version of a library you are using, change a configuration option in the service, or take no action if the third party is handling the necessary changes themselves.
Improve your first-party cookies
If your cookie is never used on a third-party site, for example if you set a cookie to manage the session on your site and it's never used in a cross-site iframe, then you should explicitly mark the cookie as SameSite=Lax or SameSite=Strict. There are a number of other sensible defaults to use for first-party cookies. For more details, check out Recipes for first-party cookies.
