Önemli: Google Haritalar Platformu Premium Planı artık kaydolan veya yeni müşteriler tarafından kullanılamaz.
Google Haritalar Platformu Premium Plan'a hoş geldiniz
Google Haritalar Platformu Premium Plan'a kaydolduktan sonra, belirttiğiniz iletişim e-posta adresine Google'dan bir karşılama mektubu gönderilir. Hoş geldiniz mektubunuzda başlangıç için ihtiyacınız olan bilgiler var:
- Proje kimliği
- İstemci Kimliği
- İstemci kimliğiniz için özel URL imzalama sırrı veya şifreleme anahtarı
- Google Hesabı
Paketinize neler dahildir?
Premium Planınızda, geliştirici ve API referans kılavuzları dahil olmak üzere her API için hizmet ve belge paketimize erişim sunulur.
| Web API'leri | Web Service API'leri | Mobil SDK'lar |
|---|---|---|
1 Places API, Premium Plan Varlık İzleme Lisansı'na dahil değildir. Öğe İzleme Lisansınız varsa ve Places API'yi kullanmak istiyorsanız Google Haritalar API'leri Satış ekibiyle iletişime geçin.
API temel hazırlığı
Google Cloud Console projenizde satın aldığınız tüm API'ler etkinleştirilir. API'lerinize erişmek için Google Hesabınızla oturum açın ve ardından İşletmeler için Google Haritalar API'leri, Google Maps for Work veya Google Haritalar ile başlayan proje kimliğinizi seçin. Hem hesap hem de proje kimliğiniz hoş geldiniz mektubunuzda yer alır.
Kimlik doğrulama ve yetkilendirme
API'lerimize istek göndermek için API anahtarı veya istemci kimliğinizle uygulamanızın kimliğini doğrulamanız gerekir. Ayrıca bazı API istekleri için dijital imza da gerekir.
API anahtarı
API'lerimizden herhangi birine gönderilen isteklerin kimliğini doğrulamak için API anahtarı kullanabilirsiniz. Anahtarınızı oluşturmak için proje kimliğinizle ilişkili Cloud Console projesini kullanırsınız. API anahtarı kullanarak şunları yapabilirsiniz:
Cloud Console'da tüm API'lerinizi yönetin
Cloud Console'da uygulamanızın gerçek zamanlı kullanım verilerine ve 30 günlük geçmiş kullanım verilerine erişme [Google Haritalar Platformu Metrikleri
İstemci Kimliği
API anahtarı yerine, aşağıdakiler haricindeki API'lerden herhangi birine istekte bulunmak için istemci kimliğinizi kullanabilirsiniz: Places API, Geolocation API, Roads API, Android için Haritalar SDK'sı ve iOS için Haritalar SDK'sı.
Müşteri kimliğinizle:
Cloud Console'da İstemci Kimliğinizi yönetin ve özel URL imzalama gizli bilginize veya şifreleme anahtarınıza erişin.
Cloud Console Metrikleri sayfasından gerçek zamanlı kullanım verilerine ve uygulamanızın 30 günlük geçmiş kullanım verilerine erişin.
Bir istemci kimliği için şu biçimde bir etiket kullanılır:
project_number:<YOUR_PROJECT_NUMBER>.Daha ayrıntılı kullanım raporları görüntüleyebilmek için isteklere
channelparametresini ekleyin.
İstemci kimliğinizi Google Cloud Console'da nereden yönetmelisiniz?
Premium Plan İstemci Kimliği yönetimi işlevi, Google Haritalar Platformu Kimlik Bilgileri sayfasının alt kısmındaki Cloud Console'daki İstemci Kimliği bölümünde bulunur.
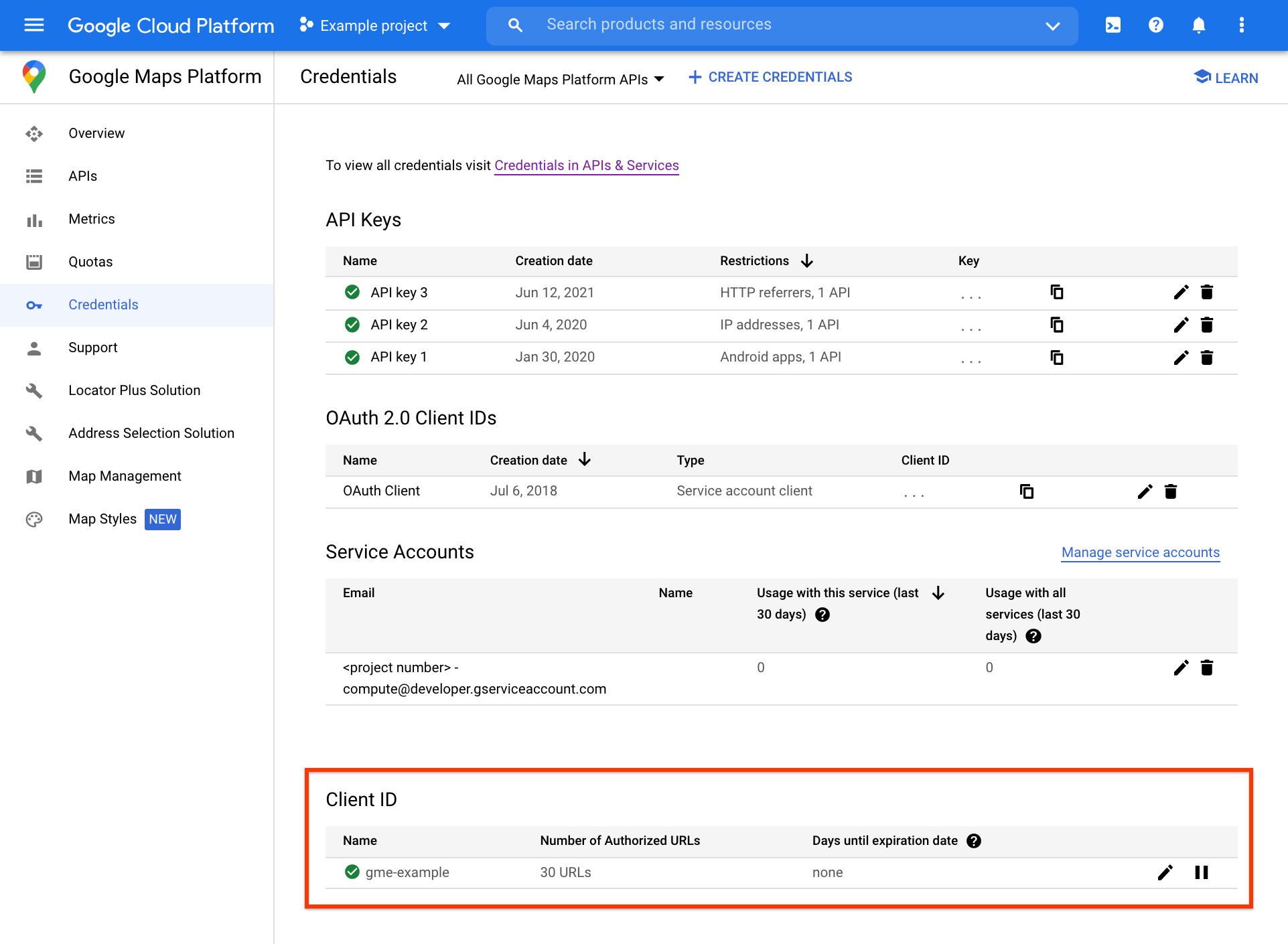
URL yetkilendirme ve istemci kimliği imzalama gizli anahtarı yönetimi de dahil olmak üzere diğer istemci kimliği yönetimi görevlerine, ayrı İstemci Kimliği sayfasından İstemci Kimliği bölümünün en sağındaki düzenle simgesi tıklanarak erişilebilir.
Dijital imzalar
Bazı API'lere yapılan istekler, API anahtarı veya istemci kimliğinin yanı sıra Premium Planınızın kota ve özelliklerine erişmek için benzersiz bir dijital imza gerektirir. Hoş geldiniz mektubunuzda sağlanan (ve Cloud Console'da bulunan) özel URL imzalama gizli anahtarını veya şifreleme anahtarını kullanarak dijital imza oluşturabilirsiniz. Özellikle aşağıdakileri kullanıyorsanız dijital imzaları kullanmanız gerekir:
Web hizmeti API'leri, Maps Static API veya Street View Static API ile istemci kimliği
Maps Static API veya Street View Static API ile bir API anahtarı
Daha fazla bilgi için
API anahtarı veya istemci kimliği kullanma ve dijital imza oluşturma hakkında ayrıntılı talimatlar için Premium Plan Kimlik Doğrulamasına Genel Bakış'a göz atın.
SSS
Google Haritalar Platformu hakkında sorularınız varsa sık sorulan sorularımıza (SSS) bakın:
Yardım alma
Google Haritalar Platformu Premium Plan müşterisi olarak, destek iletişim bilgilerine ve özel araç ve kaynaklara erişebileceğiniz Cloud Console'a erişebilirsiniz. Ayrıntılar için Google Haritalar Platformu Desteği ve Kaynakları'na göz atın.

